Abstract
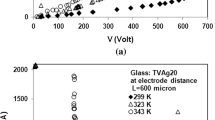
Ternary (60−x)V2O5–xSb–40TeO2 oxide glasses (with 0 ≤ x ≤15 in mol%), prepared using the usual melt quenching method, were investigated electrically (at the presence of high-dc electric fields) within the temperature range of 298–375.3 K at different electrode distances. The current–voltage characteristics show increasing deviations from Ohm’s law at electric fields of about >103 V/cm. This behavior can be attributed to the Pool–Frenkel effect, which usually occurs at the mentioned electric fields. At higher fields, switching (from low conduction state to higher conduction state) or negative resistance phenomena were observed at a threshold voltage (V th). The threshold voltage for beginning the switching/negative resistance shows a decreasing trend with increasing in temperature and also with decreasing of electrode distance. An electrothermal model (based on the Joule heating effect in the current filament) is proposed to interpret the observed electrical properties. Also, the lowering factor of potential barrier (β PF) in Pool–Frenkel effect, heat dissipation factor, and electrical activation energy of the present samples were determined. In each sample, the increase of β PF with temperature can explain the phonon-assisted hopping conduction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ovshinsky SR (1959) How liquid-state switch controls a-c. Electronics 32:76–81
Marquez E, Villares P, Jimenezgaray R (1988) On non-ohmic conduction and the threshold characteristics of a bulk-type switching device based on the chalcogenide glassy semiconductor As0.40Se0.30Te0.30. J Non-Cryst Solids 105:123–133
Mirzai M, Hekmatshoar MH (2013) Study of electrical conductivity and memory switching in the zinc–vanadium–phosphate glasses. Phys B 420:70–73
Mirzai M, Hekmatshoar MH (2013) Electrical switching in the CuO–ZnO–P 2 O 5 glasses. Phys B 405:4505–4508
Souri D, Elahi M, Yazdanpanah MS (2008) Pool-Frenkel Effect and High Frequency Dielectric Constant Determination of Semiconducting P2O5–Li2MoO4–Li2O and P2O5–Na2MoO4–Na2O Bulk Glasses. Cent Eur J Phys 6(2):306–310
Montani RA, Robledo A, Bazan JC (1998) On the behavior of the I-V characteristic curves on TeO 2 -V 2 O 5 -based glasses. Mater Chem Phys 53(1):80–82
Hirashima H, Watanabe Y, Yoshida T (1987) Switching of TiO 2 -V 2 O 5 -P 2 O 5 glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 95(96):825–832
Mansour E, Mmustafa Y, El-Damrawi GM, Abd El-Maksoud S, Doweidar H (2001) Memory switching of Fe2O3–BaOV2O5 glasses. Phys B 305:242–249
Elahi M, Souri D (2002) Effect of High Electric Field on Conduction of TeO2-V2O5-MoO3 Amorphous Thin Films. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 40:620–623
Souri D, Elahi M (2006) Effect of High Electric Field on The DC Conduction of TeO2-V2O5-MoO3 Amorphous Bulk Material;Czechoslovak. J Phys 56(4):419–425
Lebrun N, Levy M, Souquet JL (1990) Electronic conductivity in glasses of the TeO 2 -V 2 O 5 -MoO 3 system. Solid State Ionics 40–41:718–722
Pal M, Hirota K, Tsujigami Y, Sakata H (2001) Structural and electrical properties of MoO3-TeO2 glasses. J Phys D Appl Phys 34:459–464
Jose R, Suzuki T, Ohishi Y (2006) Thermal and optical properties of TeO 2 –BaO–SrO–Nb 2 O 5 based glasses: New broadband Raman gain media. J Non-Cryst Solids 352:5564–5571
Murugan GS, Suzuki T, Ohishi Y (2005) Tellurite glasses for ultrabroadband fiber Raman amplifiers. Appl Phys Lett 86(1):161109–1611012
Souri D, Mohammadi M, Zaliani H (2014) Effect of antimony on the optical and some physical properties of Sb-V2O5-TeO2 glasses. Electron Mater Lett 10(6):1103–1108
Sawa A (2008) Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater Today 11:28–36
Souri D, Azizpour P, Zaliani H (2014) Electrical conductivity of V2O5-TeO2 -Sb glasses at low temperatures. J Electron Mater 43:3672–3680
Abdel MM (2006) Aziz; Memory switching of germanium tellurium amorphous semiconductor. J Appl Surf Sci 253:2059–2065
Fritzsche H (1974) Switching and memory in amorphoussemiconductors. In: Tauc J (ed) Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors. Plenum Press, London, pp 313–359
Avila A, Asomoza R (2000) Switching in coplanar amorphous hydrogenated silicon devices. Solid-State Electron 40:17–27
Abdel A (2000) All, A. Elshafie, M.M.Elhawary; DC electric-field effect in bulk and thin-film Ge5As38Te57 chalcogenide glass. Vacuum 4:845–853
Wagle S, Shirodkar V (2000) Current controlled negative resistance phenomenon in SbPbSe system. Czechoslov J Phys 5:635–643
Warren AC (1968) Switching mechanism in chalcogenide glasses. Electron Lett 5–12:461–462
Henish HK, Fagen EA, Oshinsky SR, Fritzsche HF (1970) A qualitative theory of electrical switching processes in monostable amorphous structures. J Non-Cryst Solids 4:538–547
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souri, D., Ghasemi, R. & Shiravand, M. The study of high-dc electric field effect on the conduction of V2O5–Sb–TeO2 glasses and the applicability of an electrothermal model. J Mater Sci 50, 2554–2560 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8815-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8815-5