Abstract
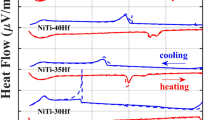
NiTiHf alloys exhibit remarkable shape memory and pseudoelastic properties that are of fundamental interest to a growing number of industries. In this study, differential scanning calorimetry and isothermal compression tests have revealed that the 51Ni–29Ti–20Hf alloy has useful shape memory properties that include a wide range of transformation temperatures as well as highly stable pseudoelastic behavior. These properties are governed by short-term aging conditions, which may be tailored to control transformation temperatures while giving rise to exceptionally high austenite yield strengths which aid transformation stability. The yield strength of the austenite phase can reach 2.1 GPa by aging for 3 h at 500 °C, while aging for 3 h at 700 °C produced an alloy with an austenite finish temperature (A f ) of 146 °C. High-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy has revealed a new precipitate phase, H′-phase, under the homogenized and extruded conditions and under the 500 °C-3-h-aged condition, but only the previously identified H-phase precipitate was observed after aging at temperatures of 600 and 700 °C for 3 h. Finally, dislocation analysis indicated that plastic deformation of the austenite phase occurred by 〈100〉 type slip, similar to that observed in binary NiTi.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Ren X (2005) Physical metallurgy of TiNi-based shape memory alloys. Prog Mater Sci 50:511–678
Van Humbeeck J (1999) High temperature shape memory alloys. J Eng Mater 121:5–8
Firstov GS, Van Humbeeck J, Koval YN (2006) High temperature shape memory alloys problems and prospects. J Int Mater Syst 17:1041–1047
Noebe R, Biles T, Padula S (2007) NiTi-based high-temperature shape-memory alloys. In: Soboyejo W, Srivastan T (eds) Advanced structural materials: properties, design optimization, and applications. CRC Press, London, pp 145–186
Ma J, Karaman I, Noebe RD (2010) High temperature shape memory alloys. Int Mater Rev 55:257–315
AbuJudom II DN, Thoma PE, Kao M, Angst DR (1992) High transformation temperature shape memory alloy. USA Patent
Karaca HE, Acar E, Tobe H, Saghaian SM (2014) NiTiHf-based shape memory alloys. Mater Sci Technol 30(13a):1530–1544
Han XD, Zou W, Jin S, Zhang Z, Yang D (1995) The studies of martensitic transformations in a TiNiHf15 alloy. Scr Mater 32:1441–1446
Wang YQ, Zheng YF, Cai W, Zhao LC (1999) The tensile behavior of Ti36Ni49Hf15 high temperature shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 40:1327–1331
Meng XL, Cai W, Zheng YF, Tong YX, Zhao LC, Zhou LM (2002) Stress-induced martensitic transformation behavior of a Ti–Ni–Hf high temperature shape memory alloy. Mater Lett 55:111–115
Otsuka K, Oda K, Piao M (1993) The shape memory effect in a Ti50Pd50 alloy. Scr Metall 29:1355–1358
Golberg D, Xu Y, Murakami Y, Morito S, Otsuka K, Ueki T, Horikawa H (1994) Characteristics of Ti50Pd30Ni20 high-temperature shape memory alloy. Scr Metall 30:1349–1354
Shimizu S, Xu Y, Okunishi E, Tanaka S, Otsuka K, Mitose K (1998) Improvement of shape memory characteristics by precipitation-hardening of TiPdNi alloys. Mater Lett 34:23–29
Angst D, Thoma P, Kao M (1995) The effect of hafnium content on the transformation temperatures of Ni49Ti51-xHfx shape memory alloys. J Phys IV 5:C8–747
Olier P, Alliages À (1996) Ti-Ni shape memory alloys: effects of the fabrication route, the oxygen content and the zirconium or hafnium additions on the metallurgical characteristics and the thermomechanical properties. PhD Dissertation
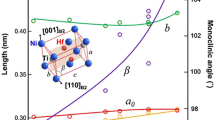
Han XD, Wang R, Zhang Z, Yang DZ (1998) A new precipitate phase in a TiNiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 46:273–281
Meng XL, Cai W, Chen F, Zhao LC (2006) Effect of aging on martensitic transformation and microstructure in Ni-rich TiNiHf shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 54:1599–1604
Meng XL, Cai W, Zheng YF, Zhao LC (2006) Phase transformation and precipitation in aged Ti–Ni–Hf high-temperature shape memory alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 666:438–440
Bigelow GS, Garg A, Padula SA II, Gaydosh DJ, Noebe RD (2011) Load-biased shape-memory and superelastic properties of a precipitation strengthened high-temperature Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20 alloy. Scr Mater 64:725–728
Yang F, Coughlin DR, Phillips PJ, Yang L, Devaraj A, Kovarik L, Noebe RD, Mills MJ (2013) Structure analysis of a precipitate phase in a Ni rich high temperature NiTiHf shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 61:3335–3346
Santamarta R, Arroyave R, Pons J, Evirgen A, Karaman I, Karaca HE, Noebe RD (2013) TEM study of structural and microstructural characteristics of a precipitate phase in Ni-rich Ni-Ti-Hf and Ni-Ti-Zr shape memory alloys. Acta Mater 61:6191–6206
Coughlin DR, Phillips PJ, Bigelow GS, Garg A, Noebe RD, Mills MJ (2012) Characterization of the microstructure and mechanical properties of a 50.3Ni–29.7Ti–20Hf shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 67:112–115
