Abstract
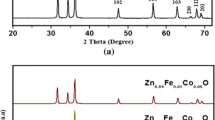
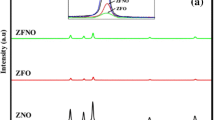
The ZnO, Zn0.96Mn0.04O, Zn0.95Mn0.04Co0.01O, Zn0.94Mn0.04Co0.02O and Zn0.92Mn0.04Co0.04O nanoparticles were synthesized by simple chemical precipitation technique. The effects of co-doping on the structure and magnetic properties of these nanoparticles were studied. The X-rays diffraction (XRD) scans were performed in the 2θ range of 20°–80°. The XRD patterns, at 300 K, of all the pure and co-doped ZnO samples confirmed the formation of wurtzite-type structure. X-ray diffraction and transmission scanning electron microscope analysis indicated that the high spin Co2+ and Mn2+ ions were substituted for the Zn2+ ions at tetrahedral sites. The average size of the nanoparticles were increased from 17 to 24 nm with the increase of dopants concentration. Moreover, Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) confirmed the synthesis results. All Zn0.96−xMn0.04Co x O (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4) nanoparticles samples were observed to be paramagnetic below 300 K. However, a large increase in the magnetization was observed below 40 K. This behavior, along with the negative value of the Curie–Weiss constant obtained from the linear fit to the susceptibility data below room temperature, indicated the ferromagnetic nature of the samples. The origin of ferromagnetism is likely to be the intrinsic characteristics of the Co and Mn doped samples. The high magnetization was noted for the 1 wt% Co co-doped Mn–ZnO annealed samples as compared to other samples with Co concentration above and below this threshold concentration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Prinz, Magneto electronics. Science 282, 1660–1663 (1998)
W. Prellier, A. Fouchet, B. Mercey, Oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors: a review of the experimental status. J. Phys. 15, R1583 (2003)
A. Stroppa, X. Duan, M. Peressi, Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-doped GaAs(1 1 0) surface. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 25, 217–221 (2006)
Y.Q. Chang, D.B. Wang, X.H. Luo, X.Y. Xu, X.H. Chen, L. Li, C.P. Chen, R.M. Wang, J. Xu, D.P. Yu, Synthesis, optical, and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic semiconductor Zn1– xMnxO nanowires via vapor phase growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4020–4022 (2003)
Y. Ohno, D.K. Young, B. Beshoten, F. Matsukura, H. Ohno, D.I. Awschalom, Electrical spin injection in a ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructure. Nature 402, 790 (1999)
Q. Wang, Q. Sun, P. Jena, Ab initio study of electronic and magnetic properties of the C-codoped Ga1–xMnxN (1010) surface. Phys. Rev. B 75, 035322 (2007)
C. Klingshirn, Optical properties of bound and localized excitons and of defect states. Phys. Status Solidi B 71, 547–556 (1975)
X.Y. Xu, C.B. Cao, Structure and ferromagnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2216–2219 (2009)
T. Dietl, A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 9, 965974 (2010)
K. Sato, H.K. Yoshida, Material design for transparent ferromagnets with ZnO-based magnetic semiconductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, L555 (2000)
Y. Lin, D. Jiang, F. Lin, W. Shi, M. Xueming, Fe-doped ZnO magnetic semiconductor by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 436, 30–33 (2007)
P.K. Sharma, R.K. Dutta, A.C. Pandey, S. Layek, H.C. Verma, Effect of iron doping concentration on magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2587–2591 (2009)
S.Y. Bae, C.W. Na, J.H. Kang, J. Park, Comparative structure and optical properties of Ga-, In-, and Sn-doped ZnO nanowires synthesized via thermal evaporation. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 2526–2531 (2005)
J.G. Wen, J.Y. Lao, D.Z. Wang, T.M. Kyaw, Y.L. Foo, Z.F. Ren, Aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy for advanced materials characterization. Chem. Phys. Lett. 372, 717–722 (2003)
S.A. Wolf, D.D. Awschalom, R.A. Buhrman, J.M. Daughton, M. Svon, M.L. Roukes, A.Y. Chtchelkanova, D.M. Treger, Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488–1495 (2001)
A. Angew, Origin, development, and future of spintronics (Nobel Lecture). Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 5956–5967 (2008)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in Zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019–1022 (2000)
