Abstract
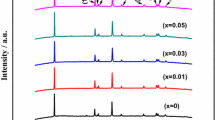
LiCoO2 is a versatile commercially available cathode electrode material for lithium–ion batteries. In an attempt to improve the performance of lithium batteries with enhanced safety, Eu- doped LiCoO2 powder was synthesized using a combustion route method. X-ray diffraction analysis reveals the existence of layered structure with the space group R-3m of hexagonal systems for all compounds. The local structure estimated by resonance spectroscopy (Laser Raman and FTIR) was reported. Surface morphology of the synthesized materials was determined by scanning electron microscope and it was found that the cathode materials consisted of highly ordered single crystalline particles with hexagonal shape. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS), was used to investigate the elementary states of the system. The electrical conductivities of the samples were measured at room temperature by the two probe method. The electrical conductivities of Eu-doped LiCoO2 system increased with Eu content. An excellent reversible capacity was observed for the composite cathode containing 5.0 mol % Eu, when 2016 type coin cells were cycled at 0.1 C rate. This has been ascribed to the improved electrical conductivity induced by Eu doping.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Armand, Solid State Ionics 69, 309 (1994)
H.V. Venkatasetty, J. Power Sources 97, 671 (2001)
M. Yoshio, H. Tanaka, K. Tomonaga, H. Noguchi, J. Power Sources 40, 347 (1992)
S. Gopukumar, Y. Jeong, K.B. Kim, Solid State Ionics 159, 223 (2003)
C.D. Jones, E. Rossen, J.R. Dahn, Solid State Ionics 68, 65 (1994)
C. Julien, M.A. Camacho-Lopez, T. Mohan, S. Chitra, P. Kalyani, S. Gopukumar, Solid State Ionics 135, 241 (2000)
I. Sadoune, C. Delmas, J. Solid State Chem. 136, 8 (1998)
H. Kobayashi, S. Shigemura, M. Tabuchi, H. Sakaebe, K. Ado, H. Kageyama, A. Hirano, R. Kanno, M. Wakita, S. Morimotoand Nasu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 960 (2000)
M. Zou, M. Yoshio, S. Gopukumar, J.I. Yamaki, Chem. Mater. 15, 4699 (2003)
M. Zou, M. Yoshio, S. Gopukumar, J.I. Yamaki, Chem. Mater. 17, 1284 (2005)
S.A. Needham, G.X. Wang, H.K. Liu, V.A. Drozd, R.S. Liu, J. Power Sources 174, 828 (2007)
J. Tu, X.B. Zhao, D.G. Zhuang, G.S. Cao, T.J. Zhu, J.P. Tu, Physica B 382, 129 (2006)
S.T. Yang, J.H. Jia, L. Ding, M.C. Zhang, Electrochim. Acta 48, 569 (2003)
X. Sun, X. Hu, Y. Shi, S. Li, Y. Zhou, Solid State Ionics 180, 377 (2009)
P. Ghosh, S. Mahanty, R.N. Basu, Electrochim. Acta 54, 1654 (2008)
P. Kalyani, N. Kalaiselvi, N. Muniyndi, J. Power Sources 111, 232 (2002)
S. Madhavi, G.V. Subba Rao, B.V.R. Chowdari, S.F.Y. Li, J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, A1279 (2001)
T. Lee, K. Cho, J. Oh, D. Shin, J. Power Sources 174, 394 (2007)
R.B. Khomane, A.C. Agarwal, B.D. Kulkarni, S. Gopukumar, A. Sivashanmugam, Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 2497 (2007)
C. Julien, G.A. Nazri, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 548, 79 (1999)
M. Inba, Y. Todzuka, H. Yoshida, Y. Grincourt, A. Tasaka, Y. Tomida, Z. Ogumi, Chem. Lett. 24, 889 (1995)
R. Alcantara, G.F. Oritz, P. Lavela, J.L. Tirado, W. Jaegermann, A. Thiben, J. Electronal. Chem. 584, 147 (2005)
J. Thirumalai, R. Chandramohan, S. Valanarasu, T.A. Vijayan, R.M. Somasundaram, T. Mahalingam, S.R. Srikumar, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 3889 (2009)
S. Huang, Z. Wen, X. Yang, Z. Gu, X. Xu, J. Power Sources 148, 72 (2005)
P. Ghosh, S. Mahanty, R.N. Basu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 110, 406 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors R. Chandramohan and S. Valanarasu thank the University Grants Commission (UGC-SERO), Hyderabad, India for the financial support for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valanarasu, S., Chandramohan, R., Somasundaram, R.M. et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of Eu-doped LiCoO2 . J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 22, 151–157 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-010-0105-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-010-0105-z