Abstract
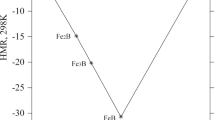
A series of high iron content Fe–B–Si–EM (EM = Early transition metal) amorphous/nanocrystalline alloy ribbons were fabricated by melt spinning. The effects of EM on glass forming ability, thermal stability and magnetic properties of Fe84B8Si5EM3 alloys were investigated. Based on XRD patterns of the melt-spun ribbons, a completely amorphous structure forms in Fe84B8Si5Mo3 alloy, and partial α-Fe phase precipitates in the (200) crystal plane in Fe84B8Si5Ti3, Fe84B8Si5Zr3 and Fe84B8Si5Hf3 alloys. These alloys show excellent thermal stability, especially for Fe84B8Si5Mo3 and Fe84B8Si5Hf3 alloys; the temperature interval between the first and the second onset crystallization temperature (∆Tx = Tx2−Tx1) can reach 298 °C. Compared with the other alloys, the Fe84B8Si5Mo3 alloy exhibits higher saturation magnetization Ms of approximately 152.8 emu/g and lower coercivity Hc of about 11.3 A/m, thereby showing excellent magnetic properties in the as-quenched state. When annealed at the temperature close to the first crystalline peak temperature (Tp1) for 0.5 h, a clear diffraction pattern consisting of three peaks appears; this pattern is identified as bcc α-Fe phase. Proper annealing treatment can optimize the magnetic properties. The optimal annealing temperature range is found to be 550–650 °C.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.C. Jiles, Recent advances and future directions in magnetic materials[J]. Acta Mater. 51(19), 5907–5939 (2003)
R. Hasegawa, Advances in amorphous and nanocrystalline magnetic materials[J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304(2), 187–191 (2006)
W. Lu, B. Yan, Y. Li et al., Structure and soft magnetic properties of V-doped finemet-type alloys[J]. J. Alloys Compd. 454(1), L10–L13 (2008)
M.E. McHenry, M.A. Willard, D.E. Laughlin, Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets[J]. Prog. Mater. Sci. 44(4), 291–433 (1999)
U. Köster, J. Meinhardt, S. Roos et al., Formation of quasicrystals in bulk glass forming Zr-Cu-Ni-Al alloys[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69(2), 179–181 (1996)
D. Hong-Yu, L. Yang, Y. Ke-Fu, Preparation of a Pd-Cu-Si bulk metallic glass with a diameter up to 11 mm[J]. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27(12), 126101 (2010)
Q.K. Jiang, G.Q. Zhang, L. Yang et al., La-based bulk metallic glasses with critical diameter up to 30 mm[J]. Acta Mater. 55(13), 4409–4418 (2007)
A. Wang, C. Zhao, A. He et al., Composition design of high Bs Fe-based amorphous alloys with good amorphous-forming ability[J]. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 729–734 (2016)
J.D. Ayers, V.G. Harris, J.A. Sprague et al., A model for nucleation of nanocrystals in the soft magnetic alloy Fe73.5Nb3Cu1Si13.5B9[J]. Nanostruct. Mater. 9(1), 391–396 (1997)
M. Ohnuma, K. Hono, S. Linderoth et al., Small-angle neutron scattering and differential scanning calorimetry studies on the copper clustering stage of Fe-Si-B-Nb-Cu nanocrystalline alloys[J]. Acta Mater. 48(20), 4783–4790 (2000)
Z. Li, A. Wang, C. Chang et al., Synthesis of FeSiBPNbCu nanocrystalline soft-magnetic alloys with high saturation magnetization[J]. J. Alloys Compd. 611, 197–201 (2014)
A.R. Yavari, D. Negri, Effect of concentration gradients on nanostructure development during primary crystallization of soft-magnetic iron-based amorphous alloys and its modelling[J]. Nanostruct. Mater. 8(8), 969–986 (1997)
Y.R. Zhang, R.V. Ramanujan, Microstructural observations of the crystallization of amorphous Fe-Si-B based magnetic alloys[J]. Thin Solid Films 505(1), 97–102 (2006)
T. Alam, T. Borkar, S.S. Joshi et al., Influence of niobium on laser de-vitrification of Fe-Si-B based amorphous magnetic alloys[J]. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 428, 75–81 (2015)
W.L. Liu, Y.G. Wang, F.G. Chen, Investigation of microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe81Si4B12–xP2Cu1Mx (M = Cr, Mn and V; x = 0, 1, 2, 3) melt spun ribbons[J]. J. Alloys Compd. 622, 751–755 (2015)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element[J]. Mater. Trans. 46(12), 2817–2829 (2005)
K.G. Pradeep, G. Herzer, P. Choi et al., Atom probe tomography study of ultrahigh nanocrystallization rates in FeSiNbBCu soft magnetic amorphous alloys on rapid annealing[J]. Acta Mater. 68, 295–309 (2014)
F. Kong, A. Wang, X. Fan et al., High Bs Fe84–xSi4B8P4Cux (x = 0-1.5) nanocrystalline alloys with excellent magnetic softness[J]. J. Appl. Phys. 109(7), 07A303 (2011)
H.R. Lashgari, Z. Chen, X.Z. Liao et al., Thermal stability, dynamic mechanical analysis and nanoindentation behavior of FeSiB(Cu) amorphous alloys[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. 626, 480–499 (2015)
Y.Q. Wu, T. Bitoh, K. Hono et al., Microstructure and properties of nanocrystalline Fe-Zr-Nb-B soft magnetic alloys with low magnetostriction[J]. Acta Mater. 49(19), 4069–4077 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20124420110007), the Demonstration Dase Fund for Joint Training Graduate of Guangdong Province (No. 2013JDXM27) and the Young Creative Talents Project of Ordinary University in Guangdong Province (No. 2015KQNCX158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Yang, Y.Z., Yao, C.L. et al. Glass forming ability and magnetic properties of Fe–B–Si–EM (EM = Ti, Zr, Mo, and Hf) alloys with high iron content. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 10218–10223 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6788-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6788-7