Abstract
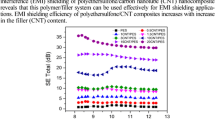
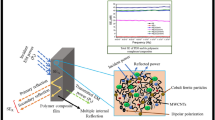
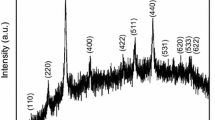
Nanocomposite films comprising of ion-conducting polymer electrolyte, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) as the electron-conducting network and ceramic (BaTiO3) as ferroelectric nanofiller have been synthesised for electromagnetic shielding application. XRD and dielectric studies of the synthesised BaTiO3 nanoparticles show a tetragonal structure and ferroelectric nature. The incorporation of nanofillers (MWCNT and BaTiO3) in the polymer electrolyte enhances the conductivity and dielectric property of the nanocomposites. Polymer nanocomposites with 7.5 wt% of BaTiO3 nanoparticles have exhibited the highest shielding effectiveness (SET) ~ 81 dB in the X-band (8–12 GHz). This enhancement in SE can be attributed to the (1) formation of micro-capacitors and interconnected network provided by MWCNTs, (2) spontaneous polarisation of BaTiO3 and its volumetric effect on the polymer nanocomposites and (3) leakage current due to the ions of the electrolyte which results in dielectric loss.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tong XC (2008) Advanced materials and design for electromagnetic interference shielding. CRC Press, London
Kheifets L, Afifi AA, Shimkhada R (2006) Public health impact of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. Environ Health Persp 114:1532–1607
Huo J, Wang L, Yu H (2009) Polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci 44:3917–3927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3561-1
Zhao B, Zhao C, Li R, Hamidinejad SM, Park CB (2017) Flexible, ultrathin, and high-efficiency electromagnetic shielding properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon composite films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:20873–20884
Kim HR, Fujimori K, Kim BS, Kim IS (2010) Light weight nanofibrous EMI shielding nanowebs prepared by electrospinning and metallization. Compos Sci Technol 72(11):1233–1239
Saini P, Choudhary V, Sood KN, Dhawan SK (2009) Electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of polyaniline/graphite composites prepared by in situ emulsion pathway. J Appl Polym Sci 113(5):3146–3155
Kong LB, Li ZW, Liu L, Huang R, Abshinova M, Yang ZH, Tang CB, Tan PK, Deng CR, Matitsine S (2013) Recent progress in some composite materials and structures for specific electromagnetic applications. Int Mater Rev 58(4):203–259
Ohlan A, Singh K, Chandra A, Dhawan SK (2010) Microwave absorption behavior of core–shell structured poly (3,4-ethylenedioxy thiophene)—barium ferrite nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:927–933
Singh AP, Mishra M, Sambyal P, Gupta BK, Chandra A, Dhawan SK (2014) Encapsulation of γ-Fe2O3 decorated reduced graphene oxide in polyaniline core–shell tubes as an exceptional tracker for electromagnetic environmental pollution. J Mater Chem A 2:3581–3593
Varshney S, Ohlan A, Jain VK, Dutta VP, Dhawan SK (2014) Synthesis of ferrofluid based nanoarchitectured polypyrrole composites and its application for electromagnetic shielding. Mater Chem Phys 143:806–814
Ke K, Wang Y, Liu XQ, Cao J, Luo Y, Yang W, Xie BH, Yang MBA (2012) Comparison of melt and solution mixing on the dispersion of carbon nanotubes in a poly(vinylidene fluoride) matrix. Compos B 43:1425–1432
Ram R, Rahaman M, Khastgir D (2015) Electrical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)/multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) semi-transparent composites: modelling of DC conductivity. Compos A 69:30–39
Bhingardive V, Sharma M, Suwas S, Madras G, Bose S (2015) Polyvinylidene fluoride based lightweight and corrosion resistant electromagnetic shielding materials. RSC Adv 5:35909–35916
Xu N, Hu L, Zhang Q, Xiao X, Yang H, Yu E (2015) Significantly enhanced dielectric performance of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropylene)-based composites filled with hierarchical flower-like TiO2 particles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:27373–27381
