Abstract
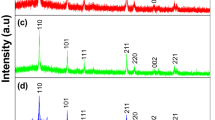
ZnO–ZnF2–B2O3 borate glass mixed with different concentrations of MoO3 were synthesized and subsequently crystallized. The X-ray diffraction studies revealed that the samples were embedded with crystalline phases in which molybdenum ions exist in Mo6+ and Mo5+ states. The results of spectroscopic studies (viz., optical absorption and electron spin resonance) have revealed that the there is an increasing proportion of Mo5+ ions with increase in the concentration of MoO3 in the glass ceramic. The results of photoluminescence spectra have indicated that if the care is taken to minimize Mo5+ ion concentration, these glass ceramics are suitable for light emission in the blue, green and red regions. The analysis of the results of IR spectra have indicated that with increase in the content of MoO3 there is an increasing degree of disorder in the glass network. The room temperature dielectric constant of these glass ceramics containing even the highest concentration of MoO3 is always found to be in between 11.5 and 12.4 suggesting that these glass ceramics would be suitable for dielectric layer in plasma display panels (PDP). The dielectric parameters have exhibited relaxation character; the relaxation effects have been attributed to molybdenyl complexes. The observed increase in the electrical conductivity with MoO3 content is attributed to the contribution of polaronic transfer between Mo5+ ⟷ Mo6+ ions. Additionally, the substantial decrement in jump distance for zinc ions between the two sites in the ceramic network (because of increase in the concentration of dangling bonds) is also found to contribute to the conductivity. The value of dielectric breakdown strength for the studied materials is measured to be in the range of 10.54–12.9 kV/cm which is far greater than the required value for a material to be used as dielectric layer in PDP.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.R. Clarke, J Am Ceram Soc 82, 485–502 (1999)
B.L. Zhu, D.W. Zeng, W.L. Song, A.H. Wang, Mater Chem Phys 89, 148–153 (2005)
D. Liu, D. Tang, L. Ci, X. Yan, Y.N. Liang, Z. Zhou, H. Yuan, W. Zhou, G. Wang, Chin Phys Lett 20, 928–931 (2003)
K.J. Kim, Y.R. Park, Appl Phys Lett 22, 475–477 (2001)
W.S. Shi, O. Agyeman, C.N. Xu, J Appl Phys 91, 5640–5644 (2002)
S.E. Derenzo, M.K. Klintenberg, Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res A 486, 214–219 (2002)
T. Shinoda, M. Wakitani, T. Nanto, N. Awaji, S. Kanagu, Electron Dev 47, 77–81 (2000)
F.H. Wang, H.P. Chang, C.C. Tseng, C.C. Huang, Surf Coat Tech 205, 5269–5277 (2011)
L. Ding, Y. Yang, X. Jiang, C. Zhu, G. Chen, J. Non-Cryst, Solids 354, 1382–1385 (2008)
M. Abdel-Baki, F. El-Diasty, J Solid State Chem 184, 2762–2769 (2011)
S. Bale, N.S. Rao, S. Rahman, Solid State Sci 10, 326–331 (2008)
Bondar IA, Toropov NA (1964) In: Porai-Koshits EA (ed) The structure of glass, vol 3, p 35
G.V. Rao, P.Y. Reddy, N. Veeraiah, Mater Lett 57, 403–408 (2002)
P.W. McMillan 2nd (ed.), Glass-ceramics (Academic Press, London, 1979)
L.S. Rao, M.S. Reddy, D.K. Rao, N. Veeraiah, J Solid State Sci 11, 578–587 (2009)
Z. Hussain, J Electron Mater 31, 615–630 (2002)
P. Naresh, G. Naga Raju, C.S. Rao, S.V.G.V.A. Prasad, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, Phys B 407, 712–718 (2012)
F. Kohlmuller, Bull. Chim. Fr., 4379 (1968)
J.C. Couturier, Rev Chim Miner 22, 753 (1986)
K.J. Rao, Structural Chemistry of Glasses (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2002)
K. Chen, Introduction to non-cryst. Semiconductor physics (Chinease Academy Press, Beijing, 1987)
