Abstract
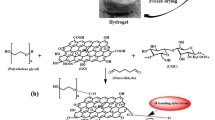
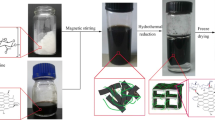
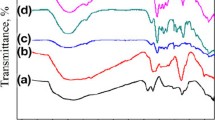
Novel environmental friendly hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) hydrogels were fabricated upon compositing with graphene oxide (GO) in this work. In order to promote a more homogeneous dispersion of GO sheets in HPC, GO was firstly modified with HPC chains through esterification. The morphology and chemical structure of the functionalized HPC-GO were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, X-ray diffraction, and thermo-gravimetric analysis. Then scanning electronic microscope was employed to compare the morphologies of the HPC and HPC-GO/HPC hydrogels. The obtained HPC-GO/HPC hydrogels exhibited excellent adsorption performance toward methylene blue. Simulation of the practical use by preparing simple adsorption columns made from in situ formation of HPC-based hydrogels had given a visible observation of the significant adsorption effect brought by the incorporation of HPC-GO sheets. Adsorption kinetics were then imitated by Lagergren pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models. Adsorption isotherms were imitated by Langmuir isotherm and Freundlich isotherm.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lei W, Portehault D, Liu D, Qin S, Chen Y (2013) Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning. Nat Commun 4:1777. doi:10.1038/ncomms2818
He F, Wang W, Moon J-W, Howe J, Pierce EM, Liang L (2012) Rapid removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions using thiol-functionalized Zn-doped biomagnetite particles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(8):4373–4379. doi:10.1021/am301031g
Warner CL, Chouyyok W, Mackie KE, Neiner D, Saraf LV, DroubayTC WM, Addleman RS (2012) Manganese doping of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: tailoring surface reactivity for a regenerable heavy metal sorbent. Langmuir 28(8):3931–3937. doi:10.1021/la2042235
Wang L (2009) Aqueous organic dye discoloration induced by contact glow discharge electrolysis. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):577–581. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.037
Khin MM, Nair AS, BabuVJ MR, Ramakrishna S (2012) A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ Sci 5(8):8075–8109. doi:10.1039/C2EE21818F
Abdel-Halim E (2013) Preparation of starch/poly (N,N-Diethylaminoethyl methacrylate) hydrogel and its use in dye removal from aqueous solutions. React Funct Polym 73(11):1531–1536
Wang WB, TianGY ZZ, Wang AQ (2015) A simple hydrothermal approach to modify palygorskite for high-efficient adsorption of methylene blue and Cu(II) ions. Chem Eng J 265:228–238. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.135
Malik P (2004) Dye removal from wastewater using activated carbon developed from sawdust: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 113(1):81–88
Adak A, Bandyopadhyay M, Pal A (2006) Fixed bed column study for the removal of crystal violet (CI Basic Violet 3) dye from aquatic environment by surfactant-modified alumina. Dyes Pigment 69(3):245–251
Paulino AT, GuilhermeMR RA, Campese GM, Muniz EC, Nozaki J (2006) Removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous media using superabsorbent hydrogel supported on modified polysaccharide. J Colloid Interface Sci 301(1):55–62
Dehabadi L, Wilson LD (2014) Polysaccharide-based materials and their adsorption properties in aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 113:471–479. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.06.083
Khan SB, Lee JW, Marwani HM, Akhtar K, Asiri AM, Seo J, Khan AAP, Han H (2014) Polybenzimidazole hybrid membranes as a selective adsorbent of mercury. Compos Part B 56:392–396. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.056
Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Wang A (2014) Highly efficient and selective adsorption of malachite green onto granular composite hydrogel. Chem Eng J 257:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.032
Tang QW, Wu JH, Lin JM, Li QH, Fan SJ (2008) Two-step synthesis of polyacrylamide/polyacrylate interpenetrating network hydrogels and its swelling/deswelling properties. J Mater Sci 43(17):5884–5890. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2857-x
Tang QW, Sun XM, Li QH, Lin JM, Wu JH (2009) Synthesis of polyacrylate/polyethylene glycol interpenetrating network hydrogel and its sorption for Fe3+ ion. J Mater Sci 44(3):726–733. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3173-1
Wang MQ, Yan J, Du SG, ZengJW CW, Guo Y, Li HG (2013) Adsorption characteristic of copper ions and its application in electroless nickel plating on a hydrogel-functionalized poly(vinyl chloride) plastic. J Mater Sci 48(20):7224–7237. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7539-7
Ekici S (2011) Intelligent poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-carboxymethyl cellulose full interpenetrating polymeric networks for protein adsorption studies. J Mater Sci 46(9):2843–2850. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5158-0
Bao Y, Ma J, Li N (2011) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 84(1):76–82. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.061
Pal A, Pan S, Saha S (2013) Synergistically improved adsorption of anionic surfactant and crystal violet on chitosan hydrogel beads. Chem Eng J 217:426–434. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.120
Zheng Y, Hua S, Wang A (2010) Adsorption behavior of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions onto starch-g-poly(acrylic acid)/sodium humate hydrogels. Desalination 263(1–3):170–175. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.054
Vecino X, Devesa-Rey R, Cruz JM, Moldes AB (2015) Study of the physical properties of calcium alginate hydrogel beads containing vineyard pruning waste for dye removal. Carbohydr Polym 115:129–138. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.088