Arjmand M, Apperley T, Okoniewski M, Sundararaj U (2012) Comparative study of electromagnetic interference shielding properties of injection molded versus compression molded multi-walled carbon nanotube/polystyrene composites. Carbon 50:5126–5134
Gupta A, Choudhary V (2011) Electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of poly(trimethylene terephthalate)/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Compos Sci Technol 71:1563–1568
Eswaraiah V, Sankaranarayana V, Ramaprabhu S (2011) Functionalized graphene–PVDF foam composites for EMI shielding. Macromol Mater Eng 296:894–898
Sharma M, Sharma K, Abraham J, Thomas S, Madras G, Bose S (2014) Flexible EMI shielding materials derived by melt blending PVDF and ionic liquid modified MWCNTs. Mater Res Express 1:035003–035020
Saleh MHA, Sundararaj U (2009) Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon 47:1738–1746
Pande S, Singh BP, Mathur RB, Dhami TL, Saini P, Dhawan SK (2009) Improved electromagnetic interference shielding properties of MWCNT–PMMA composites using layered structures. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:327–334
Sharma M, Singh MP, Srivastava C, Madras G, Bose S (2014) Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based flexible and lightweight materials for attenuating microwave radiations. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(23):21151–21160
Joseph N, Singh SK, Sirugudu RK, Murthy VRK, Kumar SA, Sebastian MT (2013) Effect of silver incorporation into PVDF-barium titanate composites for EMI shielding applications. Mater Res Bull 48:1681–1687
Pawar SP, Marathe DA, Pattabhi K, Bose S (2015) Electromagnetic interference shielding through MWNT grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles in PC/SAN blends. J Mater Chem A 3:556–669
Sabira K, Jayakrishnan MP, Saheeda P, Jayalekshmi S (2018) On the absorption dominated emi shielding effects in free standing and flexible films of poly(vinylidenefluoride)/graphene nanocomposite. Eur Polym J 99:437–444
Vyas MK, Chandra A (2016) Ion-electron-conducting polymer composites: promising electromagnetic interference shielding material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:18450–18461
Prateek Thakur VK, Gupta RK (2016) Recent progress on ferroelectric polymer-based nanocomposites for high energy density capacitors: synthesis, dielectric properties, and future aspects. Chem Rev 116(7):4260–4317
Song Y, Shen Y, Liu H, Lin Y, Li M, Nan CW (2012) Enhanced dielectric and ferroelectric properties induced by dopamine-modified BaTiO3 nanofibers in flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) nanocomposites. J Mater Chem 22:8063–8068
Tang H, Sodano HA (2013) Ultra high energy density nanocomposite capacitors with fast discharge using Ba0.2Sr0.8TiO3 nanowires. Nano Lett 13(4):1373–1379
Thomas P, Satapathy S, Dwarakanath K, Varma KBR (2010) Dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/CaCu3Ti4O12 nanocrystal composite thick films. Express Polym Lett 4(10):632–643
Bai Y, Cheng ZY, Bharti V, Xu HS, Zhang QM (2000) High-dielectric-constant ceramic-powder polymer composites. Appl Phys Lett 76:3804–3806
Olmos D, Martínez-Tarifa JM, González-Gaitano G, González-Benito J (2012) Uniformly dispersed submicrometre BaTiO3 particles in PS based composites. Morphology, structure and dielectric properties. Polym Test 31:1121–1130
Chen J, Email XY, Yang F, Fan Y, Jiang Y, Zhou Y, Duan Z (2017) Enhanced energy density of polymer composites filled with BaTiO3@Ag nanofibers for pulse power application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:8043–8050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6510-9
Luo B, Wang X, Tian E, Gong H, Zhao Q, Shen Z, Xu Y, Xiao X, Li L (2016) Dielectric enhancement in graphene/barium titanate nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:3340–3348
Liu ZD, Feng Y, Li WL (2015) High dielectric constant and low loss of polymeric dielectric composites filled by carbon nanotubes adhering BaTiO3 hybrid particles. RSC Adv 5:29017–29021
Dang ZM, Yao SH, Yuan JK, Bai J (2010) Tailored dielectric properties based on microstructure change in BaTiO3-carbon nanotube/polyvinylidene fluoride three-phase nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 114(31):13204–13209
