Abstract
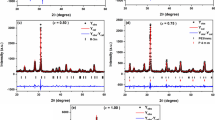
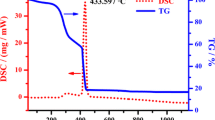
A one-pot polymerization method using citric acid and glucose for the synthesis of nano-crystalline BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 is described. Phase evolution and the development of the crystallite size during decomposition of the (Ba,Fe,Nb)-gel were examined up to 1100 °C. Calcination at 850 °C of the gel leads to a phase-pure nano-crystalline BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 powder with a crystallite size of 28 nm. The shrinkage of compacted powders starts at 900 °C. Dense ceramic bodies (relative density ≥ 90%) can be obtained either after conventional sintering above 1250 °C for 1 h or after two-step sintering at 1200 °C. Depending on the sintering regime, the ceramics have average grain sizes between 0.3 and 52 µm. The optical band gap of the nano-sized powder is 2.75(4) eV and decreases to 2.59(2) eV after sintering. Magnetic measurements of ceramics reveal a Néel temperature of about 23 K. A weak spontaneous magnetization might be due to the presence of a secondary phase not detectable by XRD. Dielectric measurements show that the permittivity values increase with decreasing frequency and rising temperature. The highest permittivity values of 10.6 × 104 (RT, 1 kHz) were reached after sintering at 1350 °C for 1 h. Tan δ values of all samples show a maximum at 1–2 MHz at RT. The frequency dependence of the impedance can be well described using a single RC-circuit.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Homes CC, Vogt T, Shapiro SM, Wakimoto S, Ramirez AP (2001) Optical response of high-dielectric-constant perovskite-related oxide. Science 293:673–676
Chung SY, Kim ID, Kang SJ (2004) Strong nonlinear current–voltage behaviour in perovskite-derivative calcium copper titanate. Nat Mater 3:774–778
Haertling GH (1999) Ferroelectric ceramics: history and technology. J Am Ceram Soc 82:797–818
Ke S, Fan H, Huang H (2009) Dielectric relaxation in A2FeNbO6 (A = Ba, Sr, and Ca) perovskite ceramics. J Electroceram 22:252–256
Patel PK, Yadav KL, Singh H, Yadav AK (2014) Origin of giant dielectric constant and magnetodielectric study in Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 nanoceramics. J Alloys Compd 591:224–229
Wang Z, Chen XM, Ni L, Liu XQ (2007) Dielectric abnormities of complex perovskite Ba(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 ceramics over broad temperature and frequency range. Appl Phys Lett 90:022904
Ke S, Lin P, Huang H, Fan H, Zeng X (2013) Mean-Field Approach to Dielectric Relaxation in Giant Dielectric Constant Perovskite Ceramics, J Ceram 2013:795827
Bochenek D, Niemiec P, Szafraniak-Wiza I, Adamczyk M, Skulski R (2015) Preparation and dielectric properties of the lead-free BaFe1/2Nb1/2O3 ceramics obtained from mechanically triggered powder. Eur Phys J B 88:277
Kantha P, Pisitpipathsin N, Pengpat K, Rujijanagul G, Guo R, Bhalla AS (2011) Microstructure and electrical properties of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 doped with GeO2 (1–5 wt%). Ferroelectrics 425:27–38
Charoenthai N, Traiphol R (2011) Progress in the synthesis of Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 ceramics: a versatile co-precipitation method. J Ceram Process Res 12:191–194
Raevski IP, Kuropatkina SA, Kubrin SP, Raevskaya SI, Titov VV, Sarychev DA, Malitskaya MA, Bogatin AS, Zakharchenko IN (2009) Dielectric and Mössbauer studies of high-permittivity BaFe1/2Nb1/2O3 ceramics with cubic and monoclinic perovskite structures. Ferroelectrics 379:48–54
Saha S, Sinha TP (2002) Low-temperature scaling behavior of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3. Phys Rev B 65:134103
Chung CY, Chang YH, Chen GJ, Chai YL (2005) Preparation, structure and ferroelectric properties of Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 powders by sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 284:100–107
Tezuka K, Henmi K, Hinutsa Y (2000) Magnetic susceptibilities and mössbauer spectra of perovskites A2FeNbO6 (A = Sr, Ba). J Solid State Chem 154:591–597
Galasso F, Darby W (1962) Ordering of the octahedrally coordinated cation position in the perovskite structure. J Phys Chem 66:131–132
Bhagat S, Prasad K (2010) Structural and impedance spectroscopy analysis of Ba(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 ceramic. Phys Status Solidi A 207:1232–1239
Kar SK, Kumar P (2013) Permittivity and modulus spectroscopic study of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 ceramics. Process Appl Ceram 7:181–187
Kar SK, Kumar P (2013) Structural, morphological and dielectric study of Ba(FeNb)0.5O3 ceramics synthesized by microwave processing technique. J Phys Chem Solids 74:1408–1413
Raevski IP, Prosandeev SA, Bogatin AS, Malitskaya MA, Jastrabik L (2003) High dielectric permittivity in AFe1/2B1/2O3 nonferroelectric perovskite ceramics (A = Ba, Sr, Ca; B = Nb, Ta, Sb). J Appl Phys 93:4130–4136
Voorhoeve RJH, Trimble LE, Khattak CP (1974) Extrapolation of perovskite-like catalysts: Ba2CoWO6 and Ba2FeNbO3 in NO reduction and CO oxidation. Mater Res Bull 9:655–666
Chung WC, Pan KL, Lee HM, Chang MB (2014) Dry reforming of methane with dielectric barrier discharge and ferroelectric packed-bed reactors. Energy Fuels 28:7621–7631
Pan KL, Chung WC, Chang MB (2014) Dry reforming of CH4 with CO2 to generate syngas by combined plasma catalysis. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 42:3809–3818
