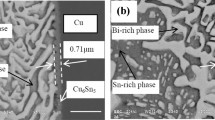
Abstract
Intermetallic compounds (IMCs) that form at eutectic Sn3.5Ag/Cu and pure Sn/Cu interfaces during solid-state aging are comparatively studied in terms of their respective morphological formations, orientation evolution behaviors, and growth kinetics. During solid-state aging, all the interfacial Cu6Sn5 grains evolve into a layer-type morphology, except for select grains that experience abnormal growth. This abnormal growth is caused by the preferential growth of the Cu6Sn5 at the grain boundary in solder matrix. Meanwhile, textured growth occurs in the Cu6Sn5 layer formed at the eutectic Sn3.5Ag/Cu interface. The morphology of each texture is determined by the initial joint preparation conditions and affects the growth of interfacial IMCs. The results reveal that Sn diffusion occurs faster along the [0001] direction of the Cu6Sn5 crystal than along angles from 25° to 50° relative to the [0001] direction. Additionally, the effects of solder composition on the interfacial IMC growth are evaluated. The results indicate that Ag addition retards IMC growth upon aging by inhibiting diffusion of Cu.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tu KN (2007) Solder joint technology: materials, properties, and reliability. Spr Ser Mater Sci 117:1–370. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-38892-2
Laurila T, Vuorinen V, Kivilahti JK (2005) Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater Sci Eng R 49:1–60. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2005.03.001
Zeng K, Tu KN (2002) Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology. Mater Sci Eng R 49:55–105. doi:10.1016/S0927-796X(02)00007-4
Choi S, Bieler TR, Lucas JP, Subramanian KN (1999) Characterization of the growth of intermetallic interfacial layers of Sn–Ag and Sn–Pb eutectic solders and their composite solders on Cu substrate during isothermal long-term aging. J Electron Mater 28(11):1209–1215. doi:10.1007/s11664-999-0159-y
Abdelhadi MO, Ladani L (2012) IMC growth of Sn-3.5Ag/Cu system: combined chemical reaction and diffusion mechanisms. J Alloy Compd 537:87–99. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.04.068
Gorlich J, Baither D, Schmitz G (2011) Reaction kinetics of Ni/Sn soldering reaction. Acta Mater 58:3187–3197. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2010.01.027
Hsiao HY, Liu CM, Lin HW, Liu TC, Lu CL (2012) Unidirectional growth of microbumps on (111)-oriented and nanotwinned copper. Science 336:1007–1010. doi:10.1126/science.1216511
Tu KN (2011) Reliability challenges in 3D IC packaging technology. Microelectron Reliab 51:517–523. doi:10.1016/j.microrel.2010.09.031
Chen YJ, Chung CK, Yang CR, Kao CR (2013) Single-joint shear strength of micro Cu pillar solder bumps with different amounts of intermetallics. Microelectron Reliab 53:47–52. doi:10.1016/j.microrel.2012.06.116
Liu ZQ, Shang PJ, Tan FF, Li DX (2013) Microstructural study on kirkendall void formation in Sn-Containing/Cu solder joints during solid-state aging. Microsc Microanal 19(S5):105–108. doi:10.1017/S1431927613012439
Ma X, Wang F, Qian Y, Yoshida F (2003) Development of Cu–Sn intermetallic compound at Pb-Free solder/Cu joint interface. Mater Lett 57:3361–3365. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00075-2
Cheng FJ, Gao F, Nishikawa H, Takemoto T (2009) Interaction behavior between the additives and Sn in Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu-based solder alloys and the relevant joint solderability. J Alloy Compd 472:530–534. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.05.017
He HW, Xu GC, Guo F (2009) Effect of small amount of rare earth addition on electromigration in eutectic SnBi solder reaction couple. J Mater Sci 44:2089–2096. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3276-3
Gong JC, Liu CQ, Conway PP, Silberschmidt VV (2008) Evolution of CuSn intermetallics between molten SnAgCu solder and Cu substrate. Acta Mater 56:4291–4297. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2008.04.063
Gong JC, Liu CQ, Conway PP, Silberschmidt VV (2009) Initial formation of CuSn intermetallic compounds between molten SnAgCu solder and Cu substrate. Scripta Mater 60:333–335. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.10.029
Yang M, Li MY, Wang L (2011) Cu6Sn5 morphology transition and its effect on mechanical properties of eutectic Sn–Ag solder joints. J Electron Mater 40:176–188. doi:10.1007/s11664-010-1430-y
Date M, Shoji T, Fujiyoshi M, Sato K, Tu KN (2004) Ductile-to-brittle transition in Sn–Zn solder joints measured by impact test. Scripta Mater 51:641–645. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.06.027
Yang M, Li MY, Wang CQ (2012) Interfacial reactions of eutectic Sn3.5Ag and pure tin solders with Cu substrates during liquid-state soldering. Intermetallics 25:86–94. doi:10.1016/j.intermet.2012.02.023