Kingston H, Jassie L (1998) Microwave-enhanced chemistry. Fundamentals, sample preparation and applications. ACS Publishing, Washington DC
Mingos M, Baghurst D (1991) Applications of microwave dielectric heating effects to synthetic problems in chemistry. Chem Soc Rev 20:1–47
Gabriel C, Gabriel S, Grant E, Halstead B, Michael D, Mingos P (1998) Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave dielectric heating. Chem Soc Rev 27:213–224
Kappe C (2005) Microwaves in organic and medicinal chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Lewandowski A, Swiderska A (2004) New composite solid, electrolytes based on a polymer and ionic liquids. Solid State Ionics 169:21–24
Wang D, Zhou T, Zha JW, Zhao J, Shi CY, Dang ZM (2013) Functionalized graphene–BaTiO3/ferroelectric polymer nanodielectric composites with high permittivity, low dielectric loss, and low percolation threshold. J Mater Chem A 1:6162–6168
Barber P, Balasubramanian S, Anguchamy Y, Gong S, Wibowo A, Gao H, Ploehn HJ, Loye HCZ (2009) Polymer composite and nanocomposite dielectric materials for pulse power energy storage. Materials 2(4):1697–1733
Shalu Chaurasia SK, Singh RK, Chandra S (2013) Thermal stability, complexing behavior, and ionic transport of polymeric gel membranes based on polymer PVdF-HFP and ionic liquid, [BMIM][BF4]. J Phys Chem B 117:897–906
Brzozowski E, Castro MS (2003) Lowering the synthesis temperature of high-purity BaTiO3 powder by modification in the processing conditions. Thermochim Acta 398:123–129
Tsuzuku K, Couzi M (2012) In situ investigation of chemical reaction between BaCO3 and anatase or rutile TiO2. J Mater Sci 47:4481–4487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6310-9
Turton DA, Hunger J, Stoppa A, Hefter G, Thoman A, Walther M, Buchner R, Wynne K (2009) Dynamics of imidazolium ionic liquids from a combined dielectric relaxation and optical Kerr Effect Study: evidence for mesoscopic aggregation. J Am Chem Soc 131:11140–11146
Ahmad S (2009) Polymer electrolytes: characteristics and peculiarities. Ionics 15:309–321
Buscaglia MT, Bassoli M, Buscaglia V (2005) Solid-state synthesis of ultrafine BaTiO3 powders from nanocrystalline BaCO3 and TiO2. J Am Ceram Soc 88:2374–2379
Yoon DH (2006) Tetragonality of barium titanate powder for a ceramic capacitor application. J Ceram Process Res 7:343–354
Lee TT, Huang CY, Chang CY, Cheng IK, Hu CL, Lee CT, Fujimoto M (2012) Phase evolution of solid-state BaTiO3 powder prepared with the ultrafine BaCO3 and TiO2. J Mater Res 27(19):2495–2502
Miao R, Liu B, Zhy Z, Liu Y, Li J, Wang X, Li O (2008) PVDF-HFP-based porous polymer electrolyte membranes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 184(2):420–426
Stephan AH, Nahm KS, Kulandainathan MA, Ravi G, Wilson J (2006) Poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) (PVdF-HFP) based composite electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Eur Polym 42:1728–1734
Zhang B, Xu Y, Zheng Y, Dai L, Zhang M, Yang J, Chen Y, Chen X, Zhou JA (2011) Facile synthesis of polypyrrole/carbon nanotube composites with ultrathin, uniform and thickness-tunable polypyrrole shells. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(431):1–9
Lotnyk A, Senz S, Hesse D (2006) Formation of BaTiO3 thin films from (110) TiO2 rutile single crystals and BaCO3 by solid state reactions. Solid State Ionics 177:429–436
Du CH, Zhu BK, Xu YY (2006) The effects of quenching on the phase structure of vinylidene fluoride segments in PVdF-HFP copolymer and PVdF-HFP/PMMA blends. J Mater Sci 41:417–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-2182-6
Ataollahi N, Ahmad A, Hamzah H, Rahman MYA, Mohamed NS (2012) Preparation and characterization of PVDF-HFP/MG49 based polymer blend electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:6693–6703
Rajendran S, Kannan R, Mahendran O (2001) Ionic conductivity studies in poly(methylmethacrylate)–polyethylene oxide hybrid polymer electrolytes with lithium salts. J Power Sources 96(2):406–410
Romann T, Oll O, Pikma P, Lust E (2012) Abnormal infrared effects on bismuth thin film–EMImBF4 ionic liquid interface. Electrochem Commun 23:118–121
