Abstract
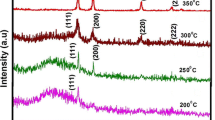
In the present work, copper oxide thin films have been deposited at different substrate temperatures from 250 to 400 °C by spray pyrolysis technique. The desired properties of phase pure CuO with good crystal quality and conductivity have been optimized with respect to pyrolytic temperature. X-ray diffraction studies and Hall effect measurements indicated that these two properties are achieved at an optimum temperature of 350 °C. The band gap of CuO films was found to decrease from 1.8 to 1.2 eV with increase in substrate temperature, based on the UV-absorption spectrum of the film. The microstructures revealed that the film optimized at 350 °C, showed uniform surface with trapezium shaped particles, which are well compacted. The dynamic sensing behavior of the optimized p-type CuO sensor, prepared at a substrate temperature of 350 °C, was used to sense ethanol for concentrations: 100 and 200 ppm. The response time and the recovery time were within the range of 15–20 s and 15–18 s, respectively. The results revealed good response even at room temperature, with characteristics dependent on the size of the grains and the concentration of ethanol.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.L. Patil, S.G. Pawar, A.T. Mane, M.A. Chougule, V.B. Patil, Nanocrystalline ZnO thin films: optoelectronic and gas sensing properties. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 21, 1332–1336 (2010)
M.R. Mohammadi, D.J. Fray, M.C. Cordero-Cabrera, Sensor performance of nano-TiO2 thin films derived from particulate sol–gel route and polymeric fugitive agents. Sens. Actuators B 124, 74–83 (2007)
D.R. Patil, L.A. Patil, Cr2O3-modified ZnO thick film resistors as LPG sensors. Talanta 77, 1409–1414 (2009)
A. Umar, M.M. Rahman, Y.B. Hahn, Ultra-sensitive hydrazine chemical sensor based on high-aspect-ratio ZnO nanowires. Talanta 77, 1376–1380 (2009)
J. Arbiol, E. Comini, G. Faglia, G. Sberveglieri, J.R. Morante, Orthorhombic Pbcn SnO2 nanowires for gas sensing applications. J. Cryst. Growth 310(1), 253–260 (2008)
M.F. Jawad, R.A. Ismail, K.Z. Yahea, Preparation of nanocrystalline Cu2O thin film by pulsed laser deposition. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 22, 1244–1247 (2011)
T. Mahalingam, J.S.P. Chitra, J.P. Chu, H. Moon, H.J. Kwon, Y.D. Kim, Photoelectrochemical solar cell studies on electroplated cuprous oxide thin films. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 17, 519–523 (2006)
M. Engin, F. Atay, S. Kose, V. Bilgin, I. Akyuz, Growth and characterization of Zn-incorporated copper oxide films. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 38, 787–796 (2009)
W. Hu, L. Zhu, D. Dong, W. He, X. Tang, X. Liu, Thermal behavior of copper powder prepared by hydrothermal treatment. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 18, 817–821 (2007)
W. Wang, O.K. Varghese, C. Ruan, M. Paulose, C.A. Grimes, Synthesis of CuO and Cu2O crystalline nanowires using Cu(OH)2 nanowire templates. J. Mater. Res. 18(12), 2756–2759 (2003)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. State. Sol. 15, 627 (1966)
T.Y. Ma, H.Y. Moon, Effects of vapor annealing on the properties of the ZnO films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 9, 435–439 (1998)
R. Mamazza Jr, D.L. Morel, C.S. Ferekides, Transparent conducting oxide thin films of Cd2SnO4 prepared by RF magnetron co-sputtering of the constituent binary oxides. Thin Solid Films 484, 26–33 (2005)
R. Ferro, J.A. Rodriguez, O. Vigil, A. Morales-Acevedo, Chemical composition and electrical conduction mechanism for CdO: F thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 87, 83–86 (2001)
J.I. Pankovem, Optical Processes in Semiconductors (Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 1971)
C. Kormann, D.W. Bahnemann, M.R. Hoffmann, Preparation and characterization of quantum-size titanium dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. 92, 5196–5201 (1988)
D.M. Jundale, P.B. Joshi, S. Sen, V.B. Patil, Nanocrystalline CuO thin films: synthesis, micro structural and optoelectronic properties. J. Mater. Sci- Mater. El. 23, 1492–1499 (2012)
N.S. Ramgir, S. Kailasa Ganapathi, M. Kaur, N. Datta, K.P. Muthe, D.K. Aswal, S.K. Gupta, J.V. Yakhmi, Sub-ppm H2S sensing at room temperature using CuO thin films. Sens. Actuators B 151, 90–96 (2010)
H. Gonga, J.Q. Hua, J.H. Wang, C.H. Onga, F.R. Zhub, Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sens. Actuators B 115, 247–251 (2006)
K. Arshak, I. Gaiden, Development of a novel gas sensor based on oxide thick films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 118, 44–49 (2005)
C.S. Prajapati, S.N. Pandey, P.P. Sahay, Sensing of LPG with nano-structured zinc oxide thin films grown by spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. B 406, 2684–2688 (2011)
S. Kar, B.N. Pal, S. Chaudhuri, D. Chakravorty, One-dimensional ZnO nanostructure array: synthesis and characterization. J. Phys. Chem. C 110, 4605–4611 (2006)
L. Liao, H.B. Lu, J.C. Li, H. He, D.F. Wang, D.J. Fu, C. Liu, W.F. Zhang, Size dependence of gas sensitivity of ZnO nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 1900–1903 (2007)
Y. Zhang, X. He, J. Li, H. Zhang, X. Gao, Gas-sensing properties of hollow and hierarchical copper oxide microspheres. Sens. Actuators B 128, 293–298 (2007)
Y. Cao, W. Pan, Y. Zong, D. Jia, Preparation and gas-sensing properties of pure and Nd-doped ZnO nanorods by low-heating solid-state chemical reaction. Sens. Actuators B 138, 480–484 (2009)
R.C. Singh, O. Singh, M.P. Singh, P.S. Chandi, Synthesis of zinc oxide nanorods and nanoparticles by chemical route and their comparative study as ethanol sensors. Sens. Actuators B 135, 352–357 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by University Grants Commission (MRP: 40-441/2011), which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopalakrishna, D., Vijayalakshmi, K. & Ravidhas, C. Effect of pyrolytic temperature on the properties of nano-structured Cuo optimized for ethanol sensing applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 1004–1011 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0866-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0866-7