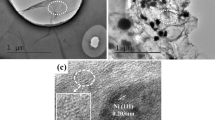
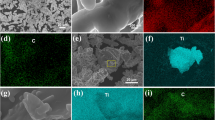
Abstract
This study investigated the preparation and mechanical performance of graphene/metal composites using Ni nanoparticles decorated graphene nanoplatelets (Ni-GPLs) as a reinforcing component in Cu matrix (Ni-GPL/Cu). Ni-GPLs consisting of well-dispersed Ni nanoparticles strongly attached on GPLs were successfully synthesized by chemically reducing Ni ions on the surface of GPLs. The Ni-GPL/Cu composites with only 0.8 vol% Ni-GPLs exhibited a significant improvement in ultimate tensile strength (UTS), being 42 % higher than that of monolithic Cu. The significant strength enhancement is attributed to the unique structure of Ni-GPLs, which was expected to generate a good dispersion and strong GPL–Cu interfacial bonding. The UTS of 0.8 vol% GPL/Cu composites was even lower than that of the monolithic Cu due to the GPL aggregates. The obtained results indicated that Ni-GPLs are novel and effective reinforcing components for greatly improving the mechanical properties of the graphene/metal composites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tjong SC, Ma Z (2000) Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng R 29:49–113
Bakshi S, Lahiri D, Agarwal A (2010) Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites—a review. Int Mater Rev 55:41–64
Chen X, Xia J, Peng J, Li W, Xie S (2000) Carbon-nanotube metal–matrix composites prepared by electroless plating. Compos Sci Technol 60:301–306
Kwon H, Estili M, Takagi K, Miyazaki T, Kawasaki A (2009) Combination of hot extrusion and spark plasma sintering for producing carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Carbon 47:570–577
Eda G, Fanchini G, Chhowalla M (2008) Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nat Nanotechnol 3:270–274
Fowler JD, Allen MJ, Tung VC, Yang Y, Kaner RB, Weiller BH (2009) Practical chemical sensors from chemically derived graphene. ACS Nano 3:301–306
Balandin AA (2011) Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat Mater 10:569–581
Kim KS, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee SY, Kim JM, Kim KS et al (2009) Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457:706–710
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Dommett GH, Kohlhaas KM, Zimney EJ, Stach EA et al (2006) Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442:282–286
Kim H, Abdala AA, Macosko CW (2010) Graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 43:6515–6530
Kuilla T, Bhadra S, Yao D, Kim NH, Bose S, Lee JH (2010) Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites. Prog Polym Sci 35:1350–1375
Goyal V, Balandin AA (2012) Thermal properties of the hybrid graphene–metal nano–micro-composites: applications in thermal interface materials. Appl Phys Lett 100:073113
Shahil KM, Balandin AA (2012) Thermal properties of graphene and multilayer graphene: applications in thermal interface materials. Solid State Commun 152:1331–1340
Goli P, Legedza S, Dhar A, Salgado R, Renteria J, Balandin AA (2013) Graphene-enhanced hybrid phase change materials for thermal management of Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 248:37–43
Shahil KM, Balandin AA (2012) Graphene—multilayer graphene nanocomposites as highly efficient thermal interface materials. Nano Lett 12:861–867
Bartolucci SF, Paras J, Rafiee MA, Rafiee J, Lee S, Kapoor D et al (2011) Graphene–aluminum nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 528:7933–7937
Chen LY, Konishi H, Fehrenbacher A, Ma C, Xu JQ, Choi H et al (2012) Novel nanoprocessing route for bulk graphene nanoplatelets reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Scripta Mater 67:29–32
Hwang J, Yoon T, Jin SH, Lee J, Kim TS, Hong SH et al (2013) Enhanced mechanical properties of graphene/copper nanocomposites using a molecular-level mixing process. Adv Mater 25:6724–6729
Kim Y, Lee J, Yeom MS, Shin JW, Kim H, Cui Y et al (2013) Strengthening effect of single-atomic-layer graphene in metal–graphene nanolayered composites. Nat Commun 4:1–7
Wang J, Li Z, Fan G, Pan H, Chen Z, Zhang D (2012) Reinforcement with graphene nanosheets in aluminum matrix composites. Scripta Mater 66:594–597
