Abstract
Mesoporous AlPO4 materials have attracted much attention in catalysis due to their high thermal and chemical stability. Of particular interest for catalysis is the pure stoichiometry high surface area (> 500 m2/g) mesoporous AlPO4 (mAlPO4) glass prepared via a template-free aqueous sol–gel synthetic route. Toward the application of this material for catalysis, we have developed methods for loading it with nanoparticles (NPs) of catalytic metals—Pd and Rh—and carried out a detailed characterization study of the resulting doped materials by a wide array of analytical methods, including synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy, inelastic neutron scattering and more. The applicability of this material for catalysis, both by itself and as a support for catalytic NPs, was then evaluated. The pure mAlPO4 exhibited excellent acid-catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition of nitriles and sodium azide. mAlPO4 loaded with the Pd NPs catalyzed very efficiently deoxygenation reactions of benzyl alcohols. mAlPO4 loaded with Rh NPs catalyzed with high selectivity, the hydrogenation of phenols and cresols and full conversion the hydrogenation of the industrially very high-volume toluene to methylcyclohexane. The materials-science aspects of these successful catalysts were studied in detail, leading, for instance, to the understanding of the important role of the interfacial Rh/Pd–O-P bonds.
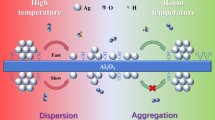
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perego C, Millini R (2013) Porous materials in catalysis: challenges for mesoporous materials. Chem Soc Rev 42:3956
Chang F, Zhou J, Chen P, Chen Y, Jia H, Saad SM, Gao Y, Cao X, Zheng T (2013) Microporous and mesoporous materials for gas storage and separation: a review. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 8:618
Makowski P, Deschanels X, Grandjean A, Meyer D, Toquer G, Goettmann F (2012) Mesoporous materials in the field of nuclear industry: applications and perspectives. New J Chem 36:531
Campelo J, Jaraba M, Luna D, Luque R, Marinas J, Romero A, Navio J, Macias M (2003) Effect of phosphate precursor and organic additives on the structural and catalytic properties of amorphous mesoporous AlPO4 materials. Chem Mater 15:3352
Ren H, Xin F (2006) In situ calcinations of precursors of mesoporous AlPO4 and application of mesoporous Mn–AlPO4. Catal Commun 7:848
Kannan C, Muthuraja K, Devi MR (2013) Hazardous dyes removal from aqueous solution over mesoporous aluminophosphate with textural porosity by adsorption. J Hazard Mater 244:10
Bautista FM, Campelo JM, Garcia A, Luna D, Marinas JM and Romero AA (1997) N-methylation of aniline over AlPO4 and AlPO4-metal oxide catalysts, In: Studies in surface science and catalysis Vol 108. Elsevier, p 123-130
Campelo J, Garcia A, Herencia J, Luna D, Marinas J, Romero A (1995) Conversion of alcohols (α-methylated series) on AlPO4 catalysts. J Catal 151:307
Machida M, Murakami K, Hinokuma S, Uemura K, Ikeue K, Matsuda M, Chai M, Nakahara Y, Sato T (2009) AlPO4 as a support capable of minimizing threshold loading of Rh in automotive catalysts. Chem Mater 21:1796
Sreenivasulu P, Nandan D, Kumar M, Viswanadham N (2013) Synthesis and catalytic applications of hierarchical mesoporous AlPO4/ZnAlPO4 for direct hydroxylation of benzene to phenol using hydrogen peroxide. J Mater Chem A 1:3268
Wang L, Tian B, Fan J, Liu X, Yang H, Yu C, Tu B, Zhao D (2004) Block copolymer templating syntheses of ordered large-pore stable mesoporous aluminophosphates and Fe-aluminophosphate based on an “acid–base pair” route. Micro Meso Mater 67:123
Li W, Zhu Y, Guo X, Nakanishi K, Kanamori K, Yang H (2013) Preparation of a hierarchically porous AlPO4 monolith via an epoxide-mediated sol–gel process accompanied by phase separation. Sci Technol Adv Mater 14:045007
Zhang L, Chan JC, Eckert H, Helsch G, Hoyer LP, Frischat GH (2003) Novel sol−gel synthesis of sodium aluminophosphate glass based on aluminum lactate. Chem Mater 15:2702
Zhang L, Eckert H (2004) Sol–gel synthesis of Al2O3–P2O5 glasses: mechanistic studies by solution and solid state NMR. J Mater Chem 14:1605
He J, Ma P, Zhang G, Li R, Zhang L (2016) Sol–gel derived mesoporous GaAlPO4 glass for heavy metal ion sequestration. RSC Adv 6:99149
Zhang L, de Araujo CC, Eckert H (2006) Aqueous sol-gel preparation of Na2O–Al2O3–B2O3 glasses: structural characterisation by liquid and solid state NMR spectroscopy. Phys Chem Glasses B 47:7
Zhang L, Eckert H (2005) Synthesis and structural evolution of Al2O3–B2O3–P2O5 gels and glasses. J Mater Chem 15:1640
Zhang L, de Araujo CC, Eckert H (2005) A new sol−gel route to aluminum fluoride phosphate glasses: mechanistic investigations by NMR spectroscopy. Chem Materials 17:3101
Zhang L, de Araujo CC, Eckert H (2007) Structural role of fluoride in aluminophosphate sol−gel glasses: high-resolution double-resonance NMR studies. J Phys Chem B 111:10402
