Abstract
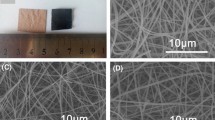
Herein, the composite carbon material of porous carbon nanofiber and carbon nanotube is developed via electro-blown spinning and one-step simultaneous carbonization and chemical vapor deposition without injecting every kind of reaction gas in proportion and removing catalyst in secondary processing. The carbon nanotubes are uniformly growing on carbon skeleton which dramatically improve the performances such as specific surface area (from 334.066 to 644.589 m2 g−1) and electrical conductivity (from 42.22 to 146.20 S cm−1) comparing with porous carbon nanofibers. The different spinning parameters are investigated to optimize parameters, and the porous carbon nanofiber and carbon nanotube are studied and used as electrode for supercapacitors. The results showed that it possesses excellent electrochemical properties, including high specific discharge capacity (216.5 F g−1 at 1.0 A g−1) and good cycle performance (retains ~ 98.68% after 5000 cycles). Moreover, the convenient one-step prepared method special throughout pores structure and superior performance provide a novel approach for designing new types of carbon composite materials which also possess potential application prospect in fields of catalyst, adsorption, etc.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hou J, Jiang K, Tahir M, Wu X, Idrees F, Shen M, Cao C (2017) Tunable porous structure of carbon nanosheets derived from puffed rice for high energy density supercapacitors. J Power Sources 371:148–155
Zha D, Sun H, Fu Y, Ouyang X, Wang X (2017) Acetate anion-intercalated nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide nanosheets supported on Ni foam for high-performance supercapacitors with excellent long-term cycling stability. Electrochim Acta 236:18–27
Zha D, Fu Y, Zhang L, Zhu J, Wang X (2018) Design and fabrication of highly open nickel cobalt sulfide nanosheets on Ni foam for asymmetric supercapacitors with high energy density and long cycle-life. J Power Sources 378:31–39
Cai Y, Luo Y, Dong H, Zhao X, Xiao Y, Liang Y, Hu H, Liu Y, Zheng M (2017) Hierarchically porous carbon nanosheets derived from Moringa oleifera stems as electrode material for high-performance electric double-layer capacitors. J Power Sources 353:260–269
Sun L, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang Q (2017) Roles of carbon nanotubes in novel energy storage devices. Carbon 122:462–474
Ni J, Li Y (2016) Carbon nanomaterials in different dimensions for electrochemical energy storage. Adv Energy Mater 6:1600278
Liu P, Yan J, Gao X, Huang Y, Zhang Y (2018) Construction of layer-by-layer sandwiched graphene/polyaniline nanorods/carbon nanotubes heterostructures for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 272:77–87
An G-H, Ahn H-J, Hong W-K (2015) Electrochemical properties for high surface area and improved electrical conductivity of platinum-embedded porous carbon nanofibers. J Power Sources 274:536–541
Zha D, Xiong P, Wang X (2015) Strongly coupled manganese ferrite/carbon black/polyaniline hybrid for low-cost supercapacitors with high rate capability. Electrochim Acta 185:218–228
Liu Y, Zhou J, Chen L, Zhang P, Fu W, Zhao H, Ma Y, Pan X, Zhang Z, Han W, Xie E (2015) Highly flexible freestanding porous carbon nanofibers for electrodes materials of high-performance all-carbon supercapacitors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23515–23520
Liu Y, Zhang N, Jiao L, Chen J (2015) Tin nanodots encapsulated in porous nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as a free-standing anode for advanced sodium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 27:6702–6707
Li Z, Zhang J-w, L-g Yu, Zhang J-w (2017) Electrospun porous nanofibers for electrochemical energy storage. J Mater Sci 52:6173–6195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0794-2
