Abstract
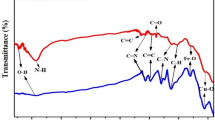
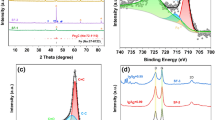
Novel porous ternary nanocomposite systems containing reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/polyaniline (PANI)/cuprous oxide (Cu2O) were prepared via one-step in situ redox method. The RGO/PANI/Cu2O nanocomposites present a flower-like structure with an average size of 2.0 μm in diameter. The morphologies and properties of the products can be controlled by adjusting the molar ratios of aniline to Cu2+. When the molar ratio of aniline to Cu2+ is 1:1, the product exhibits excellent microwave absorption property in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz. It can be seen that the maximum reflection loss (RL) of the ternary composite is up to −52.8 dB at 2.7 GHz with a thickness of only 2 mm, and the absorption bandwidth corresponding to −10 dB (90% of EM wave absorption) is 13.2 GHz. The microwave absorption property of ternary RGO/PANI/Cu2O composite is significantly improved due to its special flower-like porous structure, dielectric loss property and well impedance matching characteristics, which is 8.12 times than that of pure RGO and 5.28 times than that of pure PANI. Therefore, our study paves a new way to prepare the promising lightweight and high-performance composite materials combined with the characteristics of three components for electromagnetic absorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eun SW, Choi WH, Jang HK, Shin JH, Kim JB, Kim CG (2015) Effect of delamination on the electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of radar absorbing structures. Compos Sci Technol 116:18–25
Micheli D, Vricella A, Pastore R, Marchetti M (2014) Synthesis and electromagnetic characterization of frequency selective radar absorbing materials using carbon nanopowders. Carbon 77:756–774
Qu B, Zhu CL, Li CY, Zhang XT, Chen YJ (2016) Coupling hollow Fe3O4–Fe nanoparticles with graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:3730–3735
Cordova D, Toledo P, Klimach H, Bampi S, Fabris E (2016) EMI resisting MOSFET-only voltage reference based on ZTC condition. Analog Integr Circuits Process 89:45–59
Meshram M, Agrawal NK, Sinha B, Misra P (2004) Characterization of M-type barium hexagonal ferrite-based wide band microwave absorber. J Magn Magn Mater 271:207–214
Feng Y, Qiu T, Shen C (2007) Absorbing properties and structural design of microwave absorbers based on carbonyl iron and barium ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 318:8–13
Ali K, Iqbal J, Jan T, Ahmad I, Wan D, Bahadur A et al (2017) Synthesis of CuFe2O4–ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Alloys Compd 705:559–565
Zhang H, Hong M, Chen P, Xie A, Shen Y (2016) 3D and ternary rGO/MCNTs/Fe3O4 composite hydrogels: synthesis, characterization and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Alloys Compd 665:381–387
Han M, Yin X, Kong L, Li M, Duan W, Zhang L et al (2014) Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem A 2:16403–16409
Wang M, Huang J, Tong Z, Li W, Chen J (2013) Reduced graphene oxide–cuprous oxide composite via facial deposition for photocatalytic dye-degradation. J Alloys Compd 568:26–35
Nguyen TT, Shim J-J (2015) Rapid one-step synthesis and electrochemical properties of graphene/carbon nanotubes/MnO2 composites. Synth Metals 199:276–279
Liu P, Huang Y, Wang L, Zong M, Zhang W (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis of reduced graphene oxide–Co3O4 composites and the excellent microwave electromagnetic properties. Mater Lett 107:166–169
Wang T, Li Y, Wang L, Liu C, Geng S, Jia X et al (2015) Synthesis of graphene/α-Fe2O3 composites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. RSC Adv 5:60114–60120
Choi J, Jung HT (2015) A new triple-layered composite for high-performance broadband microwave absorption. Compos Struct 122:166–171
Ciric-Marjanovic G (2013) Recent advances in polyaniline composites with metals, metalloids and nonmetals. Synth Metals 170:31–56
Marins JA, Soares BG, Fraga M, Muller D, Barra GMO (2014) Self-supported bacterial cellulose polyaniline conducting membrane as electromagnetic interference shielding material: effect of the oxidizing agent. Cellulose 21:1409–1418
Al-Ghamdi AA, Al-Hartomy OA, Al-Solamy F, Al-Hazmi F, Al-Ghamdi AA, El-Mossalamy EH et al (2014) On the prospects of conducting polyaniline/natural rubber composites for electromagnetic shielding effectiveness applications. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 27:765–782
Jazirehpour M, Ebrahimi SAS (2015) Effect of aspect ratio on dielectric, magnetic, percolative and microwave absorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 638:188–196
