Abstract
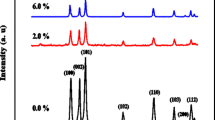
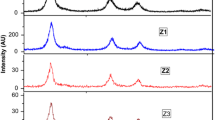
V-doped zinc oxide (Zn1−xVxO, 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1) diluted magnetic semiconductors have been synthesized by using a sol–gel method. We systematically investigated effects of V-doping concentration on the structural, magnetic and optical properties of Zn1−xVxO nanoparticles. All diffraction peaks could be indexed to wurtzite structure of ZnO with V concentration of less than or equal to 3 at.%. Secondary phase of Zn3V3O8 emerged when V concentration was higher than 3 at.%. Magnetic measurements indicated that the samples with V concentration less than or equal to 3 at.% were ferromagnetic at room temperature. Saturated magnetization of Zn1−xVxO nanoparticles increased with increase of V doping concentration. The results of Raman and photoluminescence testified that the ferromagnetism in Zn1−xVxO nanoparticles was probably originated from oxygen vacancies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Thangeeswari, J. Velmurugan, M. Priya, J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron. 24, 4817–4826 (2013)
I. Javed, J. Tariq, R.H. Yu, J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron. 24, 4393–4398 (2013)
M. Ebrahimizadeh Abrishami, S.M. Hosseini, J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron. 24, 64–69 (2013)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Science 287, 1019 (2000)
A.A. Fatima, S. Devadason, T. Mahalingam, J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron. 25, 3466–3472 (2014)
Y. Liu, J.H. Yang, Q.F. Guan, L.L. Yang, H.L. Liu, Y.J. Zhang, Y.X. Wang, D.D. Wang, J.H. Lang, Y.T. Yang, L.H. Fei, M.B. Wei, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 3559–3562 (2010)
G. Srinet, R. Kumar, V. Sajal, J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Electron. 25, 3052–3056 (2014)
Y. Liu, H.B. Liu, Z.G. Chen, N. Kadasala, C.Y. Mao, Y.X. Wang, Y.J. Zhang, H.L. Liu, Y.Q. Liu, J.H. Yang, Y.S. Yan, J. Alloy. Compd. 604, 281 (2014)
M.K. Gupta, J.H. Lee, K.Y. Lee, S.W. Kim, ACS Nano 7, 8932 (2013)
Q.B. Wang, G. Zheng, Q.L. Chen, M. Wan, X.C. Wang, Physica B Condens. Matter 407, 719 (2012)
G. Jayalakshmi, K. Saravanan, S. Balakumar, T. Balasubramanian, Vacuum 95, 66 (2013)
S. Karamat, R.S. Rawat, P. Lee, T.L. Tan, R.V. Ramanujan, W. Zhou, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 2309 (2010)
H. Saeki, H. Tabata, T. Kawai, Solid State Commun. 120, 439 (2001)
S. Ramachandran, A. Tiwari, J. Narayan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 172502 (2005)
S.Q. Zhou, K. Potzger, H. Reuther, K. Kuepper, W. Skorupa, M. Helm, J. Fassbender, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 09H109 (2007)
L.X. Zhu, M.J. Wang, Dalton Trans. 42, 16289 (2013)
W.J. Liu, X.D. Tang, Z. Tang, W. Bai, N.Y. Tang, Adv. Condens. Matter. Phys. 2013, 424398 (2013)
S.A. Ansari, M.M. Khan, M.O. Ansari, J. Lee, M.H. Cho, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 27023 (2013)
L.Q. Liu, B. Xiang, Y. Zhang, D.P. Yu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 063104 (2006)
S. Shin, S. Suga, M. Taniguchi, M. Fujisawa, H. Kanzaki, A. Fujimori, H. Daimon, Y. Ueda, K. Kosuge, S. Kachi, Phys. Rev. B 41, 4993 (1990)
P.M. Chassaing, F. Demangeot, N. Combe, L. Saint-Macary, M.L. Kahn, B. Chaudret, Phys. Rev. B 79, 155314 (2009)
L.L. Yang, Q.X. Zhao, M. Willander, J. Appl. Phys. 105, 053503 (2009)
L.V. Azaroff, Introduction to Solids (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1960), pp. 371–372
D.D. Wang, G.Z. Xing, H.Y. Peng, T. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 7065 (2009)
X.Q. Wei, B.Y. Man, M. Liu, C.S. Xue, H.Z. Zhuang, C. Yang, Physica B Condens. Matter. 388, 145–152 (2007)
L. Ma, S. Ma, H. Chen, X. Ai, X. Huang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 10036–10041 (2011)
S. Maensiri, C. Masingboon, V. Promarak, S. Seraphin, Opt. Mater. 29, 1700–1705 (2007)
J.T. Luo, X.Y. Zhu, B. Fan, F. Zeng, F. Pan, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 115109 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11204104, 61178074, 61008051, 61308095, 61378085 and 11254001), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0824 and NCET-11-0981), Program for the development of Science and Technology of Jilin province (Item No. 201201083, 201205078, 20110415, and 201115219) and the Twentieth Five-Year Program for Science and Technology of Education Department of Jilin Province (Item No. 20140156 and 20140147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Liu, Y., Yang, L. et al. Role of oxygen vacancies in V-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 2466–2470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2707-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2707-y