Abstract
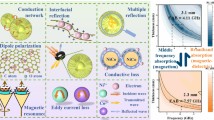
To obtain outstanding electromagnetic microwave absorption (EMWA) properties, the rambutan-like dielectric–magnetic C@NiCo2O4 material was successfully prepared by a simple hydrothermal method, followed by a carbonization process. Benefiting from the unique rambutan-like structure, the dielectric–magnetic C@NiCo2O4 composites showed excellent microwave attenuation ability: minimum reflection loss (RLmin) value of − 39.0 dB at 17.4 GHz and wide effective absorption bandwidth (EAB, reflection loss exceeding − 10 dB) of 4.16 GHz (> 13.84 GHz) with a matching thickness of only 1.5 mm, which were much better than those of pure C and NiCo2O4. The superior properties might be due to multiple synergistic effects: magnetic loss (NiCo2O4), dielectric loss (C, NiCo2O4), the multi-reflections, scattering and interface relaxation resulting from mesoporous rambutan-like structures, and the dipole polarization to get good electromagnetic matching and high attenuation efficiency.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Ding, L. Zhang, Q.L. Liao, Electromagnetic wave absorption in reduced graphene oxide functionalized with Fe3O4/Fe nanorings. Nano Res. 9(7), 2018–2025 (2016)
Y.F. Wang, D.L. Chen, X. Yin, P. Xu, F. Wu, M. He, Hybrid of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide: a lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(47), 26226–26234 (2015)
X.F. Liu, Y.X. Chen, X.R. Cui, M. Zeng, R.H. Yu, G.S. Wang, Flexible nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties based on Fe3O4/SiO2 nanorods and polyvinylidene fluoride. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(23), 12197–12204 (2015)
C.P. Li, Y.Q. Ge, X.H. Jiang, Porous Fe3O4/C microspheres for efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram. Int. 44(16), 19171–19183 (2018)
X. Wang, J.C. Shu, X.M. He, M. Zhang, X.X. Wang, C. Gao, J. Yuan, M.S. Cao, Green approach to conductive PEDOT:PSS decorating magnetic graphene to recover conductivity for highly efficient absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 14017–14025 (2018)
G.J.H. Melvin, Q.Q. Ni, Y. Suzuki, Microwave absorbing properties of silver nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 49(14), 5199–5207 (2014)
P.B. Liu, Y. Huang, L. Wang, Synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties of polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide-Co3O4 nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 573(19), 151–156 (2013)
J. Zheng, Z.Q. Liu, X.S. Zhao, One-step solvothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@C core–shell nanoparticles with tunable sizes. Nanotechnology 23(16), 165601–165610 (2012)
J.T. Feng, Y.C. Wang, Y.H. Hou, L.C. Li, Tunable design of yolk–shell ZnFe2O4@RGO@TiO2 microspheres for enhanced high-frequency microwave absorption. Inorg Chem Front 4, 935–945 (2017)
Y. Wang, Y. Fu, X. Wu, Synthesis of hierarchical coreshell NiFe2O4@MnO2 composite microspheres decorated graphene nanosheet for enhanced microwave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 43(14), 11367–11375 (2017)
J.R. Ma, X.X. Wang, W.Q. Cao, C. Han, H.J. Yang, J. Yuan, M.S. Cao, A facile fabrication and highly tunable microwave absorption of 3D flowerlike Co3O4-rGO hybrid-architectures. Chem. Eng. J. 339, 487–498 (2018)
J.Q. Zhu, X.J. Zhang, S.W. Wang, G.S. Wang, P.G. Yin, Enhanced microwave absorption material of ternary nanocomposites based on MnFe2O4@SiO2, polyaniline and polyvinylidene fluoride. Rsc Advances 6, 88104–88109 (2016)
Z.W. Shi, H. Lu, Q. Liu, K.M. Deng, L.Y. Xu, R.J. Zou, J.Q. Hu, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, L. Li, NiCoO nanostructures as a promising alternative for NiO photocathodes in p-type dye-sensitized solar cells with high efficiency. Energy Technol. 2(6), 517–521 (2014)
J. Zhang, F. Liu, J.P. Cheng, X.B. Zhang, Binary nickel-cobalt oxides electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors: influence of its composition and porous nature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(32), 17630–17640 (2015)
S. Khalid, C. Cao, L. Wang, Y. Zhu, Microwave Assisted synthesis of porous NiCo2O4 microspheres: application as high performance asymmetric and symmetric supercapacitors with large areal capacitance. Sci. Rep. 6, 22699–22712 (2016)
P. Silwal, L. Miao, I. Stern, X.L. Zhou, J. Hu, D.H. Kim, Metal insulator transition with ferrimagnetic order in epitaxial thin films of spinel NiCo2O4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(3), 118 (2016)
