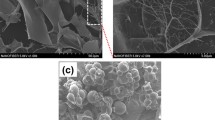
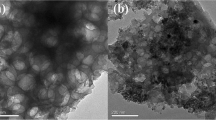
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution is one of the most serious environmental problems, posing threats to human health. Here, we developed a magnetic hybrid aerogel by integrating nanocellulose and ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for effectively adsorbing heavy metal ions from water and realizing controllable recovery under magnetic condition. The magnetic behavior and adsorbing capacity of the hybrid aerogel on removal of heavy metal chromium (Cr)(VI) ion were examined. Results show that the ferroferric oxide nanoparticles physically adsorb the nanocellulose, each of which retains the original composition and structural characteristics. The magnetic hybrid aerogel possesses good ferromagnetic property with saturation magnetization value of 53.69 emu/g, enabling effective and controllable recovery of the aerogel under magnetic condition The adsorption efficiency of the hybrid aerogel on the Cr(VI) ion reaches the highest value of 2.2 mg/g when the mass ratio of the nanocellulose to ferroferric oxide nanoparticle is 1:1. Additionally, the hybrid aerogel presents similar adsorption behavior on plumbum (Pb)(II) and copper (Cu)(II) ions, suggesting extended applications of the hybrid aerogel on removal of heavy metal ions. Such strategy could provide new applications for the abundant nanocellulose resources and could be extended to integrate nanocellulose with other functional nanomaterials into novel hybrid aerogel for water purification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Q, Yang ZM (2016) Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ Pollut 218:358–365
Li QY, Zhou DD, Zhang PL, Man P, Tian ZB, Li Y, Ai SY (2016) The BiOBr/regenerated cellulose composite film as a green catalyst for light degradation of phenol. Colloid Surface Physicochem Eng Aspect 501:132–137
Wang JL, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27(2):195–226
Bao LJ, Maruya KA, Snyder SA, Zeng EY (2012) China’s water pollution by persistent organic pollutants. Environ Pollut 163:100–108
Sun JC, Fan H, Nan B, Ai SY (2014) Fe3O4@LDH@Ag/Ag3PO4 submicrosphere as a magnetically separable visible-light photocatalyst. Sep Purif Technol 130:84–90
Jiang WJ, Wu LN, Duan JL, Yin HS, Ai SY (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for 5-hydroxymethylcytosine detection based on Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles and PAMAM dendrimers. Biosens Bioelectron 99:660–666
Shen LL, Zhang GR, Li W, Biesalski M, Etzold BJM (2017) Modifier-free microfluidic electrochemical sensor for heavy-metal detection. ACS Omega 2(8):4593–4603
Cao CY, Cui ZM, Chen CQ, Song WG, Cai W (2010) Ceria hollow nanospheres produced by a template-free microwave-assisted hydrothermal method for heavy metal ion removal and catalysis. J Phys Chem C 114(21):9865–9870
Phoebe ZR, Heather JS (2015) Inorganic nano-adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals and arsenic: a review. RSC Adv 5:29885–29907
Wang XQ, Liu WX, Tian J, Zhao ZH, Hao P, Kang XL, Sang YH, Liu H (2014) Cr(VI), Pb(II), Cd(II) adsorption properties of nanostructured BiOBr microspheres and their application in a continuous filtering removal device for heavy metal ions. J Mater Chem A 2:2599–2608
Mercy RB, Siddulu NT, Stalin J, Kavitha R, Gurwinder S, Jessica S, Ugo R, Khalid AB, Ajayan V (2018) Recent advances in functionalized micro and mesoporous carbon materials: synthesis and applications. Chem Soc Rev 47:2680–2721
Chen CJ, Song JW, Zhu SZ, Li YJ, Kuang YD, Wan JY, Kirsch D, Xu LS, Wang YB, Gao TT, Wang YL, Huang H, Gan WT, Gong A, Li T, Xie J, Hu LB (2018) Scalable and sustainable approach toward highly compressible, anisotropic, lamellar carbon sponge. Chem 4(3):544–554
Yin K, Yang S, Dong XR, Chu DK, Duan JA, He J (2018) Robust laser-structured asymmetrical PTFE mesh for underwater directional transportation and continuous collection of gas bubbles. Appl Phys Lett 112(24):243701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039789