Katsyuba SA, Dyson PJ, Vandyukova EE, Chernova AV, Vidis A (2004) Molecular structure, vibrational spectra, and hydrogen bonding of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl-1H-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate. Helv Chim Acta 87:2556–2565
Bhadra S, Singha NK, Khastgir D (2009) Dielectric properties and EMI shielding efficiency of polyaniline and ethylene 1-octene based semi-conducting composites. Curr Appl Phys 9:396–403
Zhu J, Ji X, Yin M, Guo S, Shen J (2017) Poly (vinylidene fluoride) based percolative dielectrics with tunable coating of polydopamine on carbon nanotubes: toward high permittivity and low dielectric loss. Compos Sci Technol 144:79–88
Dakin TW (2006) Conduction and polarization mechanisms and trends in dielectric. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 22(5):11–28
Luo H, Zhang D, Jiang C, Yuan X, Chen C, Zhou K (2015) Improved dielectric properties and energy storage density of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanocomposite with hydantoin epoxy resin coated BaTiO3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8061–8069
Li Y, Huang X, Hu Z, Jiang P, Li S, Tanaka T (2011) Large dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity in poly(vinylidene fluoride)/barium titanate/silicon carbide three-phase nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4396–4403
Vyas MK, Chandra A (2018) Role of organic/inorganic salts and nanofillers in polymer nanocomposites: enhanced conduction, rheological, and thermal properties. J Mater Sci 53:4987–5003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1912-x
Ye H, Huang J, Xu JJ, Khalfan A, Greenbaumb SG (2007) Li ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquid/PVDF-HFP blends. J Electrochem Soc 154(11):1048–1057
Giroud N, Rouault H, Chainet E, Poignet JC (2009) Properties of BMIBF4–LiBF4 electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. ECS Trans 16(35):75–88
Rajendran S, Prabhu MR, Rani MU (2008) Ionic conduction in poly(vinyl chloride)/poly(ethyl methacrylate)-based polymer blend electrolytes complexed with different lithium salts. J Power Sources 180:880–883
Raghavan P, Zhao X, Manuel J, Chauhan GS, Ahn JH, Ryu HS, Ahn HJ, Kim KW, Nah C (2010) Electrochemical performance of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes incorporating ceramic fillers and room temperature ionic liquid. Electrochim Acta 55:1347–1354
Singh K, Ohlan A, Bakhshi AK, Dhawan SK (2010) Synthesis of conducting ferromagnetic nanocomposite with improved microwave absorption properties. Mater Chem Phys 119:201–207
Kar GP, Biswas S, Rohini R, Bose S (2015) Tailoring the dispersion of multiwall carbon nanotubes in co-continuous PVDF/ABS blends to design materials with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Chem A 3:7974–7985
Saini P, Arora M, Gupta G, Gupta BK, Singh VN, Choudhary V (2013) High permittivity polyaniline–barium titanate nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding response. Nanoscale 5:4330–4336
JiS Im, Kim JG, Lee SH, Lee YS (2010) Effective electromagnetic interference shielding by electrospun carbon fibers involving Fe2O3/BaTiO3/MWCNT additives. Mater Chem Phys 124:434–438
Guo AP, Zhang XJ, Qu JK, Wang SW, Zhu JQ, Wang GS, Guo L (2017) Improved microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding properties based on graphene–barium titanate and polyvinylidene fluoride with varying content. Mater Chem Front 1:2519–2526
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Prof. S. A. Hashmi and Prof. S. Murugavel, University of Delhi, for, respectively, providing transport number and furnace facility. We also gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the University of Delhi, India, through the R&D Grant and USIC, University of Delhi, for providing instrumentation facility. One of the authors (MKV) is grateful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for providing a Senior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas, M.K., Chandra, A. Synergistic effect of conducting and insulating fillers in polymer nanocomposite films for attenuation of X-band. J Mater Sci 54, 1304–1325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2894-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2894-z