G.Y. Ahn, S.I. Park, C.S. Kim, Enhanced ferromagnetic properties of diluted Fe doped ZnO with hydrogen treatment. J. Magn.Magn. Mater. 303, 329–331 (2006)
S.S. Abdullahia, Y. Köseoğlu, S. Güner, S. Kazan, B. Kocaman, C.E. Ndikilar, Synthesis and characterization of Mn and Co codoped ZnO nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct. 83, 342–352 (2015)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, Z.U. Rehman, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (Al, Ni) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 4333–4339 (2017)
Y.M. Hao, S.Y. Lou, S.M. Zhou, R.J. Yuan, G.Y. Zhu, N. Li, Structural, optical, and magnetic studies of manganese-doped zinc oxide hierarchical microspheres by self-assembly of nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 100 (2012)
C.K. Ghosh, S. Malkhandi, M.K. Mitra, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Effect of Mn doping on the electric and dielectric properties of ZnO epitaxial films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 245113 (2008)
K. Lommens, K. Lambert, F. Loncke, D. De Muynck, T. Balkan, F. Vanhaecke, H. Vrielinck, F. Callens, Z. Hens, The growth of Co:ZnO/ZnO core/shell colloidal quantum dots: changes in nanocrystal size, concentration and dopant coordination. ChemPhysChem 9(3), 484–491 (2008)
J.J. Beltran, J.A. Osorio, C.A. Barrero, C.B. Hanna, A. Punnoose, Magnetic properties of Fe doped, Co doped, and Fe+ Co co-doped ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17C308 (2013)
G. Lawes, A.S. Risbud, A.P. Ramirez, R. Seshadri, Absence of ferromagnetism in Co and Mn substituted polycrystalline ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 71, 045201 (2005)
Y. Jiang, W. Yan, Z. Sun, Q. Liu, Z. Pan, T. Yao, Y. Li, Z. Qi, G. Zhang, P. Xu, Z. Wu, S. Wei, Experimental and theoretical investigations on ferromagnetic nature of Mn-doped dilute magnetic semiconductors. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 190, 012100 (2009)
L. Yang, X. Wu, G. Huang, T. Qiu, Y. Yang, In situ synthesis of Mn-doped ZnO multileg nanostructures and Mn-related Raman vibration. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 014308 (2005)
R. Khan, M.U. Zulfiqar, S. Fashu, M.U. Rahman, Effect of annealing temperature on the dielectric and magnetic response of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 28(3), 2673–2679 (2017). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-5844-z
R. Khan, Y. Zaman, Effect of annealing on structural, dielectric, transport and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 4003–4010 (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-4254-y
R. Khan, S. Fashu, M.U. Rahman, Effects of Ni co-doping concentrations on dielectric and magnetic properties of (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 27(8), 7725–7730 (2016)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, Z.U. Rehman, Zulfiqar, M.U. Rahman, Effect of annealing on Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. 28(14), 10122–10130 (2017)
C.J. Cong, L. Liao, Q.Y. Liu, J.C. Li, K.L. Zhang, Effects of temperature on the ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles and Mn-related Raman vibration. Nanotechnology 17, 1520 (2006)
R. Elilarassi, G. Chandrasekaran, Synthesis and characterization of ball milled Fe-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor. Optoelectron. Lett. 8, 109–112 (2012)
K.R. Kittilstved, D.A. Schwartz, A.C. Tuan, S.M. Heald, S.A. Chambers, D.R. Gamelin, Direct kinetic correlation of carriers and ferromagnetism in Co2+:ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 037203–037204 (2006)
S. Yin, Absence of ferromagnetism in bulk polycrystalline Zn0.9Co0.1O. Phys. Rev. B 73, 224408-1–224408-5 (2006)
T. Fukumura, Z. Jin, M. Kawasaki, Magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 958–960 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan under START-UP RESEARCH GRANT PROGRAM with a Grant No. : 21-1525/SRGP/R&D/HEC/2017 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the HEC Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R., Zulfiqar, Fashu, S. et al. Structure and magnetic properties of (Co, Mn) co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 32–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7884-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7884-4