Tian CH, Du YC, Xu P, Qiang R, Wang Y, Ding D et al (2015) Constructing uniform core-shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20090–20099
Yu HL, Wang TS, Wen B, Lu MM, Xu Z, Zhu CL et al (2012) Graphene/polyaniline nanorod arrays: synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J Mater Chem 22:21679–21685
Wang L, Huang Y, Huang HJ (2014) N-doped graphene@polyaniline nanorod arrays hierarchical structures: synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties. Mater Lett 124:89–92
Susman MD, Feldman Y, Vaskevich A, Rubinstein I (2014) Chemical deposition of Cu2O nanocrystals with precise morphology control. ACS Nano 8:162–174
Kuang M, Li TT, Chen H, Zhang SM, Zhang LL, Zhang YX (2015) Hierarchical Cu2O/CuO/Co3O4 core-shell nanowires: synthesis and electrochemical properties. Nanotechnology 26:304002–304010
Chakravarty A, Bhowmik K, Mukherjee A, De G (2015) Cu2O nanoparticles anchored on amine-functionalized graphite nanosheet: a potential reusable catalyst. Langmuir 31:5210–5219
Lee S, Oh J, Kim D, Piao Y (2016) A sensitive electrochemical sensor using an iron oxide/graphene composite for the simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. Talanta 160:528–536
Kim AY, Kim MK, Cho K, Woo JY, Lee Y, Han SH et al (2016) One-step catalytic synthesis of CuO/Cu2O in a graphitized porous C matrix derived from the Cu-based metal organic framework for Li- and Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:19514–19523
Huo HH, Guo CY, Li GL, Han X, Xu CL (2014) Reticular-vein-like Cu@Cu2O/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. RSC Adv 4:20459–20465
Ro D-K, Paradise EM, Ouellet M, Fisher KJ, Newman KL, Ndungu JM et al (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440:940–943
Fan ZJ, Luo GH, Zhang ZF, Zhou L, Wei F (2006) Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polymer composites. Mater Sci Eng B Solid State Mater Adv Technol 132:85–89
Zhang YH, Zhang N, Tang ZR, Xu YJ (2012) Graphene transforms wide band gap ZnS to a visible light photocatalyst. The new role of graphene as a macromolecular photosensitizer. ACS Nano 6:9777–9789
Wang K, Dong X, Zhao C, Qian X, Xu Y (2015) Facile synthesis of Cu2O/CuO/RGO nanocomposite and its superior cyclability in supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 152:433–442
Xi X, Liu R, Huang T, Xu Y, Wu D (2016) Strongly coupled polyaniline/graphene hybrids with much enhanced capacitance performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 483:34–40
Wu Q, Chen M, Wang S, Zhang X, Huan L, Diao G (2016) Preparation of sandwich-like ternary hierarchical nanosheets manganese dioxide/polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide as electrode material for supercapacitor. Chem Eng J 304:29–38
Miao J, Xie A, Li S, Huang F, Cao J, Shen Y (2016) A novel reducing graphene/polyaniline/cuprous oxide composite hydrogel with unexpected photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Congo red. Appl Surf Sci 360:594–600
Wang G, Zhuo S, Xing W (2012) Graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite as counter electrode of dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater Lett 69:27–29
Niu H, Zhang S, Ma Q, Qin S, Wan L, Xu J et al (2013) Dye-sensitized solar cells based on flower-shaped α-Fe2O3 as a photoanode and reduced graphene oxide–polyaniline composite as a counter electrode. RSC Adv 3:17228–17235
Li Y, Yang N, Du TT, Wang XZ, Chen W (2016) Transformation of graphene oxide by chlorination and chloramination: implications for environmental transport and fate. Water Res 103:416–423
Frost RL, Cejka J, Ayoko G (2008) Raman spectroscopic study of the uranyl phosphate minerals phosphuranylite and yingjiangite. J Raman Spectrosc 39:495–502
Ding B, Kimura E, Sato T, Fujita S, Shiratori S (2004) Fabrication of blend biodegradable nanofibrous nonwoven mats via multi-jet electrospinning. Polymer 45:1895–1902
Yec CC, Zeng HC (2012) Synthetic architecture of multiple core-shell and yolk-shell structures of (Cu2O@)(n)Cu2O (n = 1-4) with centricity and eccentricity. Chem Mater 24:1917–1929
Qiu W, Kang YL, Lei ZK, Qin QH, Li Q, Wang QA (2010) Experimental study of the Raman strain rosette based on the carbon nanotube strain sensor. J Raman Spectrosc 41:1216–1220
Yamamoto M, Wang ST, Ni MY, Lin YF, Li SL, Aikawa S et al (2014) Strong enhancement of raman scattering from a bulk-inactive vibrational mode in few-layer MoTe2. ACS Nano 8:3895–3903
Ghanbari K, Moloudi M (2016) Flower-like ZnO decorated polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Anal Biochem 512:91–102
