Abstract
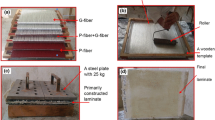
The overall objective of the investigation presented in this paper was to study the effect of dispersion of core–shell polymer (CSP) particles within the ply interfaces on damage evolution of glass/epoxy laminates under impact loading. These laminates were fabricated with the CSP particle dispersion controlled to 14 % of the total weight of the used prepreg. A series of impact experiments were done with instrumental drop tower device at all probable impact energies within a practical low velocity impact range. The damage phenomena occurring in the internal microstructure of the laminates were analysed with the help of scanning electron microscope and correlated to the structural response of the laminate. The predominant damage modes were dependent on the magnitude of the applied impact energy. The CSP particle incorporation does not change the sequence of the fracture events but it delays and mitigates the damage creation. The deformation of the CSP particles and the tearing of their outer shells absorb most of the impact energy thereby preventing initiation of matrix cracks at lower impact energies and delaying fibre damage at higher energies. The crushed particles along with their nano-size rubber cores impede crack propagation requiring the cracks to follow torturous paths consequently dissipating additional amount of energy. These particles also promote elastic energy absorption of the laminates minimizing their tendency to fracture easily under impact. The ultimate load bearing capability of the modified laminate showed 60 % improvement and the deflection characteristics indicated lower proneness to impact.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brostow W, Haley E, Lobland H (2010) J Mater Sci 45:242. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3926-5
Cartié DDR, Irving PE (2002) Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 33:483
Wang SX, Wu LZ, Ma L (2010) Mater Des 31:118
Kim KY, Ye L (2012) J Mater Sci 47:7280. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6682-x
Zumpano G, Fox M, Stronge WJ, Sutcliffe MPF (2008) J Mater Sci 43:6668. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2880-y
Pegoretti A, Fabbri E, Migliaresi C, Pilati F (2004) Polym Int 53:1290
Richardson MOW, Wisheart MJ (1996) Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 27:1123
Sela N, Ishai O (1989) Compos 20:423
Garg AC, Mai YW (1988) Compos Sci Tech 31:179
Takemura K, Fujii T (2000) JSME Int J, Ser A 43:186
Shi AX, Gong TW, Yiu WM (2013) J Mater Sci 48:3546. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7149-4
Kosar I, Ullah KS, Kim JK, Munir A (2008) Adv Mater Res 47:1205
Soliman EM, Sheyka MP, Taha MR (2012) Int J Impact Eng 47:39
Gupta A, Choudhary V (2013) J Mater Sci 48:3347. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-7025-7
Jang K, Cho WJ, Ha CS (1999) Compos Sci Tech 59:995
Caneva C, Olivieri S, Santulli C, Bonifazi G (1993) Compos Struct 25:121
Wu E, Wang J (1995) J Compos Mater 29:2254
Tan KT, Watanabe N, Iwahori Y (2012) Int J Damage Mech 2012(21):51
Zhang X, Hounslow L, Grassi M (2006) Compos Sci Tech 66:2785
Farley GL, Smith BT, Maiden J (1992) J Reinf Plast Compos 11:787
Mouritz AP, Leong KH, Herszberg I (1997) Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 28:979
Steeves CA, Fleck NA (2006) Int J Solids Struct 43:3197
Hirai Y, Hamada H, Kim JK (1998) Compos Sci Tech 58:91
Bledzki AK, Gassan J, Kessler A (1999) J Test Eval 27:36
El-Habak AM (1993) Compos 24:341
Radchenko A, Radchenko P (2011) J Mater Sci 46:2720. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5142-8
Malhotra A, Guild FJ, Pavier MJ (2008) J Mater Sci 43:6661. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2863-z
Deka LJ, Bartus SD, Vaidya UK (2008) J Mater Sci 43:4399. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2595-0
Gweon SY, Bascom WD (1992) J Mater Sci 27:2035. doi:10.1007/BF01117915
Shyr TW, Pan YH (2003) Compos Struct 62:193
Lagace PA, Wolf E (1995) AIAA J 33:1106
Belingardi G, Vadori R (2002) Int J Impact Eng 27:213
Davies GAO, Zhang X (1995) Int J Impact Eng 16:149
Feraboli P, Kedward KT (2004) AIAA J 42:2143
Feraboli P (2006) J Aircr 43:1710
Abrate S (2001) Compos Struct 51:129
Kostopoulos V, Baltopoulos A, Karapappas P, Vavouliotis A, Paipetis A (2010) Compos Sci Tech 70:553
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge and thank The Dow Chemical Company, Singapore for their kind support in providing the CSP particles for this project. The first author gratefully acknowledges the NTU research scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M., Joshi, S.C. Damage evolution in glass/epoxy composites engineered using core–shell microparticles under impact loading. J Mater Sci 48, 8354–8367 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7635-8