Abstract
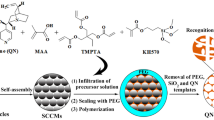
A novel water-compatible surface-imprinted core–shell microsphere, which had multiple non–covalent interactions with template molecule, was successfully prepared by the surface grafting polymerization method in acetonitrile–water systems with thymopentin as template through ionic liquid-functionalized polyethyleneglycolmethacrylate-co-vinylimidazole microsphere as the matrix. The average diameter of matrix was 1 μm ± 20 nm and the thickness of imprinted layer was about 50 nm. The results of static adsorption experiments indicated that ionic liquid-functionalized molecularly imprinted microspheres showed the good adsorption capacity and specific recognition for template peptide. The binding-isotherm analysis showed that Langmuir isotherm models gave a good fit in the range of concentrations, suggesting that there was only one kind of binding site in imprinted layer. Measurements of the binding kinetics revealed that surface-imprinted composite microspheres reached peptide-adsorption equilibrium in 60 min and the maximum adsorption capacity for TP5 was 38.4 mg g−1. The effects of pH, salt concentration, and temperature on the adsorption capacities were investigated. The microspheres were found to have a high specificity for TP5 with little affinity for BSA and Hb. Finally, the core–shell microspheres can be reused with only 15.6 % decrease in TP5 adsorption capacity after six times.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldstein G, Scheid MP, Boyse EA et al (1979) A synthetic pentapeptide with biological activity characteristic of the thymic hormone thymopoietin. Science 204:1309–1310
Bernengo MG, Doveil GC, Meregalli M et al (1988) Immunomodulation and Sézary syndrome: experience with thymopentin (TP-5). Brit J Dermatol 119:207–221
Colle R, Ceschia T, Colatritto A, Biffoni F (1988) Use of thymopentin in autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Ther Res 44:1045–1049
Bolten W, Kohler H (1990) Treatment of rheumatoid-arthritis by daily injections of thymopentin with stepwise reduction of the dosage of nonsteroidal antirheumatics. Aktuel Rheumatol 15:141–144
Hawkins DM, Ellis EA, Stevenson D, Holzenburg A, Reddy SM (2007) Novel critical point drying (CPD) based preparation and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging of protein specific molecularly imprinted polymers (HydroMIPs). J Mater Sci 42:9465–9468. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-1806-4
Yun YH, Shon HK, Yoon SD (2009) Preparation and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective separation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J Mater Sci 44:6206–6211. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3863-3
Chang L, Wu S, Chen S, Li X (2011) Preparation of graphene oxide-molecularly imprinted polymer composites via atom transfer radical polymerization. J Mater Sci 46:2024–2029. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5033-z
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Osmani Q, Hughes H, McLoughlin P (2012) Probing the recognition of molecularly imprinted polymer beads. J Mater Sci 47:2218–2227. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-6032-4
Xu X, Chen S, Zhuang L, Zheng C, Wu Y (2014) Establishment of a novel surface-imprinting system for melamine recognition and mechanism of template-matrix interactions. J Mater Sci 49:2853–2863. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7991-4
Dirion B, Cobb Z, Schillinger E, Andersson LI, Sellergren B (2003) Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymers obtained via high-throughput synthesis and experimental design. J Am Chem Soc 125:15101–15109
Sreenivasan K (2007) Synthesis and evaluation of multiply templated molecularly imprinted polyaniline. J Mater Sci 42:7575–7578. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-1625-7
Ceolin G, Orbán Á, Kocsis V, Gyurcsányi RE, Kézsmárki I, Horváth V (2013) Electrochemical template synthesis of protein-imprinted magnetic polymer microrods. J Mater Sci 48:5209–5218. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7309-6
Li X, Zhang B, Tian L, Li W, Xin T, Zhang H, Zhang Q (2014) Effect of carboxyl density at the core-shell interface of surface-imprinted magnetic trilayer microspheres on recognition properties of proteins. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 196:265–271
Cormack PA, Elorza AZ (2004) Molecularly imprinted polymers: synthesis and characterization. J Chromatogr B 804:173–182
Verheyen E, Schillemans JP, van Wijk M, Demeniex MA, Hennink WE, van Nostrum CF (2011) Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 32:3008–3020
Hart BR, Shea KJ (2002) Molecular imprinting for the recognition of N-terminal histidine peptides in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 35:6192–6201
Yano K, Karube I (1999) Molecularly imprinted polymers for biosensor applications. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 18:199–204
Hart BR, Shea KJ (2001) Synthetic peptide receptors: molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of peptides using peptide-metal interactions. J Am Chem Soc 123:2072–2073
Lin CI, Joseph AK, Chang CK, Lee YD (2004) Synthesis and photoluminescence study of molecularly imprinted polymers appended onto CdSe/ZnS core-shells. Biosens Bioelectron 20:127–131
Lin CI, Joseph AK, Chang CK, Lee YD (2004) Molecularly imprinted polymeric film on semiconductor nanoparticles: Analyte detection by quantum dot photoluminescence. J Chromatogr A 1027:259–262
Wang H, Zou M, Li N, Li K (2007) Preparation and characterization of ionic liquid intercalation compounds into layered zirconium phosphates. J Mater Sci 42:7738–7744. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-1686-7
Liu YH, Lin CW, Chang MC, Shao H, Yang ACM (2008) The hydrothermal analogy role of ionic liquid in transforming amorphous TiO2 to anatase TiO2: elucidating effects of ionic liquids and heating method. J Mater Sci 43:5005–5013. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2740-9
