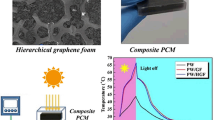
Abstract
Solar vapor generation is emerging as a reliable way to directly transfer solar illumination to vapor evaporation. Graphene-based porous photothermal materials are considered as promising absorbers in this system owing to the broadband absorption and excellent photothermal properties. In this paper, we construct a three-dimensional (3D) graphene oxide foam with a convenient surfactant foaming method for solar vapor generation. Abundant porous channels and good hydrophilicity are simultaneously achieved by means of the self-assembly and hydrophilic characteristics of the foaming agents. Detailed light absorption and vapor generation tests reveal that the foam monolith possesses an absorption rate at ~ 89% and a considerable solar vapor efficiency of ~ 81% under a solar intensity of 1 kW m−2.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Javadi FS, Saidur R, Kamalisarvestani M (2013) Investigating performance improvement of solar collectors by using nanofluids. Renew Sust Energ Rev 28:232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.06.053
Zhou X, Yang J (2008) Temperature field of solar collector and application potential of solar chimney power systems in china. J Energy Inst 81(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1179/174602208x269364
Malali PD, Chaturvedi SK, Abdel-Salam T (2017) Performance optimization of a regenerative brayton heat engine coupled with a parabolic dish solar collector. Energy Convers Manag 143:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.03.067
Pei G, Li J, Ji J (2010) Analysis of low temperature solar thermal electric generation using regenerative organic rankine cycle. Appl Therm Eng 30(8–9):998–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.01.011
Jing L, Gang P, Jie J (2010) Optimization of low temperature solar thermal electric generation with organic rankine cycle in different areas. Appl Energ 87(11):3355–3365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.05.013
Liu S, Liang Z, Gao F, Luo S, Lu G (2010) In vitro photothermal study of gold nanoshells functionalized with small targeting peptides to liver cancer cells. J Mater Sci-Mater M 21(2):665–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3895-x
Carrasco E, Del Rosal B, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Fuente AJ, Gonzalez PH, Rocha U, Kumar KU, Jacinto C, Daniel J (2015) Intratumoral thermal reading during photo-thermal therapy by multifunctional fluorescent nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater 25(4):615–626. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201403653
Wang H, Mukherjee S, Yi J, Banerjee P, Chen Q, Zhou S (2017) Biocompatible chitosan-carbon dots hybrid nanogels for NIR-imaging-guided synergistic photothermal/chemo-therapy. Acs Appl Mater Inter 9(22):18639–18649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b06062
Lei S, Yurong H, Xinzhi W, Yanwei H (2018) Recyclable photo-thermal conversion and purification systems via Fe3O4@TiO2 nanoparticles. Energy Convers Manag 171:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.106
Jin H, Lin G, Bai L, Zeiny A, Wen D (2016) Steam generation in a nanoparticle-based solar receiver. Nano Energy 28:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.08.011
Ghasemi H, Ni G, Marconnet AM, Loomis J, Yerci S, Miljkovic N, Chen G (2014) Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat Commun 5:4449. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5449
Zhao F, Zhou X, Shi Y, Qian X, Alexander M, Zhao X, Mendez S, Yang R, Qu L, Yu G (2018) Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat Nanotechnol 13(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0097-z
Hu X, Xu W, Zhou L, Tan Y, Wang Y, Zhu S, Zhu J (2017) Tailoring graphene oxide-based aerogels for efficient solar steam generation under one sun. Adv Mater 29(5):1604031. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201604031
Xu N, Hu X, Xu W, Li X, Zhou L, Zhu S, Zhu J (2017) Mushrooms as efficient solar steam-generation devices. Adv Mater 29(28):1606762. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606762
Xue G, Liu K, Chen Q, Yang P, Li J, Ding T, Duan J, Qi B, Zhou J (2017) Robust and low-cost flame-treated wood for high-performance solar steam generation. Acs Appl Mater Inter 9(17):15052–15057. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01992
Zhou L, Tan Y, Ji D, Zhu B, Zhang P, Xu J, Gan Q, Yu Z, Zhu J (2016) Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation. Sci Adv 2(4):e1501227. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1501227
Sajadi SM, Farokhnia N, Irajizad P, Hasnain M, Ghasemi H (2016) Flexible artificially-networked structure for ambient/high pressure solar steam generation. J Mater Chem A 4(13):4700–4705. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA01205A
Ito Y, Tanabe Y, Han J, Fujita T, Tanigaki K, Chen M (2015) Multifunctional porous graphene for high-efficiency steam generation by heat localization. Adv Mater 27(29):4302–4307. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501832
Hou B, Kong D, Qian J, Yu Y, Cui Z, Liu X, Wang J, Mei T, Li J, Wang X (2018) Flexible and portable graphene on carbon cloth as a power generator for electricity generation. Carbon 140:488–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.09.005
