Abstract
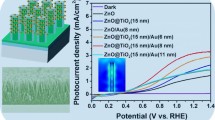
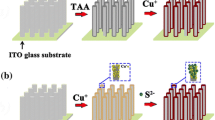
The rational design of heterojunction structure as photoanode provides an effective route to improve the efficiency of photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting. Herein, we design and fabricate CdS nanoparticle/TiO2 nanorod array heterostructures through a facile hydrothermal process. With the assistance of a ZnO interlayer between CdS and TiO2 prepared by atomic layer deposition technique followed by microwave hydrothermal reaction, uniform Zn-doped CdS/TiO2 shell/core arrays are attained. Via tuning the ZnO thickness and CdS deposition time, the optimum Zn-doped CdS/TiO2 sample exhibits a superior PEC performance with a photocurrent of 3.38 mA cm−2 at 1.23 V versus RHE, which is 6.0 and 1.4 times higher than pristine TiO2 and CdS/TiO2, respectively. Moreover, the corresponding onset potential of Zn-doped CdS/TiO2 is obviously shifted toward the negative potential direction by 450 and 130 mV, respectively. The performance enhancement is attributed to the improved electron–hole transport and separation ability, stronger light absorption and higher photoactivity.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilmaz F, Balta MT, Selbaş R (2016) A review of solar based hydrogen production methods. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 56:171–178
Wang J, Xu F, Jin H, Chen Y, Wang Y (2017) Non-noble metal-based carbon composites in hydrogen evolution reaction: fundamentals to applications. Adv Mater 29:1605838
Willkomm J, Orchard KL, Reynal A, Pastor E, Durrant JR, Reisner E (2016) Dye-sensitised semiconductors modified with molecular catalysts for light-driven H2 production. Chem Soc Rev 45:9–23
Roger I, Shipman MA, Symes MD (2017) Earth-abundant catalysts for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nat Rev Chem 1:1–13
Niu F, Wang D, Li F, Liu Y, Shen S, Meyer TJ (2020) Hybrid photoelectrochemical water splitting systems: from interface design to system assembly. Adv Energy Mater 10:1900399
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Cui H, Zhu G, Xie Y, Zhao W, Yang C, Lin T, Gu H, Huang F (2015) Black nanostructured Nb2O5 with improved solar absorption and enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Mater Chem A 3:11830–11837
Ma Y, Hu Y (2020) Efficient Ni(OH)2/WO3 photoanode for photoelectrocatalytic water splitting at low bias. J Phys Chem C 124:19447–19456
Kim TW, Choi KS (2014) Nanoporous BiVO4 photoanodes with dual-layer oxygen evolution catalysts for solar water splitting. Science 343:990–994
Wu J, Huang P, Fan H, Wang G, Liu W (2020) Metal-organic framework-derived p-Cu2O/n-Ce-Fe2O3 heterojunction nanorod photoanode coupling with a FeOOH cocatalyst for high-performance photoelectrochemical water oxidation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:30304–30312
Ge M, Li Q, Cao C, Huang J, Li S, Zhang S, Chen Z, Zhang K, Al-Deyab SS, Lai Y (2017) One-dimensional TiO2 nanotube photocatalysts for solar water splitting. Adv Sci 4:1600152
Khan SUM, Al-Shahry M, Ingler WB (2002) Efficient photochemical water splitting by a chemically modified n-TiO2. Science 297:2243–2245
Mi Y, Wen L, Xu R, Wang Z, Cao D, Fang Y, Lei Y (2016) Constructing a AZO/TiO2 core/shell nanocone array with uniformly dispersed Au NPs for enhancing photoelectrochemical water splitting. Adv Energy Mater 6:1501496
Zhang X, Liu Y, Lee ST, Yang S, Kang Z (2014) Coupling surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles with slow-photon-effect of TiO2 photonic crystals for synergistically enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. Energy Environ Sci 7:1409–1419
Hao C, Wang W, Zhang R, Zou B, Shi H (2018) Enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting with TiO2@Ag2O nanowire arrays via pn heterojunction formation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 174:132–139
Wang M, Pyeon M, Gönüllü Y, Kaouk A, Shen S, Guo L, Mathur S (2015) Constructing Fe2O3/TiO2 core–shell photoelectrodes for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nanoscale 7:10094–10100
Ai G, Li H, Liu S, Mo R, Zhong J (2015) Solar water splitting by TiO2/CdS/Co-Pi nanowire array photoanode enhanced with Co-Pi as hole transfer relay and CdS as light absorber. Adv Funct Mater 25:5706–5713