Liu P, Huang JY, Sanchez DVP, Schwartzman D, Lee SH, Yun M (2016) High yield two-dimensional (2-D) polyaniline layer and its application in detection of B-type natriuretic peptide in human serum. Sens Actuator B Chem 230:184–190
Cao J, Li JC, Liu L, Xie AJ, Li SK, Qiu LG et al (2014) One-pot synthesis of novel Fe3O4/Cu2O/PANI nanocomposites as absorbents in water treatment. J Mater Chem A 2:7953–7959
Mishra M, Singh AP, Gupta V, Chandra A, Dhawan SK (2016) Tunable EMI shielding effectiveness using new exotic carbon: polymer composites. J Alloys Compd 688:399–403
Wang L, Xing H, Gao S, Ji X, Shen Z (2017) Porous flower-like NiO@ graphene composites with superior microwave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C 5:2005–2014
Cao MS, Song WL, Hou ZL, Wen B, Yuan J (2010) The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48:788–796
Huang YH, Huang XY, Schadler LS, He JL, Jiang PK (2016) Core@double-shell structured nanocomposites: a route to high dielectric constant and low loss material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:25496–25507
Fang MS, Shi FH, Chen YH (2016) Unidirectional all-optical absorption switch based on optical Tamm state in nonlinear plasmonic waveguide. Plasmonics 11:197–203
Liu PB, Huang Y, Zhang X (2014) Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on graphene-polyaniline: synthesis, characterization and their excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J Alloys Compd 596:25–31
Han MK, Yin XW, Kong L, Li M, Duan WY, Zhang LT et al (2014) Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem A 2:16403–16409
Feng W, Wang YM, Chen JC, Wang L, Guo LX, Ouyang JH et al (2016) Reduced graphene oxide decorated with in situ growing ZnO nanocrystals: facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 108:52–60
Duong PHH, Nunes SP, Chung TS (2016) Dual-skinned polyamide/poly(vinylidene fluoride)/cellulose acetate membranes with embedded woven. J Membr Sci 520:840–849
Chen TT, Deng F, Zhu J, Chen CF, Sun GB, Ma SL et al (2012) Hexagonal and cubic Ni nanocrystals grown on graphene: phase-controlled synthesis, characterization and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. J Mater Chem 22:15190–15197
Kong L, Yin X, Zhang Y, Yuan X, Li Q, Ye F et al (2013) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide modified by maghemite colloidal nanoparticle clusters. J Phys Chem C 117:19701–19711
Hosseini SH, Mohseni SH, Asadnia A, Kerdari H (2011) Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of polyaniline/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite. J Alloys Compd 509:4682–4687
Liu XY, Lv YL, Zhuang QX, Li YM, Zhang SD, Lan FX (2016) Polybenzobisoxazoles-based nanocomposites with high microwave absorption performance and excellent thermal stability. Polymer 99:605–613
Luo JH, Shen P, Yao W, Jiang CF, Xu JG (2016) Synthesis, characterization, and microwave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide/strontium ferrite/polyaniline nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:141–154
He Z, Qi SH, Zhong XL, Ma H, Wang P, Qiu H (2015) Preparation and microwave-absorbing properties of silver-coated strontium ferrite with polyaniline via in situ polymerization. J Alloys Compd 621:194–200
Micheli D, Apollo C, Pastore R, Marchetti M (2010) X-Band microwave characterization of carbon-based nanocomposite material, absorption capability comparison and RAS design simulation. Compos Sci Technol 70:400–409
Wu F, Xie A, Sun M, Wang Y, Wang M (2015) Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) modified spongelike polypyrrole (PPy) aerogel for excellent electromagnetic absorption. J Mater Chem A 3:14358–14369
Guo J, Wang X, Miao P, Liao X, Zhang W, Shi B (2012) One-step seeding growth of controllable Ag@Ni core-shell nanoparticles on skin collagen fiber with introduction of plant tannin and their application in high-performance microwave absorption. J Mater Chem 22:11933–11942
Liu P, Yao Z, Zhou J, Yang Z, Kong LB (2016) Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J Mater Chem C 4:9738–9749
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (21671001, 21371003 and 51402002), Lab for Clean Energy and Green Catalysis of Anhui University and Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Environment-Friendly Polymer Materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, P., Miao, J., Cao, J. et al. Facile synthesis and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties of flower-like porous RGO/PANI/Cu2O nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 52, 13078–13090 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1418-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1418-6