Abstract
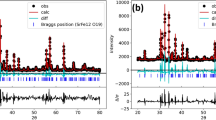
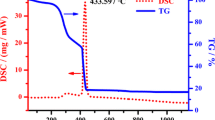
Mullite-type Bi2Mn4O10 and R2Mn4O10 (R = rare earth element) compounds are isostructural and are of ongoing research attentions because of their interesting crystal structures and the associated multiferroic properties. We report three series of mullite-type (Bi1−xRx)2Mn4O10 compounds for R = Nd, Sm and Eu prepared by solid-state synthesis methods. Each phase of the solid solutions is characterized by X-ray powder diffraction followed by Rietveld refinement. Evolutions of the metric parameters, interatomic bond distances, average crystallite size and microstrain are carried out with respect to the compositional x-value. This study also emphasizes on how the crystal chemistry changes upon successive change of the stereochemical activity of the lone electron pair of the Bi3+ cation using the Wang–Liebau eccentricity parameter. Selective vibrational features have been discussed based on the Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectra. The thermal stability of the end-members is analyzed from the thermogravimetric data, demonstrating that the end-member Bi2Mn4O10 differently decomposes than that of the other R2Mn4O10 compounds.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer RX (2005) The mullite-type family of crystal structures. In: Schneider H, Komarneni S (eds) Mullite. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 1–46
Muñoz A, Fernández-Díaz MT (2002) Magnetic structure and properties of BiMn2O5 oxide: A neutron diffraction study. Phys Rev B 65:144423. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.65.144423
Alonso JA, Casais MT, Martínez-Lope MJ, Martínez JL, Fernández-Díaz MT (1997) A structural study from neutron diffraction data and magnetic properties of RMn2O5 (R = La, rare earth). J Phys Condens Matter 9:8515–8526. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/9/40/017
Volkova LM, Marinin DV (2009) Crystal chemistry aspects of the magnetically induced ferroelectricity in TbMn(2)O(5) and BiMn(2)O(5). J Phys Condens Matter 21:015903. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/1/015903
Ziegler F, Köhler L, Gibhardt H, Gesing TM, Murshed MM, Sobolev O, Piovano A, Eckold G (2019) Characterization of multiferroic Bi2Mn4O10 by dielectric and neutron spectroscopy. Phys Status Solidi (b) 1800668:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201800668
Sun ZH, Cheng BL, Dai S, Jin KJ, Zhou YL, Lu HB, Chen ZH, Yang GZ (2006) Effect of Ce substitution on magnetic and dielectric properties of BiMn2O5. J Appl Phys 99:084105. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2190716
Van Den Brink J, Khomskii DI (2008) Multiferroicity due to charge ordering. J Phys Condens Matter 20:434217. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/43/434217
Kann ZR, Auletta JT, Hearn EW, Weber S-U, Becker KD, Schneider H, Lufaso MW (2012) Mixed crystal formation and structural studies in the mullite-type system Bi2Fe4O9–Bi2Mn4O10. J Solid State Chem 185:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.10.046
Niizeki N, Wachi M (1968) The crystal structures of Bi2Mn4O10, Bi2Al4O9 and Bi2Fe4O9. Z Krist 127:173–187. https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.1968.127.1-4.173
Murshed MM, Gesing TM (2013) Anisotropic thermal expansion and anharmonic phonon behavior of mullite-type Bi2Ga4O9. Mater Res Bull 48:3284–3291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.007
Mangir Murshed M, Mendive CB, Curti M, Šehović M, Friedrich A, Fischer M, Gesing TM (2015) Thermal expansion of mullite-type Bi2Al4O9: a study by X-ray diffraction, vibrational spectroscopy and density functional theory. J Solid State Chem 229:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2015.05.010
Murshed MM, Nénert G, Burianek M, Robben L, Mühlberg M, Schneider H, Fischer RX, Gesing TM (2013) Temperature-dependent structural studies of mullite-type Bi2Fe4O9. J Solid State Chem 197:370–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2012.08.062
Nguyen N, Legrain M, Ducouret A, Raveau B (1999) Distribution of Mn3+ and Mn4+ species between octahedral and square pyramidal sites in Bi2Mn4O10-type structure. J Mater Chem 9:731–734. https://doi.org/10.1039/a808094a
Curti M, Gesing TM, Murshed MM, Bredow T, Mendive CB (2013) Liebau density vector: a new approach to characterize lone electron pairs in mullite-type materials. Z Krist 288:629–634. https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.2013.1686
Khomskii D (2009) Classifying multiferroics: mechanisms and effects. Physics (College Park, MD) 2:20. https://doi.org/10.1103/physics.2.20