Zhang L, Bögershausen A, Eckert H (2005) Mesoporous AlPO4 glass from a simple aqueous sol–gel route. J Am Ceram Soc 88:897
Zhang L, de Araujo CC, Eckert H (2007) Aluminum lactate–an attractive precursor for sol–gel synthesis of alumina-based glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 353:1255
Kiselev GO, Kiseleva AP, Ilatovskii DA, Koshevaya ED, Nazarovskaia DA, Gets DS, Vinogradov VV, Krivoshapkin PV, Krivoshapkina EF (2019) Upconversion metal (Zr, Hf, and Ta) oxide aerogels. Chem Commun 55:8174
Wagle R, Yoo JK (2020) Preparation of highly porous Al2O3 aerogel by one-step solvent-exchange and ambient-pressure drying. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 17:1201
Ganonyan N, He J, Temkin A, Felner I, Gvishi R, Avnir D (2021) Ultralight monolithic magnetite aerogel. Appl Mater Today 22:100955
Luna AL, Matter F, Schreck M, Wohlwend J, Tervoort E, Colbeau-Justin C, Niederberger M (2020) Monolithic metal-containing TiO2 aerogels assembled from crystalline pre-formed nanoparticles as efficient photocatalysts for H2 generation. Appl Catal B 267:118660
Li R, Fan Y, Li J, Tang B, Fan J, He J, Ren J, Wang J, Zhang L (2011) Solidification and simultaneous dual-wavelength emission of Rhodamine 6g and coumarin 102 codoped in AlPO4 mesoporous glass. J Phys Chem C 115:9176
He J, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang K, Li R, Fan J, Xu S, Zhang L (2013) Tailoring the luminescence of europium ions in mesoporous AlPO4 monolithic glass. J Phys Chem C 117:21916
He J, Wang Y, Li R, Yuan X, Xu S, Zhang L (2015) Tunable and white light emitting AlPO4 mesoporous glass by design of inorganic/organic luminescent species. APL Mater 3:046101
Bai Z, He J, Wang Y, Wang K, Li R, Zhang L (2017) Colloidal PbS quantum dot-AlPO4 nanoporous glass composites: controllable emission and nonlinear absorption. J Lumin 192:675
Machida M, Minami S, Ikeue K, Hinokuma S, Nagao Y, Sato T, Nakahara Y (2014) Rhodium nanoparticle anchoring on AlPO4 for efficient catalyst sintering suppression. Chem Mater 26:5799
Machida M, Minami S, Hinokuma S, Yoshida H, Nagao Y, Sato T, Nakahara Y (2015) Unusual redox behavior of Rh/AlPO4 and its impact on three-way catalysis. J Phys Chem C 119:373
Buwono HP, Minami S, Uemura K, Machida M (2015) Surface properties of Rh/AlPO4 catalyst providing high resistance to sulfur and phosphorus poisoning. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:7233
Matsui M, Machida M, Sakaki S (2015) Characterization of AlPO4 (110) Surface in adsorption of Rh dimer and Its comparison with γ-Al2O3 (100) Surface: a theoretical study. J Phys Chem C 119:19752
Ai M, Lang L, Li B, Xu Z (2012) Mesoporous AlPO4: a highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst for synthesis of 5-substituted 1 H-tetrazoles from nitriles and sodium azide via [3+ 2] cycloaddition. Chem Lett 41:814
La Sorella G, Sperni L, Canton P, Coletti L, Fabris F, Strukul G, Scarso A (2018) Selective hydrogenations and dechlorinations in water mediated by anionic surfactant-stabilized pd nanoparticles. J Org Chem 83:7438
Schuchardt U, Carvalho WA, Spinacé EV (1993) Why is it interesting to study cyclohexane oxidation? Synlett 1993:713
Schuchardt U, Cardoso D, Sercheli R, Pereira R, Da Cruz RS, Guerreiro MC, Mandelli D, Spinacé EV, Pires EL (2001) Cyclohexane oxidation continues to be a challenge. Appl Catal A 211:1
Zhong J, Chen J, Chen L (2014) Selective hydrogenation of phenol and related derivatives. Catal Sci Tech 4:3555
Kong X, Gong Y, Mao S, Wang Y (2018) Selective hydrogenation of phenol. ChemNanoMat 4(5):432–450
Fernández L(2019), Global production capacity of toluene 2018 & 2023. Retrieved July 28, 2021, from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1065877/global-toluene-production-capacity/
More A (2021), Methylcyclohexane market size is estimated to grow with a CAGR of 2.6% during 2021–2026 with top Countries data. Retrieved July 28, 2021, from: https://www.wicz.com/story/43971123/methylcyclohexane-market-size-is-estimated-to-grow-with-a-cagr-of-26-during-2021-2026-with-top-countries-data
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52002384). The authors acknowledge the Diamond Light Source, UK (Project No. SP18835, B18 beamline), and the ISIS facility, UK (Project No. 1920102, TOSCA spectrometer), for the provision of beamtime. We thank Prof. B. Ji (Westlake U.), Prof. L. Chang (SIAP, CAS), Prof. J. Cui (Soochow U.) and Prof. J. Ren (SIOM, CAS) for the assistance in the materials characterization. J. H. acknowledges the Shanghai Pujiang Talent Plan (2020PJD079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Pedro Camargo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Guo, W., Cong, P. et al. Exact stoichiometry high surface area mesoporous AlPO4 glass for efficient catalysis. J Mater Sci 57, 17234–17246 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07577-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07577-y