Abstract
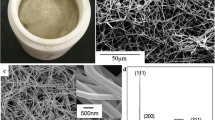
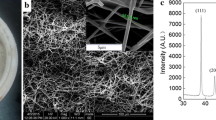
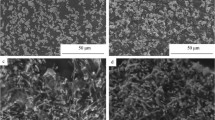
Silver nanowires have drawn remarkable attention owing to their anisotropic electrical and optical properties that differ from those observed in the bulk materials and the interesting applications in various areas such as electronic devices, chemical sensors and photonics. In this paper, silver nanowires with an average diameter of 450 nm and a length of up to 100 μm were successfully synthesized by a polyol process. The experimental results indicate that the morphologies and sintering behaviors of silver nanowires are impacted by glutaric acid and the sintering temperature. The isotropically conductive adhesives (ICAs) were made by adding silver nanowires to the polymer composites consisted mainly of epoxy resin, cure agent and catalyst, and then the electrical properties were investigated based on those physical parameters such like the fraction of the silver nanowires of the total of silver fillers and the curing temperature. The in situ monitoring of the variation in electrical resistance of the ICAs and DSC explore that silver nanowires can affect the curing behavior of the ICAs. Silver nanowires can significantly improve the electrical conductivity of the ICAs when the loading of silver nanowires is low and the curing temperature is less than about 250 °C. There is little difference of the electrical resistivity between the ICAs filled with silver nanowires and micro-sized silver flakes when the loading of silver fillers in the ICAs is 75 wt%, and this phenomenon is related to the curing temperature. The silver nanowires treated by glutaric acid can improve the electrical property of the ICAs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Dong, K.S. Moon, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 40 (2005)
H. Jiang, K.-S. Moon, J. Lu, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 11 (2006)
R. Zhang, W. Lin, K. Moon, C.P. Wong, Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 2637 (2010)
H. Cui, Q. Fan, D. Li, Polym. Int. 62, 1644 (2013)
Y. Li, K. Moon, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 99, 1665 (2006)
R. Durairaj, L.W. Man, L.J. Ping, L.S. Pheng, R.T. Subramaniam, Eng. Lett. 21, 3 (2013)
C. Yang, W. Lin, Z.Y. Li, R.W. Zhang, H.R. Wen, B. Gao, C.P. Wong, Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 23 (2011)
M. Inoue, H. Muta, S. Yamanaka, K. Suganuma, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 9 (2009)
C. Chen, L. Wang, R. Li, G. Jiang, H. Yu, T. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3172 (2007)
H.W. Cui, D.S. Li, Q. Fan, Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 3 (2013)
Z.X. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, F. Xiao, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 25, 13 (2011)
D. Chen, X. Qiao, X. Qiu, F. Tan, J. Chen, R. Jiang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 486 (2010)
Y. Li, K.-S. Moon, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1573 (2005)
H. Jiang, K.-S. Moon, J. Lu, C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1432 (2005)
T. Tao, X. Chen, G.-Q. Lu, G.-Y. Lei, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 1333 (2005)
H.P. Wu, J.F. Liu, X.J. Wu, M.Y. Ge, Y.W. Wang, G.Q. Zhang, J.Z. Jiang, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 26, 617 (2006)
H.H. Lee, K.S. Chou, Z.W. Shih, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 25, 5 (2005)
R.W. Zhang, K. Moon, W. Lin, C.P. Wong, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 10 (2010)
Z.X. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, F. Xiao, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 25, 1465 (2011)
M. Rong, M. Zhang, H. Liu, H. Zeng, Polymer 40, 6169 (1999)
R.W. Zhang, W. Lin, K.S. Moon, C.P. Wong, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 2637 (2010)
H. Jiang, K.S. Moon, Y. Li, C.P. Wong, Chem. Mater. 18, 2969 (2006)
H. Gao, L. Liu, K.H. Liu, Y.F. Luo, D.M. Jia, J.S. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 22 (2012)
A.R. Siekkinen, J.M. McLellan, J. Chen, Y. Xia, Chem. Phys. Lett. 432, 491 (2006)
M. Inoue, K. Sugamuma, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 18, 40 (2006)
M. Inoue, H. Muta, T. Markawa et al., J. Electron. Mater. 37, 462 (2007)
M. Inoue, K. Sugamuma, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 669 (2007)
H. Gao, L. Liu, Y.F. Luo, D.-M. Jia, F. Wang, K.-H. Liu, Int. J. Polym. Mater. 60, 40 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Science Foundation of China under Grants of (61302044, 51302145) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012010010646) and Zhongshan Science and Technology Projects (20123A319) and Scientific Research Team Training Project in University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Zhongshan Institute (412YT02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.H., Xiong, N.N., Xie, H. et al. New insights into silver nanowires filled electrically conductive adhesives. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 621–629 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2475-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2475-0