Meng X, Cai W, Fu Y, Li Q, Zhang J, Zhao L (2008) Shape-memory behaviors in an aged Ni-rich TiNiHf high temperature shape-memory alloy. Intermetallics 16:698–705
Karaca HE, Saghaian SM, Ded G, Tobe H, Basaran B, Maier HJ, Noebe RD, Chumlyakov YI (2013) Effects of nanoprecipitation on the shape memory and material properties of an Ni-rich NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 61:7422–7431
Stebner AP, Glen S, Bigelow GS, Yang J, Shukla DP, Saghaian SM, Rogers R, Garg A, Karaca HE, Chumlyakov Y, Bhattacharya K, Noebe RD (2014) Transformation strains and temperatures of a nickel–titanium–hafnium high temperature shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 76:40–53
Evirgen A, Karaman I, Santamarta R, Pons J, Noebe RD (2015) Microstructural characterization and shape memory characteristics of the Ni50.3Ti34.7Hf15 shape memory alloy. Acta Mater 83:48–60
Benafan O, Garg A, Noebe RD, Bigelow GS, Padula SA, Gaydosh DJ, Schell N, Mabe JH, Vaidyanathan R (2014) Mechanical and functional behavior of a Ni-rich Ni50.3Ti29.7Hf20 high temperature shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 50:94–107
Benafan O, Noebe RD, Padula SA, Vaidyanathan R (2012) Microstructural response during isothermal and isobaric loading of a precipitation strengthened Ni-29.7Ti-20Hf high-temperature shape memory alloy. Metall Mater Trans 43A:4539–45552
Fosdick R, Ketema Y, Jang-Horng Y (1998) Vibration damping through the use of materials with memory. Int J Solids Struct 35:403
DellaCorte C, Noebe RD, Stanford MK, Padula SA (2011) Resilient and corrosion proof rolling element bearings made from superealstic Ni-Ti alloys for aerospace mechanism applications, NASA/TM-2011-217105
Tang W (1997) Thermodynamic study of the low-temperature phase B19′ and the martensitic transformation in near-equiatomic Ti-Ni shape memory alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 28:537–544
Sandu AM, Tsuchiya K, Tabuchi M, Yamamoto S, Todaka Y, Umemoto M (2007) Microstructural evolution during isothermal aging in Ni-Rich Ti-Zr-Ni shape memory alloys. Mater Trans 48:432–438
Sandu AM, Tabuchi M, Yamamoto S, Todaka Y, Umemoto M (2008) Precipitation in Ni-rich Ti-Zr-Ni shape memory alloys by isothermal aging. In: Berg B, Mitchell MR, Proft J (eds) Proceedings of the international conference on shape memory and superelastic technologies. ASM International, Ohio, pp 101–108
Evirgen A, Karaman I, Noebe RD, Santamarta R, Pons J (2013) Effect of precipitation on the microstructure and shape memory response of the Ni50.3Ti29.7Zr20 high temperature shape memory alloy. Scr Mater 69:354–357
Kirkland EJ, Loane RF, Silcox J (1987) Simulation of annular dark field STEM images using a modified multislice method. Ultramicroscopy 23:77–96
Loane RF, Xu P, Silcox J (1992) Incoherent imaging of zone axis crystals with ADF STEM. Ultramicroscopy 40:121–138
Kovarik L, Yang F, Garg A, Diercks D, Kaufman M, Noebe RD, Mills MJ (2010) Structural analysis of a new precipitate phase in high-temperature TiNiPt shape memory alloys. Acta Mater 58:4660–4673
Karaca HE, Acar E, Ded GS, Basaran B, Tobe H, Noebe RD, Bigelow G, Chumlyakov YI (2013) Shape memory behavior of high strength NiTiHfPd polycrystalline alloys. Acta Mater 61:5036–5049
Phillips PJ, Brandes MC, Mills MJ, De Graef M (2011) Diffraction contrast STEM of dislocations: imaging and simulations. Ultramicroscopy 111:1483–1487
Noebe RD, Bowman RR, Nathal MV (1993) Physical and mechanical properties of the B2 compound NiAI. Int Mater Rev 38:193–232
Benafan O, Noebe RD, Padula SA, Garg A, Clausen B, Vogel S, Vaidyanathan R (2013) Temperature dependent deformation of the B2 austenite phase of a NiTi shape memory alloy. Int J Plast 51:103–121
Hull D, Bacon DJ (2001) 10: strength of crystalline solids. In: Hull D, Bacon DJ (eds) Introduction to dislocations, 4th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 193–236
Hornbuckle BC, Sasaki TT, Bigelow GS, Noebe RD, Weaver ML, Thompson GB (2015) Structure-property relationships with H-phase precipitation in a Ni-29.7Ti-20Hf (at.%) shape memory alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 637:63–69
Cooper MJ (1963) An investigation of the ordering of the phases CoAl and NiAl. Philos Mag 8(89):805–810
Wasilewski RJ (1968) Structure defects in CsCl intermetallic compounds-I. Thoery. J Phys Chem Solids 29:39–49
Taylor A, Doyle NJ (1972) Further studies on the nickel-aluminum system. I. The β-NiAI and δ-Ni2Al3 phase fields. J Appl Cryst 5:201–209
Bradley AJ, Taylor A (1937) An X-ray analysis of the nickel-aluminium system. Proc R Soc A159:56–72
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Grant #DE-SC0001258. R.D.N. acknowledges funding from the NASA FAP, Aeronautical Sciences Project, and the TAC Transformational Tools & Technologies Project, Technical Discipline Lead, Dale Hopkins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coughlin, D.R., Casalena, L., Yang, F. et al. Microstructure–property relationships in a high-strength 51Ni–29Ti–20Hf shape memory alloy. J Mater Sci 51, 766–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9400-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9400-7