Abstract
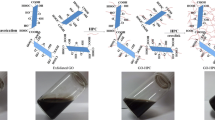
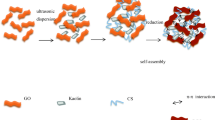
Composite hydrogels based on hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and graphene oxide (GO) were developed and used for adsorption of phenol. The single network composite hydrogel (SNCH) was first prepared by crosslinking of HPC and GO by epichlorohydrin; then the SNCH was treated with polyethyleneimine solution, forming the double network composite hydrogel (DNCH). The DNCH exhibited better adsorption capacity than the SNCH due to larger surface area and more functional groups. The possible adsorption mechanism of the composite hydrogels toward phenol involved electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, and π–π interactions. Study on dynamic adsorption behavior of phenol by SNCH and DNCH indicated that the breakthrough time increased when the initial concentration and feed flow rate of phenol decreased. Furthermore, the breakthrough time of DNCH was longer than that of SNCH at all operating conditions due to the relatively higher adsorption capacity of DNCH. The SNCH and DNCH could be repeatedly used without significant loss in the initial binding affinity after six adsorption–desorption cycles, which indicated that the composite hydrogels were qualified for practical application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Taraba and P. Bulavova: Adsorption enthalpy of lead(II) and phenol on coals and activated carbon in the view of thermodynamic analysis and calorimetric measurements. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 116, 97 (2018).
P. Podkościelny and A. Dabrowski: Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions on original and oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 35, 806 (2017).
Y. Bennani, P. Perez-Rodriguez, M.J. Alani, W.A. Smith, L.C. Rietveld, M. Zeman, and A.H.M. Smets: Photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of phenol for water treatment using a BiVO4 thin-film photoanode. J. Mater. Res. 31, 2627 (2016).
K.O. Badmus, J. Tijani, E. Massima, and L. Petrik: Treatment of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater using hydrodynamic cavitation in synergy with advanced oxidation process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 7299 (2018).
L.N. Nie and Q.C. Zhang: Recent progress in crystalline metal chalcogenides as efficient photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 4, 1953 (2017).
M. Kahoush, N. Behary, A. Cayla, and V. Nierstrasz: Bio-Fenton and Bio-electro-Fenton as sustainable methods for degrading organic pollutants in wastewater. Process Biochem. 64, 237 (2018).
N. Jiang, R. Shang, S.G.J. Heijman, and L.C. Rietveld: High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water Res. 144, 145 (2018).
S. Ozcan, A. Tor, M.E. Aydin, F. Beduk, and I. Akin: Sorption of phenol from aqueous solution by novel magnetic polysulfone microcapsules containing Cyanex 923. React. Funct. Polym. 72, 451 (2012).
H.A. Asmaly, Ihsanullah, B. Abussaud, T.A. Saleh, T. Laoui, V.K. Gupta, and M.A. Atieh: Adsorption of phenol on aluminum oxide impregnated fly ash. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 6801 (2016).
H. El-Hamshary, S. El-Sigeny, M.F.A. Taleb, and N.A. El-Kelesh: Removal of phenolic compounds using (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate/acrylamidopyridine) hydrogel prepared by gamma radiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 57, 329 (2007).
J.J. Feng, H. Ding, G. Yang, R.T. Wang, S.G. Li, J.N. Liao, Z.Y. Li, and D.M. Chen: Preparation of black-pearl reduced graphene oxide-sodium alginate hydrogel microspheres for adsorbing organic pollutants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 508, 387 (2017).
H. Kamata, Y. Akagi, Y. Kayasuga-Kariya, U. Chung, and T. Sakai: “Nonswellable” hydrogel without mechanical hysteresis. Science 343, 873 (2014).
O. Pinkas, O. Haneman, O. Chemke, and M. Zilberman: Fiber-reinforced composite hydrogels for bioadhesive and sealant applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 28, 1162 (2017).
C. Fan, L. Liao, C. Zhang, and L. Liu: A tough double network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 4251 (2013).
J. Wang, J. Wei, S. Su, J. Qiu, and S. Wang: Ion-linked double-network hydrogel with high toughness and stiffness. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 5458 (2015).
E. Badakhshanian, K. Hemmati, and M. Ghaemy: Enhancement of mechanical properties of nanohydrogels based on natural gum with functionalized multiwall carbon nanotube: Study of swelling and drug release. Polymer 90, 282 (2016).