MacKenzie KJD, Dougherty T, Barrel J (2008) The electronic properties of complex oxides of bismuth with the mullite structure. J Eur Ceram Soc 28:499–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2007.03.012
Petit S, Balédent V, Doubrovsky C, Lepetit MB, Greenblatt M, Wanklyn B, Foury-Leylekian P (2013) Investigation of the electromagnon excitations in the multiferroic TbMn2O5. Phys Rev B 87:140301. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.87.140301
Vecchini C, Chapon L, Brown P, Chatterji T, Park S, Cheong S-W, Radaelli P (2008) Commensurate magnetic structures of RMn2O5 (R = Y, Ho, Bi) determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction. Phys Rev B 77:134434. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.77.134434
Retuerto M, Muñoz A, Martínez-Lope MJ, Garcia-Hernandez M, André G, Krezhov K, Alonso JA (2013) Influence of the Bi3+ electron lone pair in the evolution of the crystal and magnetic structure of La(1−x)Bi(x)Mn2O5 oxides. J Phys Condens Matter 25:216002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/25/21/216002
Brown ID (2002) The chemical bond in inorganic chemistry: the bond valence model. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kirsch A, Murshed MM, Litterst FJ, Gesing TM (2019) Structural, spectroscopic, and thermoanalytic studies on Bi2Fe4O9: tunable properties driven by nano- and poly-crystalline states. J Phys Chem C 123:3161–3171. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09698
Burianek M, Krenzel TF, Schmittner M, Schreuer J, Fischer RX, Mühlberg M, Nénert G, Schneider H, Gesing TM (2012) Single crystal growth and characterization of mullite-type Bi2Mn4O10. Int J Mater Res 103:449–455
Balzar D (1999) Voigt-function model in diffraction line-broadening analysis. IUCr Monographs on Crystallography 10, pp 94–124
Balzar D, Audebrand N, Daymond M, Fitch A, Hewat A, Langford JI, Bail A, Louer D, Masson O, McCowan C, Popa N, Stephens P, Toby B (2004) Size–strain line-broadening analysis of the ceria round-robin sample. Appl Crystallogr 37:911–924. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889804022551
Popov G, Greenblatta M, McCarroll WH (2000) Synthesis of LnMn2O5 (Ln = Nd, Pr) crystals using fused salt electrolysis. Mater Res Bull 35:1661–1667. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-5408(00)00372-x
Kagomiya I, Matsumoto S, Kohn K, Fukuda Y, Shoubu T, Kimura H, Noda Y, Ikeda N (2003) Lattice distortion at ferroelectric transition of YMn2O5. Ferroelectrics 286:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190390206347
Popov YF, Kadomtseva AM, Vorob’ev GP, Sanina VA, Zvezdin AK, Tehranchi MM (2000) Low-temperature phase transition in EuMn2O5 induced by a strong magnetic field. Phys B 284:1402–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-4526(99)02565-x
Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr Sect A 32:751–767. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0567739476001551
Alonso JA, Casais MT, Martínez-Lope MJ, Rasines I (1997) High oxygen pressure preparation, structural refinement, and thermal behavior of RMn2O5 (R = La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu). J Solid State Chem 129:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1996.7237
Wang X, Liebau F (2007) Influence of polyhedron distortions on calculated bond-valence sums for cations with one lone electron pair. Acta Crystallogr B 63:216–228. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768106055911
Silva Júnior FM, Paschoal CWA, Almeida RM, Moreira RL, Paraguassu W, Castro Junior MC, Ayala AP, Kann ZR, Lufaso MW (2013) Room-temperature vibrational properties of the BiMn2O5 mullite. Vib Spectrosc 66:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2013.01.010
Li C, Thampy S, Zheng Y, Kweun JM, Ren Y, Chan JY, Kim H, Cho M, Kim YY, Hsu JWP, Cho K (2016) Thermal stability of mullite RMn2O5 (R = Bi, Y, Pr, Sm or Gd): combined density functional theory and experimental study. J Phys Condens Matter 28:125602. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/28/12/125602
Kerr J (1984) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, 64th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Acknowledgements
Kowsik Ghosh gratefully thanks the University of Bremen for the financial supports. He also acknowledges DAAD (Funding ID: 57340829) and BISIP (Bremen International Students Internship Program) for their supports in partly finance this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, K., Murshed, M.M. & Gesing, T.M. Synthesis and characterization of (Bi1−xRx)2Mn4O10: structural, spectroscopic and thermogravimetric analyses for R = Nd, Sm and Eu. J Mater Sci 54, 13651–13659 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03852-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03852-7