Liu P, Huang Y, Yan J, Yang Y, Zhao Y (2016) Construction of CuS nanoflakes vertically aligned on magnetically decorated graphene and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:5536–5546
Xia L, Zhang X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Zhong B, Zhang T, Wang H (2018) Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of laminated SiC NW -C f/lithium–aluminum–silicate (LAS) composites. J Alloys Compd 748:154–162
Ju J, Kang W, Li L, He H, Qiao C, Cheng B (2016) Preparation of poly (tetrafluoroethylene) nanofiber film by electro-blown spinning method. Mater Lett 171:236–239
Cheng L, He J, Jin Y, Chen H, Chen M (2015) Single-walled carbon nanotube embedded porous carbon nanofiber with enhanced electrochemical capacitive performance. Mater Lett 144:123–126
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Ajayan PM (1999) Nanotubes from carbon. Chem Rev 99:1787–1800
Park S-H, Jung H-R, Kim B-K, Lee W-J (2012) MWCNT/mesoporous carbon nanofibers composites prepared by electrospinning and silica template as counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Photochem Photobiol, A 246:45–49
Kim YK, Cha SI, Hong SH, Jeong YJ (2012) A new hybrid architecture consisting of highly mesoporous CNT/carbon nanofibers from starch. J Mater Chem 22:20554–20560
Zhang T, Xiao B, Zhou P, Xia L, Wen G, Zhang H (2017) Porous-carbon-nanotube decorated carbon nanofibers with effective microwave absorption properties. Nanotechnology 28:355708
Guo Q, Zhou X, Li X, Chen S, Seema A, Greiner A, Hou H (2009) Supercapacitors based on hybrid carbon nanofibers containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Mater Chem 19:2810–2816
Zeng L, Pan F, Li W, Jiang Y, Zhong X, Yu Y (2014) Free-standing porous carbon nanofibers–sulfur composite for flexible Li–S battery cathode. Nanoscale 6:9579–9587
Kong Y, Qiu T, Qiu J (2013) Fabrication of novel micro–nano carbonous composites based on self-made hollow activated carbon fibers. Appl Surf Sci 265:352–357
Liu Y, Ma J, Lu T, Pan L (2016) Electrospun carbon nanofibers reinforced 3D porous carbon polyhedra network derived from metal–organic frameworks for capacitive deionization. Sci Rep 6:32784
Me A Oberlin (1976) Filamentous growth of carbon through benzene decomposition. J Cryst Growth 32:335–349
Baker RTK (1989) Catalytic growth of carbon filaments. Carbon 27:315–323
Puts GJ, Crouse PL (2014) The influence of inorganic materials on the pyrolysis of polytetrafluoroethylene. Part 1: the sulfates and fluorides of Al, Zn, Cu, Ni Co, Fe and Mn. J Fluorine Chem 168:260–267
Ju J, Kang W, Deng N, Li L, Zhao Y, Ma X, Fan L, Cheng B (2017) Preparation and characterization of PVA-based carbon nanofibers with honeycomb-like porous structure via electro-blown spinning method. Microporous Microporous Mater 239:416–425
Alireza Badiei MA, Karimi Mahdi, Zarabadi-poor Pezhman (2014) Carbon nanotubes synthesis by chemical vapor deposition of methane over Zn–Fe mixed catalysts supported on alumina. J Nanostruct 4:259–265
Atchudan R, Pandurangan A, Somanathan T (2009) Bimetallic mesoporous materials for high yield synthesis of carbon nanotubes by chemical vapour deposition techniques. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 309:146–152
Deck CP, Vecchio K (2006) Prediction of carbon nanotube growth success by the analysis of carbon–catalyst binary phase diagrams. Carbon 44:267–275
Ummul Khair F, Ahmed Jalal U, Uemura K, Gotoh Y (2010) Fabrication of carbon fibers from electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Text Res J 81:659–672
Zhao M-Q, Liu X-F, Zhang Q, Tian G-L, Huang J-Q, Zhu W, Wei F (2012) Graphene/single-walled carbon nanotube hybrids: one-step catalytic growth and applications for high-rate Li–S batteries. ACS Nano 6:10759–10769
Lindemer MD, Advani SG, Prasad AK (2016) Hydrogen production via the heterogeneous hydrolysis of Zn vapor under a temperature gradient: modeling and efficiency analysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:10557–10567
