Abstract
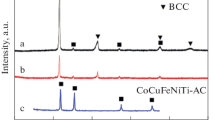
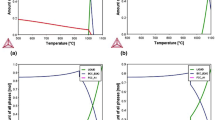
An equiatomic CuFeMnNi high-entropy alloy (HEA) was synthesized and homogenized at 1000 °C to achieve a microstructure of single face centered cubic phase based on CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) prediction. The strength and ductility of this Co-free (low cost) HEA can be tuned through thermomechanical processing (cold rolling and annealing at temperatures ranging from 650 °C to 950 °C). Electron backscattered diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy techniques were used to characterize the deformation microstructure of this new HEA. The results show that plastic deformation was achieved through the slip of full dislocations with Burgers vector of a/2 < 110 > . No dissociated dislocations and deformation twins were observed, indicating that this alloy poses high stacking-fault energy, which is supported by first principle calculations. The research suggests that further improvement on the mechanical properties of this alloy can be achieved by reducing stacking-fault energy via alloying, providing a promising low-cost alternative to CoCrFeMnNi HEAs for engineering applications.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh JW, Chen SK, Lin SJ et al (2004) Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater 6:299–303
Li Z, Pradeep KG, Deng Y et al (2016) Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off. Nature 2016(534):4–11
Senkov ON, Wilks GB, Scott JM et al (2011) Mechanical properties of Nb 25Mo 25Ta 25W 25 and V 20Nb 20Mo 20Ta 20W 20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 19:698–706
Lu Y, Dong Y, Guo S et al (2015) A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci Rep 4:6200
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D et al (2014) A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science(80-) 345:1153–1158
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Thurston KVS et al (2016) Exceptional damage-tolerance of a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi at cryogenic temperatures. Nat Commun 7:1–8
Luo H, Li Z, Mingers AM et al (2018) Corrosion behavior of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy compared with 304 stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros Sci 134:131–139
Vaidya M, Guruvidyathri K, Murty BS (2019) Phase formation and thermal stability of CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi equiatomic high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd 774:856–864
Deng HW, Xie ZM, Zhao BL et al (2019) Tailoring mechanical properties of a CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy by controlling nanotwin-HCP lamellae and annealing twins. Mater Sci Eng A 744:241–246
Pradeep KG, Tasan CC, Yao MJ et al (2015) Non-equiatomic high entropy alloys: approach towards rapid alloy screening and property-oriented design. Mater Sci Eng A 648:183–192
Zhao YL, Yang T, Zhu JH et al (2018) Development of high-strength Co-free high-entropy alloys hardened by nanosized precipitates. Scr Mater 148:51–55
Zhang M, Zhang L, Fan J, et al. (2019) Novel Co-free CrFeNiNb0.1Ti high-entropy alloys with ultra high hardness and strength. Mater Sci Eng A 764 138212.
Li C, Hu X, Yang T et al (2019) Neutron irradiation response of a Co-free high entropy alloy. J Nucl Mater 527:151838
USGS. Mineral Industry Surveys [Internet]. Available from: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nmic/mineral-industry-surveys.
Tung CC, Yeh JW, Shun T, Tsung et al (2007) On the elemental effect of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system. Mater Lett 61:1–5
Ren B, Liu ZX, Li DM et al (2010) Effect of elemental interaction on microstructure of CuCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy system. J Alloys Compd 493:148–153
Ng C, Guo S, Luan J et al (2014) Phase stability and tensile properties of Co-free Al 0.5CrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd 584:530–537
Ma SG, Qiao JW, Wang ZH et al (2005) Microstructural features and tensile behaviors of the Al0.5CrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys by cold rolling and subsequent annealing. Mater Des 88:1057–1062
Rao ZY, Wang X, Zhu J et al (2016) Affordable FeCrNiMnCu high entropy alloys with excellent comprehensive tensile properties. Intermetallics 77:23–33
Ren B, Liu ZX, Cai B et al (2012) Aging behavior of a CuCr2Fe2NiMn high-entropy alloy. Mater Des 33:121–126
MacDonald BE, Fu Z, Wang X et al (2019) Influence of phase decomposition on mechanical behavior of an equiatomic CoCuFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Acta Mater 181:25–35
Chen X, Zhai SD, Gao D et al (2019) Microstructural transition of (CuFeMnNi)1−xCrx (x = 0–0.25) high-entropy alloys. J Mater Eng Perform 28:4502–4509
Miao J, Singh S, Tessmer J et al (2018) Dislocation characterization using weak beam dark field STEM imaging. Microsc Microanal 24:2202–2203
Kocks UF, Mecking H (2003) Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: the FCC case. Prog Mater Sci 48:171–273
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B - Condens Matter Mater Phys 54:11169–11186
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Zunger A, Wei S-H, Ferreira LG et al (1990) Special quasirandom structures. Phys Rev Lett 65:353–356
Van de Walle A, Asta M, Ceder G (2002) The alloy theoretic automated toolkit: a user guide. Calphad Comput Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem 26:539–553
Byun TS (2003) On the stress dependence of partial dislocation separation and deformation microstructure in austenitic stainless steels. Acta Mater 51:3063–3071
Laplanche G, Kostka A, Reinhart C et al (2017) Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater 128:292–303
Zhang Z, Sheng H, Wang Z et al (2017) Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nat Commun 8
Liu S, Wei Y (2017) The Gaussian distribution of lattice size and atomic level heterogeneity in high entropy alloys. Extrem Mech Lett 11:84–88
Zhao S, Stocks GM, Zhang Y (2017) Stacking fault energies of face-centered cubic concentrated solid solution alloys. Acta Mater 134:334–345
Okamoto NL, Fujimoto S, Kambara Y et al (2016) Size effect, critical resolved shear stress, stacking fault energy, and solid solution strengthening in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Sci Rep 6:1–10
Otto F, Dlouhý A, Somsen C et al (2013) The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater 61:5743–5755
Wu Z, Bei H, Pharr GM et al (2014) Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater 81:428–441
Komarasamy M, Kumar N, Tang Z et al (2014) Effect of microstructure on the deformation mechanism of friction stir-processed Al0.1CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater Res Lett 3:30–34
Stepanov ND, Shaysultanov DG, Tikhonovsky MA et al (2015) Tensile properties of the Cr-Fe-Ni-Mn non-equiatomic multicomponent alloys with different Cr contents. Mater Des 87:60–65
Wang Z, Baker I, Cai Z et al (2016) The effect of interstitial carbon on the mechanical properties and dislocation substructure evolution in Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 high entropy alloys. Acta Mater 120:228–239
Li P, Wang A, Liu CT (2017) A ductile high entropy alloy with attractive magnetic properties. J Alloys Compd 694:55–60
Seol JB, Bae JW, Li Z et al (2018) Boron doped ultrastrong and ductile high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 151:366–376
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from The Ohio State University (OSU). Thanks also go to Greg Scantlen of CreativeC for providing access to its workstation in support our density functional theory calculations and OSU Simulation Innovation and Modeling Center (SIMCenter) for providing access to supercomputers for simulation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest publication of this article.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Sophie Primig.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Miao, J., Li, S. et al. Co-free CuFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with tunable tensile properties by thermomechanical processing. J Mater Sci 56, 7670–7680 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05686-0