Abstract
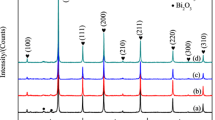
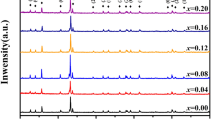
Different components of La0.7−x Ho x Sr0.3MnO3 (LHSMO, x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) ceramics were fabricated by Plasma-Activated Sintering (PAS), so as to study the correlation between the contents of Ho3+ and the structural, electrical, magnetic properties. XRD and SEM confirmed that LHSMO ceramics prepared by PAS exhibited high-purity phase and dense microstructure. The measurement of electrical resistivity showed that the resistivity of LHSMO ceramics increased, and the metal–insulator transition temperature decreased with the increasing Ho-doping content. The resistivity data were then fitted using various empirical equations, and the conduction mechanism of LHSMO ceramics was found to be in accord with the electron–magnon scattering process in the low-temperature region and the small polaron hopping model in the high-temperature region. Lastly, we calculated the values of magnetoresistance of the LHSMO ceramics, which increased with increasing Ho-doping content, from 3.5% for x = 0 to 14.6% for x = 0.3. Therefore, the doping of Ho3+ into La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 can effectively enhance the low-field magnetoresistance effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen M, Bibes M, Barthélémy A, Contour JP, Anane A, Lemaı̂tre A, Fert A (2003) Nearly total spin polarization in La2/3Sr1/3MnO3 from tunneling experiments. Appl Phys Lett 82:233–235
Haghiri-Gosnet AM, Renard JP (2003) CMR manganites: physics, thin films and devices. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R127
Tokura Y, Tomioka Y (1999) Colossal magnetoresistive manganites. J Magn Magn Mater 200:1–23
Hwang HY, Cheong SW, Ong NP, Batlogg B (1996) Spin-polarized intergrain tunneling in La2/3Sr1/3MnO3. Phys Rev Lett 77:2041–2044
Balcells L (1998) Magnetic surface anisotropy and low-temperature magnetoresistance in manganese perovskites. J Phys Condens Matter 10:1883
Tokura Y (2006) Critical features of colossal magnetoresistive manganites. Rep Prog Phys 69:797
Coey JMD, Viret MV, Molnar SV (2009) Mixed-valence manganites. Adv Phys 58:571–697
Salamon MB, Jaime M (2001) The physics of manganites: structure and transport. Rev Mod Phys 73:583
Siwach PK, Singh HK, Srivastava ON (2008) Low field magnetotransport in manganites. J Phys Condens Matter 20:273201
Mitra C, Raychaudhuri P, Dhar SK, Nigam AK, Pinto R, Pattalwar SM (1999) Evolution of transport and magnetic properties with dysprosium doping in La0.7−xDyxSr0.3MnO3 (x = 0–0.4). J Magn Magn Mater 192:130–136
Roy B, Poddar A, Das A (2006) Electrical transport properties and magnetic cluster glass behavior of Nd0.7Sr0.3MnO3 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 10:104318
Chen Y, Ueland BG, Lynn JW, Bychkov GL, Barilo SN, Mukovskii YM (2008) Polaron formation in the optimally doped ferromagnetic manganites La0.7Ba0.3MnO3 and La0.7Ba0.3MnO3. Phys Rev B 78:212301
Xu LS, Chen LL, Fan JY, Bärner K, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Pi L, Zhang YH, Shi DN (2016) Room-temperature large magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior in La0.6Dy0.1Sr0.3MnO3. Ceram Int 42:8234–8239
Hwang HY, Cheong SW, Radaelli PG, Marezio M, Batlogg B (1995) Lattice effects on the magnetoresistance in doped LaMnO3. Phys Rev Lett 75:914–917
Veverka P, Kaman O, Knížek K, Novák PI, Maryško M, Jirák Z (2016) Magnetic properties of rare-earth-doped La0.7Sr0.3MnO3. J Phys Condens Matter 29:035803
Sun BZ, Zhou SL, Shen T (2013) Effects of Ho-doping on crystal structure and microstructure of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 ceramics. Mater Sci Forum 745–746:96–101
