Abstract
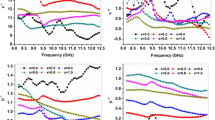
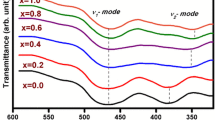
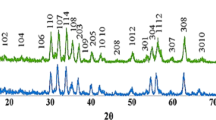
M-type Barium-Stronium hexaferrites with the chemical composition Ba0.5Sr0.5CoxGdxFe12−2xO19 (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) were prepared using a conventional ceramic method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique was used to explore the structure characterization and phase purity of the prepared compositions. The absorber testing device method was adopted for investigating the dependence of microwave absorption of ferrite compositions on substitution and thickness from 8.2 to 12.4 GHz. The quarter wavelength and impedance matching mechanism are explored to evaluate the microwave absorption. XRD analysis revealed formation of M (magnetoplumblite) phase in compositions x = 0.0, 0.2, while doped compositions (x = 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) displayed coexistence of M-phase along with orthorhombic phase (BaFe2O4). For maximum microwave absorption, the doping of Co2+ and Gd3+ leads to the reduction in thickness of composition and frequency shift from the high to low frequency region. Composition x = 0.8 exhibits good microwave absorber characteristics with 96.90% absorbed power and reflection loss of −15.0 dB at matching frequency and thickness of 8.2 GHz and 2.9 mm respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M.S. Awan, M. Ahmad, M.N. Ashiq, S. Naseem, Effect of Tb3+ substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of M-type hexaferrites synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J. Alloys Comp. 550, 564–572 (2013)
Z.W. Li, L. Chen, C.K. Ong, Studies of static and high-frequency magnetic properties for M-type ferrite BaFe12–2xCoxZrxO19. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3902–3907 (2002)
Y.J. Kim, S.S. Kim, Microwave absorbing properties of Co-substituted Ni/sub 2/W hexaferrites in Ka-band frequencies (26.5–40 GHz). IEEE Trans. Magn. 38, 3108–3110 (2002)
O. Kubo, T. Ido, H. Yokoyama, Properties of Ba ferrite particles for perpendicular magnetic recording media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 18, 1122–1124 (1982)
H. F. Yu, K. C. Huang, Effects of pH and citric acid contents on characteristics of ester-derived BaFe12O19 powder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260, 455–461 (2003)
D. Ravinder, P.V.B. Reddy, High-frequency dielectric behaviour of Li–Mg ferrites. Mater. Lett. 57, 4344–4350 (2003)
G. Asghar, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Cr–Zn doped strontium hexa-ferrites for high frequency applications. J. Alloys Comp. 526, 85–90 (2012)
F.L. Wei, Magnetic properties of BaFe12–2xZnxZrxO19 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 87(12), 8636–8639 (2000)
X. Liu, Research on La3+–Co2+-substituted strontium ferrite magnets for high intrinsic coercive force. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305(2), 524–528 (2006)
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57(7), 1191–1334 (2012)
F.M.M. Pereira, M.R.P. Santos, R.S.T.M. Sohn, J.S. Almeida, A.M.L. Medeiros, M.M. Costa, A.S.B. Sombra, Magnetic and dielectric properties of the M-type barium strontium hexaferrite (Ba xSr1−x Fe12O19) in the RF and microwave (MW) frequency range. J. Mater. Sci. 20, 408–417 (2009)
K.K. Mallick, Magnetic and structural properties of M-type barium hexaferrite prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311, 683–692 (2007)
D. Seifert, J. Töpfer, M. Stadelbauer, R. Grössinger, J.-M. Le Breton, Rare-earth-substituted Sr1− xLnxFe12O19 hexagonal ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94(7), 2109–2118 (2011)
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, A. Poorbaferani, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ce-doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 397, 101–107 (2016)
S.S.S. Afghahi, M. Jafarian, Y. Atassi, Microstructural and magnetic studies on BaMgxZnxX2xFe12–4xO19 (x = Zr,Ce,Sn) prepared via mechanical activation method to act as a microwave absorber in X-band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 184–191 (2006)
R.S. Alam, M. Moradi, H. Nikmanesh, J. Ventura, M. Rostami, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMgx/2Mnx/2CoxTi2xFe12–4xO19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 20–27 (2016)