Subrahmanyam K, Manna AK, Pati SK, Rao C (2010) A study of graphene decorated with metal nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 497:70–75
Muszynski R, Seger B, Kamat PV (2008) Decorating graphene sheets with gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 112:5263–5266
Xu C, Wang X, Zhu J (2008) Graphene–metal particle nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 112:19841–19845
Pasricha R, Gupta S, Srivastava AK (2009) A facile and novel synthesis of Ag–graphene-based nanocomposites. Small 5:2253–2259
May P, Khan U, Coleman JN (2013) Reinforcement of metal with liquid-exfoliated inorganic nano-platelets. Appl Phys Lett 103:163106
Li D, Mueller MB, Gilje S, Kaner RB, Wallace GG (2008) Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat Nanotechnol 3:101–105
Wang Y, Zhao Y, Bao T, Li X, Su Y, Duan Y (2012) Preparation of Ni-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites by Pd-activated electroless deposition and their magnetic properties. Appl Surf Sci 258:8603–8608
Ji Z, Shen X, Zhu G, Zhou H, Yuan A (2012) Reduced graphene oxide/nickel nanocomposites: facile synthesis, magnetic and catalytic properties. J Mater Chem 22:3471–3477
Munir Z, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Ohyanagi M (2006) The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. J Mater Sci 41:763–777. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-6555-2
Zeng Q, Cheng J, Tang L, Liu X, Liu Y, Li J et al (2010) Self-assembled graphene-enzyme hierarchical nanostructures for electrochemical biosensing. Adv Funct Mater 20:3366–3372
Guo HL, Wang XF, Qian QY, Wang FB, Xia XH (2009) A green approach to the synthesis of graphene nanosheets. ACS Nano 3:2653–2659
Wang G, Yang J, Park J, Gou X, Wang B, Liu H et al (2008) Facile synthesis and characterization of graphene nanosheets. J Phys Chem C 112:8192–8195
Park J, Kang E, Son SU, Park HM, Lee MK, Kim J et al (2005) Monodisperse nanoparticles of Ni and NiO: synthesis, characterization, self-assembled superlattices, and catalytic applications in the Suzuki coupling reaction. Adv Mater 17:429–434
Wang C, Zhang Q, Wu QH, Ng TW, Wong T, Ren J et al (2012) Facile synthesis of laminate-structured graphene sheet–Fe3O4 nanocomposites with superior high reversible specific capacity and cyclic stability for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 2:10680–10688
Murugan AV, Muraliganth T, Manthiram A (2009) Rapid, facile microwave–solvothermal synthesis of graphene nanosheets and their polyaniline nanocomposites for energy strorage. Chem Mater 21:5004–5006
Bagri A, Mattevi C, Acik M, Chabal YJ, Chhowalla M, Shenoy VB (2010) Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide. Nat Chem 2:581–587
Nicholas M, Valentine T, Waite M (1980) The wetting of alumina by copper alloyed with titanium and other elements. J Mater Sci 15:2197–2206. doi:10.1007/BF00552307
Ang L, Hor TA, Xu G, Tung C, Zhao S, Wang J (2000) Decoration of activated carbon nanotubes with copper and nickel. Carbon 38:363–372
Cha SI, Kim KT, Arshad SN, Mo CB, Hong SH (2005) Extraordinary strengthening effect of carbon nanotubes in metal–matrix nanocomposites processed by molecular-level mixing. Adv Mater 17:1377–1381
Kim JK, Mai YW (1991) High strength, high fracture toughness fibre composites with interface control—a review. Compos Sci Technol 41:333–378
Jiang L, Li Z, Fan G, Cao L, Zhang D (2012) Strong and ductile carbon nanotube/aluminum bulk nanolaminated composites with two-dimensional alignment of carbon nanotubes. Scripta Mater 66:331–334
Lee C, Wei X, Kysar JW, Hone J (2008) Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321:385–388
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Science and Technology Research Foundation of Hebei Education Department for Young Teachers in University (No. QN20131168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Che, H., Liu, X. et al. Highly enhanced mechanical properties in Cu matrix composites reinforced with graphene decorated metallic nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 49, 3725–3731 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8082-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8082-x