Z. Li, M. Qi, C. Tu, W. Wang, J. Chen, and A.J. Wang: Highly efficient removal of chlorotetracycline from aqueous solution using graphene oxide/TiO2 composite: Properties and mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 765 (2017).
İ. Duru, D. Ege, and A.R. Kamali: Graphene oxides for removal of heavy and precious metals from wastewater. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 6097 (2016).
W.S. Hummers and R.E. Offeman: Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339 (1958).
L. Yan, Q. Shuai, X. Gong, Q. Gu, and H. Yu: Synthesis of microporous cationic hydrogel of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and its application on anionic dye removal. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 37, 392 (2009).
X. Chen, S. Zhou, L. Zhang, T. You, and F. Xu: Adsorption of heavy metals by graphene oxide/cellulose hydrogel prepared from NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Materials 9, 582 (2016).
S. Sun and P. Wu: A one-step strategy for thermal- and pH-responsive graphene oxide interpenetrating polymer hydrogel networks. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 4095 (2011).
H.Y. Liu, T. Kuila, N.H. Kim, B.C. Ku, and J.H. Lee: In situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-polyethyleneimine composite and its gas barrier properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 3739 (2013).
J. Wang and J. Li: One-pot synthesis of IPN hydrogels with enhanced mechanical strength for synergistic adsorption of basic dyes. Soft Mater. 13, 160 (2015).
J. Wang and J. Li: Cu2+ adsorption onto ion-imprinted composite hydrogels: Thermodynamics and mechanism studies. Polym. Bull. 72, 2143 (2015).
Z. Guan, L. Liu, L. He, and S. Yang: Amphiphilic hollow carbonaceous microspheres for the sorption of phenol from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 196, 270 (2011).
Y. Piao and B. Chen: Synthesis and mechanical properties of double cross-linked gelatin-graphene oxide hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 101, 791 (2017).
C. Spagnol, F.H.A. Rodrigues, A.G.B. Pereira, A.R. Fajardo, A.F. Rubira, and E.C. Muniz: Superabsorbent hydrogel composite made of cellulose nanofibrils and chitosan-graft-poly(acrylic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 2038 (2012).
X. Wang, Q. Liu, J. Liu, R. Chen, H. Zhang, R. Li, Z. Li, and J. Wang: 3D self-assembly polyethyleneimine modified graphene oxide hydrogel for the extraction of uranium from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 426, 1063 (2017).
Y. Zhuang, F. Yu, H. Chen, J. Zheng, J. Ma, and J. Chen: Alginate/graphene double-network nanocomposite hydrogel beads with low-swelling, enhanced mechanical properties, and enhanced adsorption capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 10885 (2016).
R. Sahraei and M. Ghaemy: Synthesis of modified gum tragacanth/graphene oxide composite hydrogel for heavy metal ions removal and preparation of silver nanocomposite for antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 157, 823 (2017).
J. Wang, D. Song, S. Jia, and Z. Shao: Poly(N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)/graphene oxide hybrid hydrogels: pH and temperature sensitivities and Cr(VI) adsorption. React. Funct. Polym. 81, 8 (2014).
S.F. Xiang, W.Q. Qian, T. Li, Y. Wang, M.Q. Chen, P.M. Ma, and W.F. Dong: Hierarchical structural double network hydrogel with high strength, toughness, and good recoverability. New J. Chem. 41, 14397 (2017).
J.H. Wang, X.L. Yin, and Y.F. Ji: Cr(VI) adsorption on polyethyleneimine modified graphite oxide. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 31, 1185 (2015).
A.G. Zakharov, М.I. Voronova, О.V. Surov, and D.V. Batov: Phenol sorption on cellulose from binary aqueous-organic mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 151, 74 (2010).
J. Huang, X. Jin, and S. Deng: Phenol adsorption on an N-methylacetamide- modified hypercrosslinked resin from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 192, 192 (2012).
M. Masomi, A.A. Ghoreyshi, G.D. Najafpour, and A.R.B. Mohamed: Dynamic adsorption of phenolic compounds on activated carbon produced from pulp and paper mill sludge: Experimental study and modeling by artificial neural network (ANN). Desalin. Water Treat. 55, 1453 (2015).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 51672236), Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PPZY2015A025), “Six Top Talents” program of Jiangsu Province (2015-XCL-034), and science and technology project from Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (2014-K7-007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, N., Jiang, C. et al. Adsorptive removal of phenol by single and double network composite hydrogels based on hydroxypropyl cellulose and graphene oxide. Journal of Materials Research 33, 3898–3905 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.385
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.385