Huang ML, Loeher T, Ostmann A, Reichi H (2005) Role of Cu in dissolution kinetics of Cu metallization in molten Sn-based solders. Appl Phys Lett 86:101908. doi:10.1063/1.1925317
Wang HQ, Zhao H, Sekulic DP, Qian YY (2008) A comparative study of reactive wetting of lead and lead-free solders on Cu and (Cu6Sn5/Cu3Sn)/Cu substrates. J Electron Mater 37:1640–1646. doi:10.1007/s11664-008-0502-8
Zou HF, Yang HJ, Zhang ZF (2011) Coarsening mechanisms, texture evolution and size distribution of Cu6Sn5 between Cu and Sn-based solders. Mater Chem Phys 131:190–198. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.08.061
Flanders DR, Jacobs EG, Pinizzotto RF (1997) Activation energies of intermetallic growth of Sn–Ag eutectic solder on copper substrates. J Electron Mater 26:883–887. doi:10.1007/s11664-997-0268-4
Vianco PT, Erickson KL, Hopkins PL (1994) Solid state intermetallic compound growth between copper and high temperature, tin-rich solders-part I: experimental analysis. J Electron Mater 23:721–727. doi:10.1007/BF02651365
Deng X, Piotrowski G, Williams JJ, Chawla N (2003) Influence of initial morphology and thickness of Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn intermetallics on growth and evolution during thermal aging of Sn–Ag solder/Cu joints. J Electron Mater 32:1403–1413. doi:10.1007/s11664-003-0108-0
Choi WK, Lee HM (2000) Effect of soldering and aging time on interfacial microstructure and growth of intermetallic compounds between Sn–3.5Ag solder alloy and Cu substrate. J Electron Mater 29:1207–1213. doi:10.1007/s11664-000-0014-7
Yang M, Li M, Wang L, Fu Y, Kim J, Weng L (2011) Growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 grains formed at an Sn3.5Ag/Cu interface. Mater Lett 65:1506–1509. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2011.02.056
Li M, Yang M, Kim J (2012) Textured growth of Cu6Sn5 grains formed at a Sn3.5Ag/Cu interface. Mater Lett 66:135–137. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2011.08.014
Lu M, Shih DY, Lauro P, Goldsmith C, Henderson DW (2008) Effect of Sn grain orientation on electromigration degradation mechanism in high Sn-based Pb-free solders. Appl Phys Lett 92:211909. doi:10.1063/1.2936996
Yang M, Cao Y, Joo S, Chen HT, Ma X, Li MY (2014) Cu6Sn5 precipitation during Sn-based solder/Cu joint solidification and its effects on the growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds. J Alloy Compd 582:688–695. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.013
Li JF, Mannan SM, Clode MP, Whalley DC, Hutt DA (2006) Interfacial reactions between molten Sn–Bi–X solders and Cu substrates for liquid solder interconnects. Acta Mater 54:2907–2922. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2006.02.030
Feng D (1990) Metal physics (Volume 2) the phase transition, 1st edn. Science Press, Beijing
Porter DA, Easterling KE (1992) Phase transformation in metals and alloys, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Ghosh G (2000) Coarsening kinetics of Ni3Sn4 scallops during interfacial reaction between liquid eutectic solders and Cu/Ni/Pd metallization. J Appl Phys 88:6887–6896. doi:10.1063/1.1321791
Bernal JD (1928) The complex structure of the copper-tin intermetallic compounds. Nature 122:54. doi:10.1038/122054a0
Gangulee A, Das GC, Bever MB (1973) An X-ray diffraction and calorimetric investigation of the compound Cu6Sn5. Metall Trans 4:2063–2066. doi:10.1007/BF02643268
Larsson AK, Stenberg L, Lidin S (1995) Crystal structure modulations in η-Cu5Sn4. Z Kristallogr 210:832–837. doi:10.1524/zkri.1995.210.11.832
Larsson AK, Stenberg L, Lidin S (1994) The superstructure of domain-twinned η’-Cu6Sn5. Acta Crystallogr B 50:636–643. doi:10.1107/S0108768194004052
Li M, Zhang Z, Kim J (2011) Polymorphic transformation mechanism of η and η’ in single crystalline Cu6Sn5. Appl Phys Lett 98:201901. doi:10.1063/1.3590715
Shang PJ, Liu ZQ, Pang XY, Li DX, Shang JK (2009) Growth mechanisms of Cu3Sn on polycrystalline and single crystalline Cu substrates. Acta Mater 57:4697–4706. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2009.06.025
Gao F, Qu JM (2012) Calculating the diffusivity of Cu and Sn in Cu3Sn intermetallic by molecular dynamics simulations. Mater Lett 73:92–94. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2012.01.014
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51175116, and the Shenzhen Special Funds for Development of Strategic Emerging Industries (No. CXZZ20120829103358067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Chen, H., Ma, X. et al. Solid-state interfacial reaction of eutectic Sn3.5Ag and pure tin solders with polycrystalline Cu substrate. J Mater Sci 49, 3652–3664 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8069-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8069-7