Rama N, Phillip JB, Opel M, Chandrasekaran K, Sankaranarayanan V, Gross R, Rao MSR (2004) Study of magnetic properties of A2B´NbO6 (A = Ba, Sr, BaSr; and B´ = Fe and Mn) double perovskites. J Appl Phys 95:7528–7530
Intatha U, Eitssayeam S, Tunkasiri T (2008) Giant dielectric behavior of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 perovskite ceramic. Int J Mod Phys 22:4717–4723
Sun XH, Wang CC, Wang GJ, Lei CM, Li T, Mei JY, Cui YM (2012) Relationship between the dielectric properties and the conductivity of Ba2FeNbO6. J Electroceram 29:187–191
Battle PD, Gibb TC, Herod AJ, Kim SH, Munns PH (1995) Investigation of magnetic frustration in A2FeMO6, (A = Ca, Sr, Ba; M = Nb, Ta, Sb) by magnetometry and mossbauer spectroscopy. J Mater Chem 5:865–870
Wang Z, Wen YF, Li HJ, Fang MR, Wang C, Pu YP (2016) Excellent stability and low dielectric loss of Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 synthesized by a solution precipitation method. J Alloys Compd 656:431–438
Charoenthai N, Traiphol R, Rujijanagul G (2008) Microwave synthesis of barium iron niobate and dielectric properties. Mater Lett 62:4446–4448
Jha AK, Prasad K (2014) Green synthesis and characterization of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 nanoparticles. J Chin Adv Mater Sci 2:294–302
Program WinXPOW v2.11, Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, 2004
Rodriguez-Carvajal J (1993) Recent advances in magnetic structure determination neutron powder diffraction. Phys B 192:55–69
Köferstein R (2014) Synthesis, phase evolution and properties of phase-pure nanocrystalline BiFeO3 prepared by a starch-based combustion method. J Alloys Compd 590:324–330
Deshpande K, Mukasyan A, Varma A (2004) Direct synthesis of iron oxide nanopowders by the combustion approach: reaction mechanism and properties. Chem Mater 16:4896–4904
Hirata Y, Hara A, Aksay IA (2009) Thermodynamics of densification of powder compact. Ceram Int 35:2667–2674
Köferstein R, Walther T, Hesse D, Ebbinghaus SG (2013) Preparation and characterization of nanosized magnesium ferrite powders by a starch-gel process and corresponding ceramics. J Mater Sci 48:6509–6518. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7447-x
Eitssayeam S, Intatha U, Pengpat K, Tunkasiri T (2006) Preparation and characterization of barium iron niobate (BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3) ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 6:316–318
Mendelson MI (1969) Average grain size in polycrystalline ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 52:443–446
Kubelka P, Munk F (1931) Ein beitrag zur optik der farbanstriche. Z Techn Phys 11:593–601
Kortüm G, Vogel J (1958) Die Theorie der diffusen Reflexion von Licht an pulverförmigen Stoffen. Z Phys Chem 18:110–122
Patel PK, Yadav KL, Kaur G (2014) Reduced dielectric loss in Ba0.95Sr0.05(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 thin film grown by pulsed laser deposition. RSC Adv 4:28056–28061
Köferstein R, Buttlar T, Ebbinghaus SG (2014) Investigations on Bi25FeO40 powders synthesized by hydrothermal and combustion-like processes. J Solid State Chem 217:50–56
Kar SK, Swain S, Kumar P (2015) High dielectric constant and low optical band gap studies of La-modified Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 ceramics. Mater Chem Phys 155:171–177
Yu J, Tang S, Zhai L, Shi Y, Du Y (2009) Synthesis and magnetic properties of single-crystalline BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. Phys B 404:4253–4256
Shafie MSE, Hashim M, Ismail I, Kanagesan S, Fadzidah MI, Idza IR, Hajalilou A, Sabbaghizadeh R (2014) Magnetic M-H loops family characteristics in the microstructure evolution of BaFe12O19. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 25:3787–3794
Raevski IP, Titov VV, Malitskaya MA, Eremin EV, Kubrin SP, Blazhevich AV, Chen H, Chou CC, Raevskaya SI, Zakharchenko IN, Sarychev DA, Shevtsova SI (2014) Studies of ferroelectric and magnetic phase transitions in multiferroic PbFe0.5Ta0.5O3–PbTiO3 solid solution ceramics. J Mater Sci 49:6459–6466. doi:10.1080/00150193.2015.995009
Puri M, Bahel S, Raevski IP, Narang SB (2016) Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (Pb1-xCax)(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 solid solution ceramics. J Magnet Magnet Mater 407:195–200
Amonpattaratkit P, Jantaratana P, Ananta S (2015) Influences of PZT addition on phase formation and magnetic properties of perovskite Pb(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3-based ceramics. J Magnet Magnet Mater 389:95–100
Intatha U, Eitssayeam S, Pengpat K, MacKenzie KJD, Tunkasiri T (2007) Dielectric properties of low temperature sintered LiF doped BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3. Mater Lett 61:196–200
Oehler F, Langhammer HT, Ebbinghaus SG (2017) Preparation and dielectric properties of CaTaO2N and SrNbO2N ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:2129–2136
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. E. Pippel (Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, Halle/Saale) for the TEM images. Financial support by the German Research Foundation within the Collaborative Research Centre (SFB 762) Functionality of Oxide Interfaces is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köferstein, R., Oehler, F. & Ebbinghaus, S.G. Magnetic, optical, dielectric, and sintering properties of nano-crystalline BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 synthesized by a polymerization method. J Mater Sci 53, 1024–1034 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1609-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1609-1