Abstract
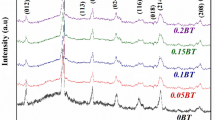
Gadolinium doped BiFeO3:BaTiO3 (3:2) polycrystalline multiferroic ceramics have been prepared by high-temperature solid state reaction technique. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis at room temperature of the prepared materials confirmed the formation of the compounds with rhombohedral crystal structure. The average particle size of as prepared samples have been found in the range of 35 nm to 55 nm for different doping concentrations. The average grain size of as prepared samples are less than 100 nm which is confirmed from SEM study. The SEM of annealed compounds showed the uniform distribution of grains and the formation of dense ceramic with average grain size in the order of 4 µm. Dielectric studies of the materials reveals that the dielectric constant (\({\varepsilon _r}\)) and tangent loss (tan δ) decreases with doping concentrations at room temperature. The variation of \({\varepsilon _r}\) and tan δ with temperature was explained on the basis of Maxwell–Wagner mechanism. The values of grain resistance (\({R_b}\)) and grain capacitance (Cb) were obtained from Nyquist plots for the different doping concentrations at 300 °C. The activation energy (\({E_a}\)) was calculated from the curve of frequency dependent ac conductivity (\({\sigma _{ac}}\)) within the range 0.19 eV to 0.45 eV. The remnant polarization of the samples (0.53 µC/cm2) was measured from polarization versus electric field (P–E) hysteresis curves. The ferromagnetic behaviour of the Gd-doped BiFeO3:BaTiO3 (3:2) sample has been studied by SQUID for the lowest doping concentration. The value of remnant magnetization was found 0.0235 emu/g at room temperature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Cai, J. Zhai, C.W. Nan, Y. Lin, Phys. Rev. B 68, 224103 (2003)
P.E. Janolin, N.A. Pertsev, D. Shichuga, L. Bellaiche, Phys. Rev. B 85, 140401 (2012)
J.M. Caicedo, J.A. Zapata, M.E. Gómez, P. Prieto, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07E306 (2008)
I. Calisir, A.A. Amirov, A.K. Kleppe, D.A. Hall, J. Mater. Chem. A (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta09497c
C.W. Nan, M.I. Bichurin, S. Dong, D. Viehland, G. Srinivasan, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 031101 (2008)
Y. Li, N. Jiang, K. Ho Lam, Y. Guo, Q. Zheng, Q. Li, W. Zhou, Y. Wan, D. Lin, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 3602 (2014)
B. Kaur, L. Singh, V.A. Reddy, D.Y. Jeong, N. Dabra, J.S. Hundal, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 4120–4135 (2016)
V.R. Palkar, J. John, R. Pinto, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1628–1630 (2002)
G.S. Lotey, N.K. Verma, J. Nanopart. Res. 1, 742 (2012)
A.T. Mulder, N.A. Benedek, J.M. Rondinelli, C.J. Fennie, Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(38), 4810–4820 (2013)
N.A. Benedek, C.J. Fennie, PRL 106, 107204 (2011)
S. Hajra, S. Sahoo, R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Alloys Compounds 750, 507–514 (2018)
B. Sun, Y. Liu, W. Zha, P. Chen, JSC Adv. 5, 13513–13518 (2015)
V.A. Khomchenko, D.A. Kiselev, J.M. Vieira, L. Jian, A.L. Kholkin, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 024105 (2008)
A. Bai, S. Zhao, J. Chen, J. Nanomaterials (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/509408
P. Lin, S. Cui, X. Zeng, H. Huang, S. Ke, J. Alloys Compd. 600, 118–124 (2014)
A. Kumar, K.L. Yadav, Phys. B 405, 4650–4654 (2010)
S. Hussaina, S.K. Hasanaina, G.H. Jaffaria, N.Z. Alib, M. Siddiquec, S.I. Shahd, J. Alloys Compd, S0925-8388(14) 02449–9 (2014)
B.K. Barick, R.N.P. Choudhary, D.K. Pradhan, Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 1007–1014 (2012)
H. Zhanga, W. Joa, K. Wanga, K.G. Webber, Ceram. Int. 40, 4759–4765 (2014)
L. Cao, C. Zhou, J. Xu, Q. Li, C. Yuan, G. Chen, Phys. Status Solidi A 213(1), 52–59 (2016)
C. Li, B. Yang, S.T. Zhang, R. Zhang, Y. Sun, H.J. Zhang, W.W. Cao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97(3), 816–825 (2014)
T.-H. Wang, C.-S. Tu, H.-Y. Chen, Y. Ding, T.C. Lin, Y.-D. Yao, V.H. Schmidt, K.-T. Wu1. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 044101 (2011)
D. Wanga, Z. Fanb, W. Lic, D. Zhou, A. Feteirad, G. Wanga, S. Murakamia, S. Sun, Q. Zhao, X. Tan, I.M. Reaney, Appl. Energy Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01099
F. Prihor, A. Ianculescu, L. Mitoseriu, P. Postolache, L. Curecheriu, N. Dragan, D. Crisan, Ferroelectrics 391, 76–82 (2009)
C.B. Sawyer, C.H. Tower, Phys. Rev. 35, 269 (1930)
R. Raia, I. Bdikina, M.A. Valenteb, A.L. Kholkina, Materials Chem Phys. 119, 539–545 (2010)
S. Sharma, V. Singh, R.K. Kotnala, R. Ranjan, R.K. Dwivedi, J. Alloys and Compounds 614, 165–172 (2014)
R. Bartikans, R.M. Eichhorn, Eng. Dielectrics (ASTM), 671 (1983)
E.H. Nicollian, Goetzberger, Bell Syst. Tech. 73, 1055 (1967)
W. Shockley, W.T. Read, Phys. Rev. 87, 835 (1952)
S. Sahoo, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, M.L. Nandagoswami, A. Kumar, Mater. Res. Express 3, 065017 (2016)
A. Singh, R. Chatterjee, S.K. Mishra, P.S.R. Krishna, S.L. Chaplot, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 014113 (2012)
S. Sahoo, S. Hajra, M. De, K. Mohanta, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Alloys Compd. 766, 2532 (2018)
S. Sahoo, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, M.L. Nandagoswamy, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6572–6584 (2015)
F. Huang, X. Lu, W. Lin, X. Wu, Y. Kan, J. Zhu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 242914 (2006)
P. Dey, T.K. Nath, M.N. Goswami, T.K. Kundu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 162510 (2007)
T.J. Park, G.C. Papaefthymiou, A.J. Viescas, A.R. Moodenbaugh, S.S. Wong, Nano Lett. 7(3), 766–772 (2007)
B. Sun, P. Han, W. Zhao, Y. Liu, P. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 18814–18819 (2014) (2014)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to IIT, Kharagpur, India and UGC, DAE CSR, Kolkata, India for SEM and SQUID measurements. This exertion is partially supported by DST research project (Memo No.: 296 (Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/16G-17/2017) from DST, West Bengal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, B.S., Goswami, M.N., Jana, P.C. et al. Structural and electrical properties of Gd-doped BiFeO3:BaTiO3 (3:2) multiferroic ceramic materials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 2154–2165 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0487-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0487-x