Liu ZT, Shen LH, Liu ZW, Lu J (2009) Acetylation of β-cyclodextrin in ionic liquid green solvent. J Mater Sci 44:1813–1820. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3238-1
Han DD, Row KH (2010) Recent applications of ionic liquids in separation technology. Molecules 15:2405–2426
Nagaraju G, Manjunath K, Ravishankar TN, Ravikumar BS, Nagabhushan H, Ebeling G, Dupont J (2013) Ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles and its application in photocatalysis. J Mater Sci 48:8420–8426. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7654-5
Olsson C, Hedlund A, Idström A, Westman G (2014) Effect of methylimidazole on cellulose/ionic liquid solutions and regenerated material therefrom. J Mater Sci 49:3423–3433. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8052-3
Berthod A, Ruiz-Angelb MJ, Carda-Broch S (2008) Ionic liquids in separation techniques. J Chromatogr A 1184:6–18
Yang Q, Xing H, Su BGYuK, Bao Z, Yang Y, Ren Q (2012) Improved separation efficiency using ionic liquid-cosolvent mixtures as the extractant in liquid-liquid extraction: a multiple adjustment and synergistic effect. Chem Eng J 181:334–342
Ni X, Xing H, Yang Q, Wang J, Su B, Bao Z, Yang Y, Ren Q (2012) Selective liquid-liquid extraction of natural phenolic compounds using amino acid ionic liquids: a case of α-tocopherol and methyl linoleate separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6480–6488
Tian M, Bi W, Row KH (2011) Molecular imprinting in ionic liquid-modified porous polymer for recognitive separation of three tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:2495–2502
Guo L, Deng Q, Fang G, Gao W, Wang S (2011) Preparation and evaluation of molecularly imprinted ionic liquids polymer as sorbent for on-line solid-phase extraction of chlorsulfuron in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:6271–6277
Bi W, Tian M, Row KH (2012) Separation of phenolic acids from natural plant extracts using molecularly imprinted anion-exchange polymer confined ionic liquids. J Chromatogr A 1232:37–42
Luo X, Zhan Y, Tu X, Huang Y, Luo S, Yan L (2011) Novel molecularly imprinted polymer using 1-(α-methyl acrylate)-3-methylimidazolium bromide as functional monomer for simultaneous extraction and determination of water-soluble acid dyes in wastewater and soft drink by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:1115–1121
Uğuzdoğan E, Denkbaş EB, Öztürk E, Tuncel SA, Kabasakal OS (2009) Preparation and characterization of polyethyleneglycolmethacrylate (PEGMA)-co-vinylimidazole (VI) microspheres to use in heavy metal removal. J Hazard Mater 162:1073–1080
Lane TJ, Nakagawa I, Walter JL, Kandathil AJ, Walter JL (1962) Infrared investigation of certain imidazole derivatives and their metal chelates. Inorg Chem 1:267–276
Overberger CG, Vorchheimer N (1963) Imidazole-containing polymers. Synthesis and polymerization of the monomer 4 (5)-vinylimidazole. J Am Chem Soc 85:951–955
Kara A, Uzun L, Beşirli N, Denizli A (2004) Poly(ethylene glycol dimethacrylate-n-vinyl imidazole) beads for heavy metal removal. J Hazard Mater 106:93–99
Qiu H, Takafuji M, Sawada T, Liu X, Jiang S, Ihara H (2010) New strategy for drastic enhancement of selectivity via chemical modification of counter anions in ionic liquid polymer phase. Chem Commun 46:8740–8742
Fei Z, Zhao D, Geldbach TJ, Scopelliti R, Dyson PJ (2004) Brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their zwitterions: synthesis, characterization and pKa determination. Chem-Eur J 10:4886–4893
Wagner CD, Riggs WM, Davis LE, Moulder JM, Muilenberg GE (1979) Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer, Eden Prairie
Xue G, Dai Q, Jiang S (1988) Chemical reactions of imidazole with metallic silver studied by the use of SERS and XPS techniques. J Am Chem Soc 110:2393–2395
Wiertz V, Bertrand P (1998) Identification of the N-containing functionalities introduced at the surface of ammonia plasma treated carbon fibres by combined ToF-SIMS and XPS. Universitaires de Namur, Louvain
Pan J, Yao H, Guan W, Ou H, Huo P, Wang X, Zou X, Li C (2011) Selective adsorption of 2, 6-dichlorophenol by surface imprinted polymers using polyaniline/silica gel composites as functional support: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics modeling. Chem Eng J 172:847–855
Wang C, Howell M, Raulji P, Davis Y, Mohapatra S (2011) Preparation and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles for Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP). Adv Funct Mater 21:4423–4429
Marchese J, Campderros M, Acosta A (1995) Transport and separation of cobalt, nickel and copper ions with alamine liquid membranes. J Chem Technol Biot 64:293–297
Denizli A, Salih B, Pişkin E (1997) New sorbents for removal of heavy metal ions: diamine-glow-discharge treated polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate microspheres. J Chromatogr A 773:169–178
Üçer A, Uyanik A, Aygün ŞF (2006) Adsorption of Cu (II), Cd (II), Zn (II), Mn(II) and Fe(III) ions by tannic acid immobilised activated carbon. Sep Purif Technol 47:113–118
Guo C, Hu F, Li CM, Shen PK (2008) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin on carbonized titania nanotubes and its application in a sensitive reagentless hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:819–824
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L (2012) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J Colloid and Interf Sci 368:540–546
Acknowledgements
The authors were grateful to the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21174111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, C., Hu, X., Guan, P. et al. Synthesis of water-compatible surface-imprinted composite microspheres with core–shell structure for selective recognition of thymopentin from aqueous solution. J Mater Sci 50, 427–438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8602-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8602-8