R.R. Salunkhe, K. Jang, H. Yu, S. Yu, T. Ganesh, S.H. Han, H. Ahn, Chemical synthesis and electrochemical analysis of nickel cobaltite nanostructures for supercapacitor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 509(23), 6677–6682 (2011)
X.F. Liu, C.C. Hao, H. Jiang, Hierarchical NiCo2O4/Co3O4/NiO porous composite: a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber with tunable absorbing performance. J Mater Chem C 5(15), 3770–3778 (2017)
J. Zhan, Y.L. Yao, C.F. Zhang, C.J. Li, Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of quasione-dimensional mesoporous NiCo2O4 nanostructure. J. Alloys Compd. 585(6), 240–244 (2014)
M. Zhou, F. Lu, B. Chen, X. Zhu, X. Shen, W. Xia, H. He, X. Zeng, Thickness dependent complex permittivity and microwave absorption of NiCo2O4 nanoflakes. Mater. Lett. 159, 498–501 (2015)
F.L. Wang, J.R. Liu, J. Kong, Z.J. Zhang, X.Z. Wang, M. Itoh, K.I. Machida, Template free synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of monodispersed hollow magnetite nano-spheres. J. Mater. Chem. 21(12), 4314–4320 (2011)
H.J. Wu, G.L. Wu, Y.Y. Ren, L. Yang, L.D. Wang, X.H. Li, Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 7677–7690 (2015)
Y. Xia, Y. Xiong, B. Li, Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: simple chemistry meets complex physics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38(4), 335–344 (2009)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan, Synthesis of flower-like CuS hollow microspheres based on nanoflakes self-assembly and their microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 10345–10352 (2015)
L. Shen, C. Qian, H. Li, X. Zhang, Mesoporous NiCo2O4 nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles as binder-free flexible electrodes for energy storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(18), 2630–2637 (2014)
G.L. Wu, Y.H. Cheng, Y.Y. Ren, Y.Q. Wang, Z.D. Wang, H.J. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod-carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 652, 346–350 (2015)
N.D. Wu, X.G. Liu, C.Y. Zhao, Effects of particle size on the magnetic and microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated nickel nanocapsules. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 628–634 (2016)
Y.Y. Lü, Y.T. Wang, H.L. Li, MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(24), 13604–13611 (2015)
R. Qiang, Y.C. Du, Electromagnetic functionalized Co/C composites by in situ pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-67). J. Alloys Compd. 681, 384–393 (2016)
Q.L. Liu, D. Zhang, T.X. Fan, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(1), 401 (2008)
N.N. Wu, H.L. Lv, J.R. Liu, Improved electromagnetic wave absorption of Co nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes derived from synergistic magnetic and dielectric losses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(46), 31542–31550 (2016)
H. Lv, G.B. Ji, H.Q. Zhang, M. Li, Z.Z. Zuo, Y. Zhao, B.S. Zhang, D.M. Tang, Y.W. Du, CoxFey@C composites with tunable atomic ratios for excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. Sci. Rep. 5, 18249–18259 (2015)
M.H. Xu, W. Zhong, Z.H. Wang, Highly stable FeCo/carbon composites: magnetic properties and microwave response. Phys. E. 52(3), 14–20 (2013)
G.M. Li, L.C. Wang, W. Li, CoFe2O4 and/or Co3Fe7 loaded porous activated carbon balls as a lightweight microwave absorbent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(24), 12385–12392 (2014)
H.Y. Lin, H. Zhu, H.F. Guo, Microwave-absorbing properties of Co-filled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Res. Bull. 43(10), 2697–2702 (2008)
M.S. Cao, J. Yang, W.L. Song, D.Q. Zhang, B. Wen, H.B. Jin, Z.L. Hou, J. Yuan, Ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube vs polyaniline/ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube multiheterostructures for highly effective microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater. Interfaces 4(12), 6949–6956 (2012)
Z.R. Jia, D. Lan, K.J. Lin, M. Qin, K.C. Kou, G.L. Wu, H.J. Wu, Progress in low-frequency microwave absorbing materials. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 17122–17136 (2018)
Y.C. Yin, X.F. Liu, X.J. Wei, Porous CNTs/Co composite derived from zeolitic imidazolate framework: a lightweight, ultrathin, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(50), 34686–34698 (2016)