Yin K, Chu DK, Dong XR, Wang C, Duan JA, He J (2017) Femtosecond laser induced robust periodic nanoripples structured mesh for highly efficient oil–water separation. Nanoscale 9:14229–14235
Kabiri S, Tran DNH, Azari S, Losic D (2015) Graphene-diatom silica aerogels for efficient removal of mercury ions from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(22):11815–11823
Fu JJ, He CX, Wang SQ, Chen YS (2018) A thermally stable and hydrophobic composite aerogel made from cellulose nanofibril aerogel impregnated with silica particles. J Mater Sci 53(9):7072–7082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2034-9
Jiang F, Liu H, Li YJ, Kuang YD, Xu X, Chen CJ, Huang H, Jia C, Zhao XP, Hitz E, Zhou YB, Yang RG, Cui LF, Hu LB (2018) Lightweight, mesoporous, and highly absorptive all-nanofiber aerogel for efficient solar steam generation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(1):1104–1112
Chavan AA, Li HB, Scarpellini A, Marras Sergio, Manna L, Athanassiou A, Fragouli D (2015) Elastomeric nanocomposite foams for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(27):14778–14784
Gu XY, Yang Y, Hu Y, Hu M, Wang CY (2015) Fabrication of graphene-based xerogels for removal of heavy metal ions and capacitive deionization. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3(6):1056–1065
Lamymendes A, Rui FS, Durães L (2018) Advances in carbon nanostructure-silica aerogel composites: a review. J Mater Chem A 6:1340–1369
Zhu HL, Luo W, Ciesielski PN, Fang ZQ, Zhu JY, Henriksson G, Himmel ME, Hu LB (2016) Wood-derived materials for green electronics, biological devices, and energy applications. Chem Rev 116(16):9305–9374
Santos SM, Carbajo JM, Gómez N, Ladero M, Villar JC (2017) Paper reinforcing by in situ growth of bacterial cellulose. J Mater Sci 52(10):5882–5893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0824-0
Tian Zhengbin, Zong Lei, Niu Rujie, Wang Xiao, Li Yan, Ai Shiyun (2015) Recovery and characterization of lignin from alkaline straw pulping black liquor: as feedstock for bio-oil research. J Appl Polym Sci 132:42057–42065
Yue YY, Han JQ, Han GP, Aita GM, Wu QL (2015) Cellulose fibers isolated from energycane bagasse using alkaline and sodium chlorite treatments: structural, chemical and thermal properties. Ind Crops Prod 76:355–363
Nair SS, Kuo PY, Chen HY, Yan N (2017) Investigating the effect of lignin on the mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of cellulose nanofibril reinforced epoxy composite. Ind Crops Prod 100:208–217
Zhuo X, Liu C, Pan RT, Dong XY, Li YF (2017) Nanocellulose mechanically isolated from Amorpha fruticosa Linn. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(5):4414–4420
Zhuo X, Wei J, Xu JF, Pan RT, Zhang G, Guo YL, Dong XY, Long L, Li YF (2017) Nanocellulose isolation from Amorpha fruticosa by an enzyme-assisted pretreatment. Appl Environ Biotech 2:34–39
Huang JD, Wang SQ, Lyu SY, Fu F (2018) Preparation of a robust cellulose nanocrystal superhydrophobic coating for self-cleaning and oil–water separation only by spraying. Ind Crops Prod 122:438–447
Zhang XT, Jing SS, Chen ZH, Zhong LX, Liu QZ, Peng XW, Sun RC (2017) Fabricating 3D hierarchical porous TiO2 and SiO2 with high specific surface area by using nanofibril-interconnected cellulose aerogel as a new biotemplate. Ind Crops Prod 109:790–802
Chen CJ, Hu LB (2018) Nanocellulose toward advanced energy storage devices: structure and electrochemistry. Acc Chem Res. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00391
Osorio DA, Seifried B, Moquin P, Grandfield K, Cranston ED (2018) Morphology of cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels: cryo-templating versus pressurized gas expansion processing. J Mater Sci 53(13):9842–9860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2235-2
Zhu H, Yang X, Cranston ED, Zhu SP (2016) Flexible and porous nanocellulose aerogels with high loadings of metal–organic-framework particles for separations applications. Adv Mater 28(35):7652–7657
Geng BY, Wang Y, Wu S, Ru J, Tong CC, Chen YF, Liu HZ, Wu SC, Liu XY (2017) Surface-tailored nanocellulose aerogels with thiol-functional moieties for highly efficient and selective removal of Hg(II) ions from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(12):11715–11726
