Abstract
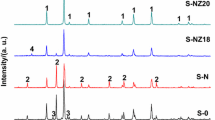
The pure hexagonal phase (Zn, Mg) TiO3 (abbreviated to ZMT) micro/nano crystals were prepared by a molten salt method. The influences of the molten salt system and the heat treatment temperature on ZMT crystalline powders phase composition and particles morphology were studied. The results show that the formation of ZMT phase takes place at about 530 °C and the hexagonal phase stability region is 530–810 °C in KCl–NaCl salt system when MgCl2·6H2O taken in excess. Compared to the conventional solid phase process, the formation temperature of hexagonal ZMT via the molten salt method is lower. The ZMT powders prepared by the molten salt method are indicative more uniform grain size distribution and small grain size (the average grain size is about 150 nm).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Butee, A.R. Kulkarni, O. Prakash, R.P.R.C. Aiyar, I. Wattamwar, D. Bais, K. Sudheendran, R.K.C. James, Significant enhancement in quality factor of Zn2TiO4 with Cu-substitution. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 567–572 (2011)
X.C. Liu, F. Gao, C.S. Tian, Synthesis, low-temperature sintering and the dielectric properties of the ZnO–(1–x) TiO2–xSnO2 (x = 0.04–0.2). Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 693–699 (2008)
X.C. Liu, M. Zhao, F. Gao, L.L. Zhao, C.S. Tian, Effects of WO3 additions on the phase structure and transition of zinc titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 450, 440–445 (2008)
Y.R. Wang, S.F. Wang, Y.M. Lin, Low temperature sintering of (Zn1−x , Mg x ) TiO3 microwave dielectrics. Ceram. Int. 31, 905–909 (2005)
H.T. Kim, S. Nahm, J.D. Byun, Low-fired (Zn, Mg) TiO3 microwave dielectrics. J. Am. Cream. Soc. 82, 3476–3480 (1999)
Z. Ding, H. Su, X. Tang, H. Zhang, Y. Jing, B. Liu, Low: temperature: sintering characteristic and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn0.7Mg0.3)TiO3 ceramics with LBSCA glass. Ceram. Int. 41, 10133–10136 (2015)
B. Li, B. Tang, S. Zhang, H. Jiang, Low temperature sintering and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn0.65Mg0.35) TiO3 ceramics with BiVO4. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 6461–6466 (2010)
N. Obradovic, M. Mitric, M.V. Nikolic, D. Minic, N. Mitrovic, M.M. Ristic, Influence of MgO addition on the synthesis and electrical properties of sintered zinc–titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 471, 272–277 (2009)
Y.C. Lee, Y.Y. Yeh, P.R. Tsai, Effect of microwave sintering on the microstructure and electric properties of (Zn, Mg) TiO3-based multilayer ceramic capacitors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 1725–1732 (2012)
K. He, R.Y. Hong, W.G. Feng, D. Badami, A facile co-precipitation synthesis of hexagonal (Zn, Mg) TiO3. Powder Technol. 239, 518–524 (2013)
X.C. Liu, Molten salt synthesis of ZnTiO3 powders with around 100 nm grain size crystalline morphology. Mater. Lett. 80, 69–71 (2012)
L. Liu, F. Gao, J. Li, J. Liu, G. Hu, H. Sun, Molten salt synthesis of acicular sodium strontium niobate particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178, 1359–1364 (2013)
L. Liu, F. Gao, Y. Zhang, F. Gao, Preparation of cubic Na0.5Sr0.25NbO3 particles by molten salt synthesis. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 1136–1141 (2015)
X. Tian, F. Gao, S. Qu, H. Ma, B. Wang, Effects of molten salt content and reaction temperature on molten salt preparation of CaNaBi2Nb3O12 powder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6189–6193 (2015)
D. Zhou, H. Wang, H. Zhou, X. Xie, X. Yao, Y. Cheng, Preparation of Sb3Nb3O13 powders using molten salt method. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 8387–8390 (2007)
T. Lusiola, F. Bortolani, Q. Zhang, R. Dorey, Molten hydroxide synthesis as an alternative to molten salt synthesis for producing K0.5Na0.5NbO3 lead free ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 1938–1942 (2012)
C.L. Huang, Y.W. Tseng, J.Y. Chen, Y.C. Kuo, Dielectric properties of high-Q (Mg1–x Zn x )1.8Ti1.1O4 ceramics at microwave frequency. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 2365–2371 (2012)
M.K. Ekmekçi, M. Erdem, A.S. Başak, M. İlhan, A. Mergen, Molten saltsynthesis and optical properties of Eu3+, Dy3+ or Nd3+ doped NiNb2O6 columbite-type phosphors. Ceram. Int. 41, 9680–9685 (2015)
J. Wu, S. Hao, J. Lin, M. Huang, Y. Huang, Z. Lan, P. Li, Crystal morphology of anatase titania nanocrystals used in dye-sensitized solar cells. Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 247–252 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 51372197) and the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (Project 14JK1483).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zuo, C. Molten salt synthesis of (Zn, Mg) TiO3 micro/nano crystals with pure hexagonal ilmenite structure. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 8319–8324 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4840-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4840-7