C. Singh, S.B. Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, K. Marina, Hysteresis analysis of Co–Ti substituted M-type Ba–Sr hexagonal ferrite. Mater. Lett. 63, 1991–1994 (2009)
M.R. Meshram, N.K. Agrawal, B. Sinha, P.S. Misra, Characterization of M-type barium hexagonal ferrite-based wide band microwave absorber. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 271, 2007–2014 (2004)
P. Singh, V.K. Babbar, A. Razdan, R.K. Puri, T.C. Goel, Complex permittivity, permeability, and X-band microwave absorption of CaCoTi ferrite composites. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4362–4366 (2000)
F.M.M. Pereria, C.A.R. Junior, M.R.P. Santosh, R.S.T.M. Sohn, F.N.A. Freire, J.M. Sasaki, J.A.C. De-Paiva, A.B.S. Sombra, Sructural and dielectric spectroscopic studies of M-type barium hexaferrite alloys (BaxSr1–xFe12O19). J. Mater. Sci. 19, 627–638 (2008)
F. Song, X. Shen, J. Xiang, H. Song, Formation and magnetic properties of M–Sr ferrite hollow fibers via organic gel-precursor transformation process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 213–216 (2010)
P.N. Vasambekar, C.B. Kolekar, A.S. Vaigankar, Electrical switching in CdxCo1–xFe2–yCryO4 system. Mater. Res. Bull. 34, 863–868 (1999)
R.S. Patil, S.V. Kakatkar, A.M. Sankpal, S. R. Sawant, S.S. Suryavanshi, U.R. Ghodke, K. Kamat, Infrared absorption of Ti4+ and Zr4+ substituted Li–Zn ferrites. Indian J. Pure. Appl. Phys. 32, 193–194 (1994)
N.W. Grimes, A.J. Collet, Correlation of infra-red spectra with structural distortions in the spinel series Mg(CrxAl2–x)O4. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 43, 591–594 (1971)
J. Preudhomme, P. Tarte, Spectrochimica Acta part A: molecular spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta 27, 1817–1835 (1971)
M.C. Chhantbar, U.N. Trivedi, P.V. Tanna, H.J. Shah, R.P. Vara, H.H. Joshi, K.B. Modi, Infrared spectral studies of Zn-substituted CuFeCrO4 spinel ferrite system. Indian J. Phys. 78 321–326 (2004)
M. Aliahmad, M. Noori, Synthesis and characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles by chemical method. Indian J. Phys. 87, 431–434 (2013)
M.M. Rashad, I.A. Ibrahim, A novel approach for synthesis of M-type hexaferrites nanopowders via the co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1796–1803 (2011)
T.R. Wagner, Preparation and Crystal Structure Analysis of Magnetoplumbite-Type BaGa12O19. J. Solid State Chem. 136, 120–124 (1998)
C. Singh, S. Bindra Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, F. Tabatabaei, Static magnetic properties of Co and Ru substituted Ba–Sr ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 176–184 (2008)
M.T. Rahman, M. Vargas, C.V. Ramana, Structural characteristics, electrical conduction and dielectric properties of gadolinium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Comp. 617, 547–562 (2014)
B. Wang, J. Wei, Y. Yang, T. Wang, F. Li, Investigation on peak frequency of the microwave absorption for carbonyl iron/epoxy resin composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323 1101–1103 (2011)
N.-N. Song, Y.J. Ke, H.-T. Yang, H. Zhang, X.-Q. Zhang, B.-G. Shen, Z.-H. Cheng, Integrating giant microwave absorption with magnetic refrigeration in one multifunctional intermetallic compound of LaFe11.6Si1.4C0.2H1.7. Sci. Rep. 2291, 1–5 (2013)
A.M. Nicolson, G.F. Ross, Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time-domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 19, 377–382 (1970)
T. Inui, K. Konishi, K. Oda, Fabrications of broad-band RF-absorber composed of planar hexagonal ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 3148–3150 (1999)
P.T. Tho, C.T.A. Xuan, D.M. Quang, T.N. Bach, T.D. Thanh, N.T.H. Le, D.H. Manh, N.X. Phuc, D.N.H. Nam, Microwave absorption properties of dielectric La1.5Sr0.5NiO4 ultrafine particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. 186, 101–105 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, R., Singh, C., Singh, J. et al. A study of microwave absorbing properties in Co–Gd doped M-type Ba–Sr hexaferrites prepared using ceramic method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 11969–11978 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7006-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7006-3