Gao H, Sun Y, Zhou J, Xu R, Duan H (2012) Mussel-inspired synthesis of polydopamine-functionalized graphene hydrogel as reusable adsorbents for water purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(2):425–432. doi:10.1021/am302500v
Huang X, Liao X, Shi B (2009) Hg(II) removal from aqueous solution by bayberry tannin-immobilized collagen fiber. J Hazard Mater 170(2–3):1141–1148. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.086
Salama A, Shukry N, El-Sakhawy M (2015) Carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) hydrogel as adsorbent for dye removal. Int J Biol Macromol 73:72–75. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.11.002
Yan L, Shuai Q, Gong X, Gu Q, Yu H (2009) Synthesis of microporous cationic hydrogel of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and its application on anionic dye removal. Clean 37(4–5):392–398. doi:10.1002/clen.200900006
Faruk O, Bledzki AK, Fink H-P, Sain M (2012) Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog Polym Sci 37(11):1552–1596. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.04.003
Okamoto M, John B (2013) Synthetic biopolymer nanocomposites for tissue engineering scaffolds. Prog Polym Sci 38(10):1487–1503
Li D, Muller MB, Gilje S, KanerRB WG (2008) Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat Nano 3(2):101–105
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, AlemanyLB L, Tour JM (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4(8):4806–4814. doi:10.1021/nn1006368
Zhang Y, Liu J-W, Chen X-W, Wang J-H (2015) A three-dimensional amylopectin-reduced graphene oxide framework for efficient adsorption and removal of hemoglobin. J Mater Chem B 3(6):983–989. doi:10.1039/C4TB01792G
Chen YQ, Chen LB, Bai H, Li L (2013) Graphene oxide-chitosan composite hydrogels as broad-spectrum adsorbents for water purification. J Mater Chem A 1(6):1992–2001. doi:10.1039/c2ta00406b
Xu Y, Sheng K, Li C, Shi G (2010) Self-assembled graphene hydrogel via a one-step hydrothermal process. ACS Nano 4(7):4324–4330
XuYX W, Sun YQ, Bai H, Shi GQ (2010) Three-dimensional self-assembly of graphene oxide and DNA into multifunctional hydrogels. ACS Nano 4(12):7358–7362. doi:10.1021/nn1027104
Bai H, Li C, Wang XL, Shi GQ (2011) On the gelation of graphene oxide. J Phys Chem C 115(13):5545–5551. doi:10.1021/jp1120299
Liao R, Lei Y, Wan J, Tang Z, Guo B, Zhang L (2012) Dispersing graphene in hydroxypropyl cellulose by utilizing its LCST behavior. Macromol Chem Phys 213(13):1370–1377. doi:10.1002/macp.201200137
Yeo MY, Park SY, In I (2012) Temperature-dependent optical transmittance of chemically reduced graphene oxide/hydroxypropyl cellulose assembly. Chem Lett 41(2):197–199
Hu HT, Wang XB, Wang JC, Liu FM, Zhang M, Xu CH (2011) Microwave-assisted covalent modification of graphene nanosheets with chitosan and its electrorheological characteristics. Appl Surf Sci 257(7):2637–2642. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.035
Xu CH, Wang JC, Wan L, Lin JJ, Wang XB (2011) Microwave-assisted covalent modification of graphene nanosheets with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin and its electrochemical detection of phenolic organic pollutants. J Mater Chem 21(28):10463–10471. doi:10.1039/c1jm10478k
Yang Q, Pan X, Clarke K, Li K (2011) Covalent functionalization of graphene with polysaccharides. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(1):310–317
Chen CM, Yang QH, Yang YG, Lv W, Wen YF, Hou PX, Wang MZ, Cheng HM (2009) Self-assembled free-standing graphite oxide membrane (vol 21, pg 3007. Adv Mater 21(35):3541–3541. doi:10.1002/adma.200803726
Hirsch SG, Spontak RJ (2002) Temperature-dependent property development in hydrogels derived from hydroxypropyl cellulose. Polymer 43(1):123–129
Kabra BG, Gehrke SH, Spontak RJ (1998) Microporous, responsive hydroxypropyl cellulose gels. 1. Synthesis and microstructure. Macromolecules 31(7):2166–2173. doi:10.1021/ma970418q
Bao HQ, Pan YZ, Ping Y, Sahoo NG, Wu TF, Li L, Li J, Gan LH (2011) Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for drug and gene delivery. Small 7(11):1569–1578. doi:10.1002/smll.201100191
Han DL, Yan LF, Chen WF, Li W (2011) Preparation of chitosan/graphene oxide composite film with enhanced mechanical strength in the wet state. Carbohydr Polym 83(2):653–658. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.038
Jung I, Dikin D, Park S, Cai W, Mielke SL, Ruoff RS (2008) Effect of water vapor on electrical properties of individual reduced graphene oxide sheets. J Phys Chem C 112(51):20264–20268. doi:10.1021/jp807525d
ShenJF YB, Li T, Long Y, Li N, Ye MX (2012) Study on graphene-oxide-based polyacrylamide composite hydrogels. Compos Part A 43(9):1476–1481. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.04.006
Li L, Luo C, Li X, Duan H, Wang X (2014) Preparation of magnetic ionic liquid/chitosan/graphene oxide composite and application for water treatment. Int J Biol Macromol 66:172–178. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.031
Li LL, Fan LL, Sun M, Qiu HM, Li XJ, Duan HM, Luo CN (2013) Adsorbent for chromium removal based on graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin-chitosan. Colloids Surf B 107:76–83. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.074
Namvari M, Namazi H (2014) Synthesis of magnetic citric-acid-functionalized graphene oxide and its application in the removal of methylene blue from contaminated water. Polym Int 63(10):1881–1888
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51403003), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1408085ME86, 1508085QE105), Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Provincial Education Department (KJ2013A014), Startup Foundation for Doctors of Anhui University, Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Anhui Province (01001419), and the 211 Project of Anhui University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Nie, W. et al. Fabrication of hydrogel of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) composited with graphene oxide and its application for methylene blue removal. J Mater Sci 50, 6113–6123 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9166-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9166-y