Li J, Cushing SK, Zheng P, Senty T, Meng F, Bristow AD, Manivannan A, Wu N (2014) Solar hydrogen generation by a CdS-Au-TiO2 sandwich nanorod array enhanced with Au nanoparticle as electron relay and plasmonic photosensitizer. J Am Chem Soc 136:8438–8449
Su F, Lu J, Tian Y, Ma X, Gong J (2013) Branched TiO2 nanoarrays sensitized with CdS quantum dots for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:12026–12032
Yao L, Wei D, Ni Y, Yan D, Hu C (2016) Surface localization of CdZnS quantum dots onto 2D g-C3N4 ultrathin microribbons: highly efficient visible light-induced H2-generation. Nano Energy 26:248–256
Li K, Chen R, Li S, Xie S, Dong L, Kang Z, Bao J, Lan Y (2016) Engineering Zn1-xCdxS/CdS heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:14535–14541
Chen J, Chen J, Li Y (2017) Hollow ZnCdS dodecahedral cages for highly efficient visible-light-driven hydrogen generation. J Mater Chem A 5:24116–24125
Liu M, Jing D, Zhou Z, Guo L (2013) Twin-induced one-dimensional homojunctions yield high quantum efficiency for solar hydrogen generation. Nat Commun 4:1–8
Li Q, Meng H, Zhou P, Zheng Y, Wang J, Yu J, Gong J (2013) Zn1-xCdxS solid solutions with controlled bandgap and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2-production activity. ACS Catal 3:882–889
Kozlova EA, Kurenkova AY, Semeykina VS, Parkhomchuk EV, Cherepanova SV, Gerasimov EY, Saraev AA, Kaichev VV, Parmon VN (2015) Effect of titania regular macroporosity on the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on Cd1-xZnxS/TiO2 catalysts under visible light. ChemCatChem 7:4108–4117
Yang F, Yan N, Huang S, Sun Q, Zhang L, Yu Y (2012) Zn-doped CdS nanoarchitectures prepared by hydrothermal synthesis: mechanism for enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible light. J Phys Chem C 116:9078–9084
Luo M, Liu Y, Hu J, Liu H, Li J (2012) One-pot synthesis of CdS and Ni-doped CdS hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity and durability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1813–1821
Wakerley DW, Kuehnel MF, Orchard KL, Ly KH, Rosser TE, Reisner E (2017) Solar-driven reforming of lignocellulose to H2 with a CdS/CdOx photocatalyst. Nat Energy 2:1–9
Zou JP, Lei SL, Yu J, Luo SL, Luo XB, Tang XH, Dai WL, Sun J, Guo GC, Au CT (2014) Highly efficient and stable hydrogen evolution from water with CdS as photosensitizer-a noble-metal-free system. Appl Catal B-Environ 150:466–471
Lim YR, Song W, Han JK, Lee YB, Kim SJ, Myung S, Lee SS, An KS, Choi CJ, Lim J (2016) Wafer-Scale, Homogeneous MoS2 layers on plastic substrates for flexible visible-light photodetectors. Adv Mater 28:5025–5030
Wu D, Wang W, Ng TW, Huang G, Xia D, Yip HY, Lee HK, Li G, An T, Wong PK (2016) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic bacterial inactivation and the mechanism of zinc oxysulfide under LED light irradiation. J Mater Chem A 4:1052–1059
Gupta S, Whittles TJ, Batra Y, Satsangi V, Krishnamurthy S, Dhanak VR, Mehta BR (2016) A low-cost, sulfurization free approach to control optical and electronic properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 via precursor variation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 157:820–830
Wang Y, Yang X, Ye T, Xu C, Xia F, Meng D (2017) Comparative study of structural and photocatalytic properties of M-doped (M = Ce3+, Zn2+, Cu2+) dendritic-like CdS. J Electron Mater 46:1598–1606
Liu Q, Wu F, Cao F, Chen L, Xie X, Wang W, Tian W, Li L (2015) A multijunction of ZnIn2S4 nanosheet/TiO2 film/Si nanowire for significant performance enhancement of water splitting. Nano Res 8:3524–3534
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support from the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Province (BK20200877), College Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of the Jiangsu Province (202013984007Y).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Christopher Blanford.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Xing, Q., Zhang, X. et al. Photoelectrochemical water splitting using TiO2 nanorod arrays coated with Zn-doped CdS. J Mater Sci 56, 11059–11070 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06008-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06008-8