Raychaudhuri P, Nath TK, Sinha P, Mitra C, Nigam AK, Dhar SK, Pinto R (1997) The effect of holmium doping on the magnetic and transport properties of La0.7-xHoxSr0.3MnO3 (0 ≤ x≤0.4). J Phys Condens Matter 9:10919–10927
Aparnadevi M, Mahendiran R (2013) Electrical detection of spin reorientation transition in ferromagnetic La0.4Sm0.3Sr0.3MnO3. J Appl Phys 113:17D719
Hammouche A (1991) Electrocatalytic properties and nonstoichiometry of the high temperature air electrode La1-xSrxMnO3. J Electrochem Soc 138:1212–1216
Wang SW, Chena LD, Kangb YS, Niinob M, Hiraia T (2000) Effect of plasma activated sintering (PAS) parameters on densification of copper powder. Mater Res Bull 35:619–628
Kamiya A (1998) Effect of plasma activated sintering (PAS) parameters on densification of copper powder. J Mater Sci Lett 17:49–51
Yamazaki K, Risbud SH, Aoyama H, Shoda K (1996) PAS (Plasma Activated Sintering) transient sintering process control for rapid consolidation of powders. J Mater Process Technol 56:955–965
Munir ZA, Anselmitamburini U, Ohyanagi M (2006) The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. J Mater Sci 41:763–777. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/26/6/064203/meta
Zener C (1951) Interaction between the d-Shells in the transition metals. Phys Rev 81:440–444
Anderson PW, Hasegawa H (1955) Considerations on double exchange. Phys Rev 100:675–681
Zhao S, Yue XJ, Liu X (2017) Tuning room temperature Tp and MR of La1-y(Cay-xSrx)MnO3 polycrystalline ceramics by Sr doping. Ceram Int 43:4594–4598
Millis AJ, Littlewood PB, Shraiman BI (1995) Double exchange alone does not explain the resistivity of La1-xSrxMnO3. Phys Rev Lett 74:5144
Young SL, Chen HZ, Ho YW, Kao HCI (2012) Comparison of the magnetization behaviors in perovskite compounds La0.7-xLnxPb0.3MnO3 (Ln = Pr and Sm). Int J Mod Phys B 19:563–568
Zhao S, Yue XJ, Yan YZ, Liu X (2016) Effects of Ag addition on the structural and electrical properties of La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 ceramics. Adv Appl Ceram 116:180–184
Gennes PGD (2014) Effects of double exchange in magnetic crystals. Phys Rev 118:141–154
Schiffer P, Ramirez AP, Bao W, Cheong SW (1995) Low temperature magnetoresistance and the magnetic phase diagram of La1-xCaxMnO3. Phys Rev Lett 75:3336
Snyder GJ, Hiskes R, Dicarolis SA, Beasley MR, Geballe TH (1996) Low temperature magnetoresistance and the magnetic phase diagram of La1-xCaxMnO3. Phys Rev B 53:14434–14444
Yue XJ, Zhan YH, Liu X, Gu G, Wang QS, Yin XP (2015) Enhanced electrical properties of La0.7(Ca0.2Sr0.1)MnO3 polycrystalline composites with Ag addition. J Low Temp Phys 180:356–362
Banerjee A, Pal S, Rozenberg E, Chaudhuri BK (2001) Adiabatic and non-adiabatic small-polaron hopping conduction in La1-xPbxMnO3+δ (0.0 ≤ x≤0.5)-type oxides above the metal–semiconductor transition. J Phys Condens Matter 13:9489–9504
Yin XP, Liu X, Yan YZ, Chen QM (2014) Preparation of La0.67Ca0.33MnO3: Agx polycrystalline by sol–gel method. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 70:361–365
Jung WH (1998) Evaluation of Mott’s parameters for hopping conduction in La0.67Ca0.33MnO3 above Tc. J Mater Sci Lett 17:1317–1319
Khan W, Naqvi AH, Gupta M, Husain S, Kumar R (2011) Small polaron hopping conduction mechanism in Fe doped LaMnO3. J Chem Phys 135:054501
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51272195, 51521001), 111 project (B13035), International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Hubei Province (2016AHB008) and Nature Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2015CFB724, 2016CFA006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H.X., Wang, C.B., Wu, L. et al. Effect of Ho-doping on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 ceramics prepared by Plasma-Activated Sintering. J Mater Sci 53, 2375–2382 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1684-3