Hou B, Cui Z, Zhu X, Liu X, Wang G, Wang J, Mei T, Li J, Wang X (2019) Functionalized carbon materials for efficient solar steam and electricity generation. Mater Chem Phys 222:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.10.006
Zhang L, Tang B, Wu J, Li R, Wang P (2015) Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv Mater 27(33):4889–4894. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502362
Jiang Q, Tian L, Liu KK, Tadepalli S, Raliya R, Biswas P, Naik RR, Singamaneni S (2016) Bilayered biofoam for highly efficient solar steam generation. Adv Mater 28(42):9400–9407. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201601819
Wang Y, Zhang L, Wang P (2016) Self-floating carbon nanotube membrane on macroporous silica substrate for highly efficient solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(3):1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01274
Ren H, Tang M, Guan B, Wang K, Yang J, Wang F, Wang M, Shan J, Chen Z, Wei D, Peng H, Liu Z (2017) Hierarchical graphene foam for efficient omnidirectional solar-thermal energy conversion. Adv Mater 29(38):1702590. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702590
Chen Y, Zhu Y, Feng B, Weng J, Wang J, Lu X (2011) Preparation and characterization of a novel porous titanium scaffold with 3d hierarchical porous structures. J Mater Sci-Mater M 22(4):839–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4280-0
Du X, Zhao L, He X, Wang X, Qu W, Chen H, Chen H, Wang J, Lei Z (2016) A novel method based on ultrastable foam and improved gelcasting for fabricating porous mullite ceramics with thermal insulation–mechanical property trade-off. J Porous Mater 23(2):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-0091-x
Xin Z, Li W, Fang W, He X, Zhao L, Chen H, Zhang W, Sun Z (2017) Enhanced specific surface area by hierarchical porous graphene aerogel/carbon foam for supercapacitor. J Nanopart Res 19(12):386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4080-7
Du X, He X, Zhao L, Chen H, Li W, Fang W, Zhang W, Wang J (2016) TiO2 hierarchical porous film constructed by ultrastable foams as photoanode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Power Sources 332:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.09.103
Hsieh AG, Korkut S, Punckt C, Aksay IA (2013) Dispersion stability of functionalized graphene in aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions. Langmuir 29(48):14831–14838. https://doi.org/10.1021/la4035326
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, Alemany LB, Lu W, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Sham AYW, Notley SM (2016) Foam stabilisation using surfactant exfoliated graphene. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 469:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.02.015
Hao Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Ni Z, Wang Z, Wang R, Koo CK, Shen Z, Thong JTL (2010) Probing layer number and stacking order of few-layer graphene by raman spectroscopy. Small 6(2):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200901173
Chen WF, Yan LF, Bangal P (2010) Chemical reduction of graphene oxide to graphene by sulfur-containing compounds. J Phy Chem C 114(47):19885–19890. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp107131v
Wei G, Miao YE, Zhang C, Yang Z, Liu Z, Tjiu WW, Liu T (2013) Ni-doped graphene/carbon cryogels and their applications as versatile sorbents for water purification. Acs Appl Mater Inter 5(15):7584–7591. https://doi.org/10.1021/am401887g
Arslan Y, Kadir P, Yildiz A (2004) Electropolymerization of self-doped polythiophene in acetonitrile containing FSO3H. Synthetic Met 142(1–3):0–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2003.07.001
Liu X, He J (2009) Superhydrophilic and antireflective properties of silica nanoparticle coatings fabricated via layer-by-layer assembly and postcalcination. J Phys Chem C 113(1):148–152. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp808324c
Yu S, Zhang Y, Duan H, Liu Y, Quan X, Tao P, Shang W, Wu J, Song C, Deng T (2015) The impact of surface chemistry on the performance of localized solar-driven evaporation system. Sci Rep-UK 5:13600. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13600
Bernadet S, Tavernier E, Ta DM, Vallée RAL, Ravaine S, Fécant A, Backov R (2019) Bulk photodriven CO2 conversion through TiO2@Si(HIPE) monolithic macrocellular foams. Adv Funct Mater 29(9):1807767. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201807767
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61604110, 51802234), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Provincial China (2018CFC796, 2017CFC829, 2017CFB291), Department of Education Science Research Program of Hubei Province (Q20161110) and Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Green Chemical Process of Wuhan Institute of Technology (NRGCT201503), Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates of Hubei Province (201510488022), Scientific Research Program of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (B2017014, D20171505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, W., Zhao, L., Chen, H. et al. Graphene oxide foam fabricated with surfactant foaming method for efficient solar vapor generation. J Mater Sci 54, 12782–12793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03794-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03794-0