Q. He, T. Yuan, X. Zhang, Electromagnetic field absorbing polypropylene nanocomposites with tuned permittivity and permeability by nanoiron and carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(42), 24784–24796 (2014)
H.J. Wu, G.L. Wu, L.D. Wang, Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: Facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 269, 443–451 (2015)
D. Lan, M. Qin, R.S. Yang, S. Chen, H.J. Wu, Y.C. Fan, Q.H. Fu, F.L. Zhang, Facile synthesis of hierarchical chrysanthemum-like copper cobaltate-copper oxide composites for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 533, 481–491 (2019)
C.Y. Liang, Y.J. Gou, L.N. Wu, Nature of electromagnetic-transparent SiO2 shell in hybrid nanostructure enhancing electromagnetic attenuation. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(24), 12967–12973 (2016)
F. Nanni, P. Travaglia, M. Valentini, Effect of carbon nanofibres dispersion on the microwave absorbing properties of CNF/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69(3), 485–490 (2009)
F. Wu, A. Xie, M. Sun, Y. Wang, M. Wang, Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) modified spongelike polypyrrole (PPy) aerogel for excellent electromagnetic absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(27), 14358–14369 (2015)
H.J. Wu, S.H. Qu, K.J. Lin, Y.C. Qing, L.D. Wang, Y.C. Fan, Q.H. Fu, F.L. Zhang, Enhanced low-frequency microwave absorbing property of SCFs@TiO2 composite. Powder Technol. 333, 153–159 (2018)
Y.N. Li, Y. Zhao, X.Y. Lu, Self-healing superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/Fe3O4 @polypyrrole fiber with core-sheath structures for superior microwave absorption. Nano Research 9(7), 2034–2045 (2016)
X. Sun, J. He, G. Li, J. Tang, T. Wang, Y. Guo, Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electro-magnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C 1(4), 765–777 (2012)
M. Wu, Y.D. Zhang, S. Hui, T.D. Xiao, S. Ge, W. Hines, Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80(23), 4404–4410 (2002)
W.Z. Li, T. Qiu, L.L. Wang, S.S. Ren, J.R. Zhang, L.F. He, X.Y. Li, Preparation and electromagnetic properties of core/shell polystyrene@polypyrrole@nickel composite microspheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(3), 883–891 (2013)
G.Z. Wang, Z. Gao, S.W. Tang, C.Q. Chen, F.F. Duan, S.C. Zhao, S.W. Lin, Y.H. Feng, L. Zhou, Y. Qin, Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12), 11009–11017 (2012)
M.S. Cao, X.L. Shi, X.Y. Fang, H.B. Jin, Z.L. Hou, W. Zhou, Y. Chen, Microwave absorption properties and mechanism of cagelike ZnO/SiO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(20), 203110–203113 (2007)
R.F. Zhuo, Morphology-controlled synthesis, growth mechanism, optical and microwave absorption properties of ZnO nanocombs. J. Phys. D 41(18), 185405–185413 (2008)
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, Z.L. Hou, W.L. Song, L. Zhang, M.M. Lu, H.B. Jin, X.Y. Fang, W.Z. Wang, J. Yuan, Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65, 124–139 (2013)
M.M. Lu, M.S. Cao, Y.H. Chen, W.Q. Cao, J. Liu, H.L. Shi, D.Q. Zhang, W.Z. Wang, J. Yuan, Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: a smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(34), 19408–19415 (2015)
M.S. Cao, X.X. Wang, W.Q. Cao, X.Y. Fang, B. Wen, J. Yuan, Thermally Driven Transport and Relaxation Switching Self-Powered Electromagnetic Energy Conversion. Small 14, 1800987–1800994 (2018)
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, M.M. Lu, W.Q. Cao, H.L. Shi, J. Liu, X.X. Wang, H.B. Jin, X.Y. Fang, W.Z. Wang, J. Yuan, Reduced graphene oxides: light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26(21), 3484–3489 (2014)
X.Y. Fang, M.S. Cao, X.L. Shi, Z.L. Hou, W.L. Song, J. Yuan, Microwave responses and general model of nanotetraneedle ZnO: integration of interface scattering, microcurrent, dielectric relaxation, and microantenna. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 054304 (2010)
W.Q. Cao, X.X. Wang, J. Yuan, W.Z. Wang, M.S. Cao, Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 10017–10022 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41476059) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M600557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Ge, Y., Jiang, X. et al. The rambutan-like C@NiCo2O4 composites for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 3124–3136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00592-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00592-3