Abstract
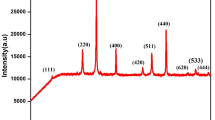
A polycrystalline magnetic materials series produced from the same batch of high-reactivity powder by multi-sample sintering in a range of increasing temperatures can supposedly reveal its property and microstructural evolution through magnetic property measurement and clear morphological changes. Hence, in our work, we attempt to find out the variation of magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 against its evolving microstructure. Hexagonal BaFe12O19 nanometer-sized powder with the M-type structure was synthesized by the mechanical alloying method. The crystal structure, grain size and magnetic properties were studied by means of XRD, field emission scanning electron microscopy and a vibrating sample magnetometer. The ferrite materials were obtained from a mixture of barium carbonate and iron oxide by mixing them using conventional ball milling (12 h) and then assisted by high energy ball milling for 6 h. The comminuted powder was divided into several batches, moulded in pellet shape and sintered at different temperatures ranging from 400 to 1400 °C for a constant sintering time of 10 h in a static air atmosphere. Effects of sintering temperature on the formation, crystallite size, morphology and magnetic properties were systematically studied. In the sintering temperature range from 800 to 1200 °C, the coercivity (Hc) gradually increased due to the effect of rapid grain growth. This is because the fine starting powder was so reactive that rapid grain growth easily occurred. In the grains, strong interaction of magnetic moments within domains due to exchange forces led to strong anisotropy. It was also observed that three M–H-loop groups each belonging to a particular range of grain sizes exhibited different strengths of magnetism. It is believe of similar results have never been reported before and should be useful to the permanent-magnet industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Qiu, M. Gu, Magnetic nanocomposite thin films of BaFe12O19 and TiO2 prepared by sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 888–892 (2005)
B. Zibowicz, D. Szewieczek, L.A. Dobrzaski, New possibilities of application of composite materials with soft magnetic properties. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 20, 207–210 (2007)
L.A. Dobrzaski, M. Drak, B. Zibowicz, Materials with specific magnetic properties. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 17, 37–40 (2006)
M. Drak, L.A. Dobrzaski, Corrosion of Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 20, 239–241 (2007)
N. Shams, X. Liu, M. Matsumoto, A. Morisako, Manipulation of crystal orientation and microstructure of barium ferrite thin film. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 290–291, 138–140 (2005)
O. Carp, R. Barjega, E. Segal, M. Brezeanu, Nonconventional methods for obtaining hexaferrites. Thermochim. Acta 318, 57–62 (1998)
J.F. Wang, C.B. Ponton, I.R. Harris, A study of Sm-substituted SrM magnets sintered using hydrothermally synthesized powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 298(2), 122–131 (2006)
J. Ding, W.F. Miao, P.G. McCormick, R. Street, High coercivity ferrite magnets prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys. Compd. 281, 32–36 (1998)
M.M. Rashad, I.A. Ibrahim, A novel approach for synthesis of M-type hexaferrites nanopowders via the co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 19–709 (2011)
P.M. Md Gazzali, G. Chandrasekaran, Enhanment of hard magnetic porperties of BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 19–709 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The researcher was gratefully thank Universiti Putra Malaysia for Research University Grant, scholarship under MyBrain PhD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafie, M.S.E., Hashim, M., Ismail, I. et al. Magnetic M–H loops family characteristics in the microstructure evolution of BaFe12O19 . J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 3787–3794 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2090-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2090-0