G.L. Flower, G.S. Baskaran, N. Veeraiah, Mater Chem Phys 100, 211–216 (2006)
W. Vogel, Glass chemistry (Springer, Berlin, 1994)
N. Machida, H. Eckert, Solid State Ion 107, 255–268 (1998)
T. Komatsu, N. Soga, M. Kunugi, J Appl Phys 50, 6469–6474 (1979)
G. Srinivasarao, N. Veeraiah, J Solid State Chem 166, 104–117 (2002)
C.J.F. Böttcher, P. Bordewijk, Theory of electrical polarization (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1978)
K. Srilatha, K.S. Rao, Y. Gandhi, V.R. Kumar, N. Veeraiah, J Alloys Compd 507, 391–398 (2010)
T. Srikumar, ChS Rao, Y. Gandhi, N. Venkatramaiah, V. Ravikumar, N. Veeraiah, J Phys Chem Solids 72, 190–200 (2011)
L. Pavic, N.N. Rao, A.M. Milankovic, A. Santic, V. Ravi Kumar, M. Piasecki, I.V. Kityk, N. Veeraiah, Ceram Int 40, 5989–5996 (2014)
E.T.Y. Lee, E.R.M. Taylor, J Phys Chem Solids 66, 47–51 (2005)
R.K. Brow, J. Non-Cryst, Solids 194, 267–273 (1996)
P. Syam Prasad, M.S. Reddy, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, Philos Mag 87, 5763–5787 (2007)
F. Branda, A. Buri, A. Marotta, S. Saiello, Thermochim Acta 77, 13–18 (1984)
R. Lordanova, Y. Dimitriev, S. Kassabov, D. Klissurski, J Non Cryst Solids 231, 227–233 (1998)
G. Calas, M. Le Grand, L. Galoisy, D. Ghaleb, J Nucl Mater 322, 15–20 (2003)
O. Cozar, D.A. Magdas, I. Ardelean, Non Cryst Solids 354, 1032–1035 (2008)
B.V.R. Chowdari, P. Pramoda, Kumari. Solid State Ion 113, 665–675 (1998)
N.Y. Garces, M.M. Chirila, H.J. Murphy, J.W. Foise, E.A. Thomas, C. Wicks, K. Grencewicz, L.E. Halliburton, N.C. Giles, J Phys Chem Solids 64, 1195–1200 (2003)
D. Boudlich, M. Haddad, R. Berger, J. Kliava, J Non Cryst Solids 224, 135–142 (1998)
A. Bals, J. Kliava, J Magn Reson 53, 243 (1983)
M. Nagarjuna, T. Satyanarayana, V. Ravi Kumar, N. Veeraiah, Phys B 404, 3748–3755 (2009)
R. Berger, P. Beziade, A. Levasseur, Y. Servant, J Phys Chem Glasses 31, 231 (1990)
A.V. Rao, C. Laxmikanth, B.A. Rao, N. Veeraiah, J Phys Chem Solids 67, 2263–2274 (2006)
D.K. Durga, N. Veeraiah, J Phys Chem Solids 64, 133–146 (2003)
P.N. Rao, B.V. Raghavaiah, D.K. Rao, N. Veeraiah, Mater Chem Phys 91, 381–390 (2005)
T. Satyanarayana, I.V. Kityk, M. Piasecki, P. Bragiel, M.G. Brik, Y. Gandhi, N. Veeraiah, J Phys Condens Matter 21, 245104–245112 (2009)
P. Naresh, G. Naga Raju, V. Ravi Kumar, M. Piasecki, I.V. Kiytyk, N. Veeraiah, Ceram Int 40, 2249–2260 (2014)
P. Raghava Rao, L. Pavić, A. Moguš-Milanković, V. Ravi Kumar, I.V. Kityk, N. Veeraiah, J Non Cryst Solids 358, 3255–3267 (2012)
S. Mukherjee, A.K. Pal, J Phys Condens Matter 20, 255202–255211 (2008)
A. Gajovic, A. Santic, I. Djerdj, N. Tomasic, A. Mogus-Milankovic, D. Sheng Su, J Alloys Compd 479, 525–531 (2009)
S.R. Elliott, Adv Phys 36, 135 (1987)
C. Cramer, K. Funke, B. Roling, T. Saatkamp, D. Wilmer, M.D. Ingram, A. Pradel, M. Ribes, G. Taillades, Solid State Ion 86, 481–486 (1996)
I.G. Austin, N.F. Mott, Adv Phys 18, 41–102 (1969)
R. Vijay, P. Ramesh Babu, B.V. Raghavaiah, P.M. Vinaya Teja, M. Piasecki, N. Veeraiah, D. Krishan Rao, J Non Cryst Solids 386, 67–75 (2014)
S. Joon-Young, S. Young Cho, Displays 27, 112–116 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to DST, Govt. of India for the financial support through FIST programme to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naresh, P., Naga Raju, G., Reddy, M.S. et al. Dielectric and spectroscopic features of ZnO–ZnF2–B2O3:MoO3 glass ceramic—a possible material for plasma display panels. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 4902–4915 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2251-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2251-1