Yao C, Wang F, Cai Z, Wang X (2016) Aldehyde-functionalized porous nanocellulose for effective removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:92648–92654
Liu HZ, Geng BY, Chen YF, Wang HY (2017) Review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(1):49–66
Shaghaleh H, Xu X, Wang S (2018) Current progress in production of biopolymeric materials based on cellulose, cellulose nanofibers, and cellulose derivatives. RSC Adv 8:825–842
Song JW, Chen CJ, Yang Z, Kuang YD, Li T, Li YJ, Huang H, Kierzewski I, Liu BY, He SM, Gao TT, Yuruker SU, Gong A, Yang B, Hu LB (2018) Highly compressible, anisotropic aerogel with aligned cellulose nanofibers. ACS Nano 12:140–147
An F, Li XF, Min P, Li HF, Dai Z, Yu ZZ (2018) Highly anisotropic graphene/boron nitride hybrid aerogels with long-range ordered architecture and moderate density for highly thermally conductive composites. Carbon 126:119–127
Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Wang F, Wang A (2016) Fabrication of magnetic macroporous chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel for removal of Cd(2+) and Pb(2.). Int J Biol Macromol 93(Part A):483–492
Fu F, Chen R, Xiong Y (2006) Application of a novel strategy—coordination polymerization precipitation to the treatment of Cu2+-containing wastewaters. Sep Purif Technol 52(2):388–393
Lu N, Bu YX, Luo GM (2017) Cu-wire-mediated dipyrimidine base pairs as the building blocks for conductive and magnetic Cu–DNA nanowires. J Math Chem 55(6):1301–1321
Shang K, Sun B, Sun JC, Li J, Ai SY (2013) Poly-(3-thiopheneacetic acid) coated Fe3O4@LDHs magnetic nanospheres as a photocatalyst for the efficient photocatalytic disinfection of pathogenic bacteria under solar light irradiation. New J Chem 37:2509–2514
Gao H, Liu Y, Zeng G, Xu W, Li Y, Xia W (2008) Characterization of Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions by a surplus agricultural waste–rice straw. J Hazard Mater 150(2):446–452
Aliabadi M, Morshedzadeh K, Soheyli H (2006) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by lignocellulosic solid wastes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3(3):321–325
Dehghani MH, Taher MM, Bajpai AK, Heibati B, Tyagi I, Asif M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Removal of noxious Cr(VI) ions using single-walled carbon nanotubes and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 279:344–352
Dubey SP, Gopal K (2007) Adsorption of chromium(VI) on low cost adsorbents derived from agricultural waste material: a comparative study. J Hazard Mater 145(3):465–470
Garg UK, Kaur MP, Garg VK, Sud D (2007) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by agricultural waste biomass. J Hazard Mater 140:60–68
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2004) Cr(VI) removal from synthetic wastewater using coconut shell charcoal and commercial activated carbon modified with oxidizing agents and/or chitosan. Chemosphere 54(7):951–967
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial supports from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, Doctoral Branch (Grant No. ZR2017BC042), the Forestry Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Province (Grant No. LYCX10-2018-50), the Key Special Foundation for the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFD0600704) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31700497, 31300479).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW, ZY, XD and YL designed the experiment. JW, ZY, YS, CW and JF performed the whole experiments. JW and YS drew the figures. GK and RZ carried out the evaluation of magnetic properties of the aerogels. JW, XD and YL wrote the paper. Everybody comments on the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Yang, Z., Sun, Y. et al. Nanocellulose-based magnetic hybrid aerogel for adsorption of heavy metal ions from water. J Mater Sci 54, 6709–6718 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03322-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03322-0