Cao L, Z-h Li YGu, Li D-h, K-m Su, Yang D-j, Cheng B-w (2017) Rational design of N-doped carbon nanobox-supported Fe/Fe2N/Fe3C nanoparticles as efficient oxygen reduction catalysts for Zn–air batteries. J Mater Chem A 5:11340–11347
Fatema UK, Tomizawa C, Harada M, Gotoh Y (2011) Iodine-aided fabrication of hollow carbon fibers from solid poly(vinyl alcohol) fibers. Carbon 49:2158–2161
Xu X, Liu Y, Wang M, Zhu C, Lu T, Zhao R, Pan L (2016) Hierarchical hybrids with microporous carbon spheres decorated three-dimensional graphene frameworks for capacitive applications in supercapacitor and deionization. Electrochim Acta 193:88–95
Zuliani JE, Tong S, Kirk DW, Jia CQ (2015) Isolating the effect of pore size distribution on electrochemical double-layer capacitance using activated fluid coke. J Power Sources 300:190–198
Zhang L, Jiang Y, Wang L, Zhang C, Liu S (2016) Hierarchical porous carbon nanofibers as binder-free electrode for high-performance supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 196:189–196
Zhao Y, Kang W, Li L, Yan G, Wang X, Zhuang X, Cheng B (2016) Solution blown silicon carbide porous nanofiber membrane as electrode materials for supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 207:257–265
Ju J, Zhao H, Kang W, Tian N, Deng N, Cheng B (2017) Designing MnO2 and carbon composite porous nanofiber structure for supercapacitor applications. Electrochim Acta 258:116–123
Wang J, Tang J, Xu Y, Ding B, Chang Z, Wang Y, Hao X, Dou H, Kim JH, Zhang X, Yamauchi Y (2016) Interface miscibility induced double-capillary carbon nanofibers for flexible electric double layer capacitors. Nano Energy 28:232–240
Wang B, Lu G, Luo Q-P, Wang T (2016) Free-standing porous carbon nanofiber networks from electrospinning polyimide for supercapacitors. J Nanomater 2016:4305437
Simotwo SK, Chinnam PR, Wunder SL, Kalra V (2017) Highly durable, self-standing solid-state supercapacitor based on an ionic liquid-rich ionogel and porous carbon nanofiber electrodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:33749–33757
Perananthan S, Bonso JS, Ferraris JP (2016) Supercapacitors utilizing electrodes derived from polyacrylonitrile fibers incorporating tetramethylammonium oxalate as a porogen. Carbon 106:20–27
Ma C, Song Y, Shi J, Zhang D, Zhong M, Guo Q, Liu L (2012) Phenolic-based carbon nanofiber webs prepared by electrospinning for supercapacitors. Mater Lett 76:211–214
Fan L, Yang L, Ni X, Han J, Guo R, Zhang C (2016) Nitrogen-enriched meso-macroporous carbon fiber network as a binder-free flexible electrode for supercapacitors. Carbon 107:629–637
Hyun BG, Son HJ, Ji S, Jang J, Hur S-H, Park J-U (2016) Multi-dimensional carbon nanofibers for supercapacitor electrodes. J Electroceram 38:43–50
Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Guo S, Wang K, Liang Z, Xu Q (2014) Nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon nanowhisker ensembles on carbon nanofiber for high-performance supercapacitors. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1525–1533
Xie Q, Zhou S, Wu S, Zhang Y, Zhao P (2017) Supercapacitive behavior of laminar-structured carbon cloth with alternating graphene and hybrid nanofibers: a synergistic effect of graphene-coating and post-oxidization. Appl Surf Sci 407:36–43
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51673148, 51678411), the Science and Technology Plans of Tianjin (17JCYBJC41700, 17JCZDJC38100, 16PTSYJC00110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, J., Deng, N., Zhang, D. et al. Facile construction of PCNF&CNT composite material by one-step simultaneous carbonization and chemical vapor deposition. J Mater Sci 54, 1616–1628 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2932-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2932-x