Abstract
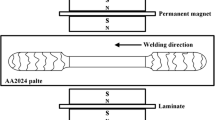
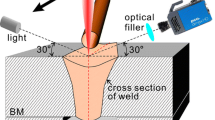
An external magnetic field was firstly been applied to laser welding of Al/Ti alloys. Microstructure and tensile strength for Al/Ti laser-welded joint under external magnetic field were investigated. The results indicate that the strength of Al/Ti joint is improved by 44.4% via application of an external vertical magnetic field with an intensity of 120 mT. The enhancement of strength is attributed to the diminishment of intermetallic compounds, that is, the volume of TiAl3 is decreased from 10.69 to 6.44%. It is deemed that, on the one hand, the induced Lorentz force via the interaction between horizontal fluid flow and perpendicular magnetic field suppresses the horizontal convection, leading to the decreased thickness of intermetallic compounds. On the other hand, the thermoelectric magnetic convection contributes to the heat and solute transfer at the Al/Ti interface, leading to the redistribution of elements with disordered and decreased intermetallic compounds.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang T, Li X, Zhang Y, Li H, Zhang B, Feng J (2017) Regulating the interfacial morphology of electron beam welded pure Ti/2024Al dissimilar joint. J Mater Process Tech 245:227–231
Vacchi GS, Plaine AH, Silva R, Sordi VL, Suhuddin UFH, Alcântara NG, Rovere CAD (2017) Effect of friction spot welding (FSpW) on the surface corrosion behavior of overlapping AA6181-T4/Ti–6Al–4V joints. Mater Design 131:127–134
Huang Y, Lv Z, Wan L, Shen J, Dos Santos JF (2017) A new method of hybrid friction stir welding assisted by friction surfacing for joining dissimilar Ti/Al alloy. Mater Lett 207:172–175
Lucadamo G, Barmak K, Lavoie C, JrC Cabral, Michaelsen C (2002) Metastable and equilibrium phase formation in sputter-deposited Ti/Al multilayer thin films. J Appl Phys 91(12):9575–9583
Peyre P, Berthe L, Dal M, Pouzet S, Sallamand P, Tomashchuk I (2014) Generation and characterization of T40/A5754 interfaces with lasers. J Mater Process Tech 214(9):1946–1953
Chen S, Li L, Chen Y, Dai J, Huang J (2011) Improving interfacial reaction nonhomogeneity during laser welding–brazing aluminum to titanium. Mater Design 32(8–9):4408–4416
Casalino G, Mortello M, Peyre P (2015) Yb–YAG laser offset welding of AA5754 and T40 butt joint. J Mater Process Tech 223:139–149
Tomashchuk I, Sallamand P, Cicala E, Peyre P, Grevey D (2015) Direct keyhole laser welding of aluminum alloy AA5754 to titanium alloy Ti6Al4 V. J Mater Process Tech 217:96–104
Chen R, Jiang P, Shao XY, Mi GY, Wang CM (2017) Effect of magnetic field applied during laser-arc hybrid welding in improving the pitting resistance of the welded zone in austenitic stainless steel. Corros Sci 126:385–391
Chen R, Jiang P, Shao XY, Mi GY, Wang CM (2017) Effect of static magnetic field on microstructures and mechanical properties of laser-MIG hybrid welding for 304 stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 91(9–12):3437–3447
Steinbach S, Ratke L (2005) The effect of rotating magnetic fields on the microstructure of directionally solidified Al–Si–Mg alloys. Mat Sci Eng A Struct 413:200–204
Tang Z, Gatzen M (2010) Influence on the dilution by laser welding of aluminum with magnetic stirring. Phys Procedia 5:125–137
Yuan Z, Ren Z, Li C, Xiao Q, Wang Q, Dai Y, Wang H (2013) Effect of high magnetic field on diffusion behavior of aluminum in Ni–Al alloy. Mater Lett 108:340–342
Lim YC, Yu X, Cho JH, Sosa J, Farson DF, Babu SS, Flesner B (2010) Effect of magnetic stirring on grain structure refinement: part 1–Autogenous nickel alloy welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(7):583–589
Lim YC, Yu X, Cho JH, Sosa J, Farson DF, Babu SS, Flesner B (2010) Effect of magnetic stirring on grain structure refinement Part 2–Nickel alloy weld overlays. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(5):400–406
Li ZF, Dong J, Zeng XQ, Lu C, Ding WJ, Ren ZM (2007) Influence of strong static magnetic field on intermediate phase growth in Mg–Al diffusion couple. J Alloy Compd 440(1–2):132–136
Ren X, Chen GQ, Zhou WL, Wu CW, Zhang JS (2009) Effect of high magnetic field on intermetallic phase growth in Ni–Al diffusion couples. J Alloy Compd 472(1–2):525–529
Li X, Fautrelle Y, Gagnoud A, Du D, Wang J, Ren Z, Mangelinck-Noel N (2014) Effect of a weak transverse magnetic field on solidification structure during directional solidification. Acta Mater 64:367–381
Bachmann M, Avilov V, Gumenyuk A, Rethmeier M (2013) About the influence of a steady magnetic field on weld pool dynamics in partial penetration high power laser beam welding of thick aluminium parts. Int J Heat Mass Transf 60:309–321
Bachmann M, Avilov V, Gumenyuk A, Rethmeier M (2014) Experimental and numerical investigation of an electromagnetic weld pool support system for high power laser beam welding of austenitic stainless steel. J Mater Process Tech 214(3):578–591
Üstündağ Ö, Avilov V, Gumenyuk A, Rethmeier M (2019) Improvement of filler wire dilution using external oscillating magnetic field at full penetration hybrid laser-arc welding of thick materials. Metals 9(5):594
Sun QJ, Li JZ, Liu YB, Li BP, Xu PW, Feng JC (2017) Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of Al/Ti joint welded by CMT method—Assisted hybrid magnetic field. Mater Design 116:316–324
Liu Y, Sun Q, Liu J, Wang S, Feng J (2015) Effect of axial external magnetic field on cold metal transfer welds of aluminum alloy and stainless steel. Mater Lett 152:29–31
Jiang P, Chen R (2019) Research on interfacial layer of laser-welded aluminum to titanium. Mater Charact 154:264–268
Ma Z, Zhao W, Yan J, Li D (2011) Interfacial reaction of intermetallic compounds of ultrasonic-assisted brazed joints between dissimilar alloys of Ti6Al4V and Al4Cu1Mg. Ultrason Sonochem 18(5):1062–1067
Shiue RK, Wu SK, Chen SY (2003) Infrared brazing of TiAl using Al-based braze alloys. Intermetallics 11(7):661–671
Chen R, Jiang P, Shao XY, Mi GY, Wang C (2018) Effect of magnetic field on crystallographic orientation for stainless steel 316L laser-MIG hybrid welds and its strengthening mechanism on fatigue resistance. Inter J Fatigue 112:308–317
Kao A (2010) Thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamics in dendritic solidification. Doctoral dissertation, University of Greenwich
Chen X, Pang S, Shao X, Wang C, Xiao J, Jiang P (2017) Three-dimensional transient thermoelectric currents in deep penetration laser welding of austenite stainless steel. Opt Laser Eng 91:196–205
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the technical support from Analytical and Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Special thanks are to Mrs. Gao for her assistance with the EBSD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R. Effect of external magnetic field on the microstructure and strength of laser-welded aluminum to titanium. J Mater Sci 55, 4054–4064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04249-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04249-2