Abstract
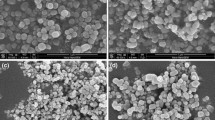
The paper reports the synthesis, structural and high frequency dielectric properties of Ba(Zr x Ti1−x )O3,BZT, nanopowders where x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3. These powders were synthesized using both microwave assisted and conventional heating, with the former requiring lower temperature and shorter times compared to the latter, viz., 700 °C for 30 min versus 900 °C for 5 h. The synthesized nanopowders were characterized using X-ray diffraction, micro-Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, BET surface area analysis, differential scanning calorimetry and high frequency dielectric measurements. All the microwave synthesized BZT compositions were found to have well crystallized, finer nanoparticles with less agglomeration and higher dielectric permittivity compared to the conventionally prepared powders. The rapidity and less demanding processing conditions associated with the microwave assisted method augers well for the general applicability of the technique for the production of nanocrystalline powders.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe B, Cook WR, Jaffe H (1981) Piezoelectric ceramics. Academic Press, New York, p 271
Bernadi MLB, Antoneli E, Lourenco AB, Feitosa CAC, Maia LJQ, Hernades AC (2007) J Therm Anal Calorim 87:725
Landolt-Bornstein (1981) Landolt-Bornstein numerical data and functional relationship in science and technology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, vol III/28a, p 268; vol III/16a, p 422
Hennings D, Schnell A (1982) J Am Ceram Soc 65:539
Neirman SM (1988) J Mater Sci 23:3973. doi:10.1007/BF01106823
McCauley D, Newnham RE, Randall CA (1998) J Am Ceram Soc 81:979
Chen JF, Shen ZG, Liu FT, Liu XL, Yun J (2003) Scripta Mater 49:509
Tang XG, Wang J, Wang XX, Chan HLW (2004) Solid State Commun 131:163
Kumar M, Garg A, Kumar R, Bhatnagar MC (2008) Phys B 403:1819
Reddy SB, Rao KP, Rao MSR (2007) Scripta Mater 57:591
Outzourhit A, Idrissi Raghni MAE, Hafid ML, Bensamka F, Abdelkader O (2002) J Alloys Compd 340:214
Gogotsi Y (2006) Nanomaterials handbook. Taylor & Francis, London, p 363
Binner J, Vaidhyanathan B (2008) J Eur Ceram Soc 28:1329
Rao KJ, Vaidhyanathan B, Ganguli M, Ramakrishnan PA (1999) Chem Mater 11:882
Janney MA, Kimrey HD (1991) Microwave processing of materials II. In: Snyder WB Jr, Sutton WH, Iskander MF, Johnson DL (eds) Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, vol 189, p 215
Sutton WH (1992) Microwave processing of materials III. In: Beatty RL, Sutton WH, Iskander MF (eds) Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, vol 269, p 3
Clark DE (1997) Microwaves: theory and application in materials processing IV. In: Clark D, Sutton WH, Lewis DA (eds) Ceramics Transactions, vol 80, p 61
Robb GR, Harrison A, Whittaker AG (2002) Phys Chem Commun 19:135
Vinothini V, Singh P, Balasubramanian M (2006) Ceram Int 32:99
Vaidhyanathan B, Wang J, Binner JGP, Raghavendra R (2003) The effect of conventional, microwave and hybrid heating on the sintering of ceramics. In: 9th international conference on microwave and high frequency heating, Loughborough, p 31
Vaidhyanathan B, Annapoorani K, Binner JGP, Raghavendra R (2009) Ceram Eng Sci Proc 30:11
Wang J, Binner J, Vaidhyanathan B (2006) J Am Ceram Soc 89:1977
Dimitrakis GA (2005) PhD Thesis, University of Nottingham
Plonskii YA, Pavlova GA, Savel’ev VN, Milovidova TV, Vinogradov VB (1971) Glass Ceram 28:182
Dobal PS, Dixit A, Katiyar RS, Yu Z, Guo R, Bhalla AS (2001) J Raman Spectrosc 32:69
Qi JQ, Wang Y, Chen WP, Li LT, Chan HTW (2006) J Nanoparticle Res 8:959
Thakur OP, Prakash C, Agarwal DK (2002) Mater Sci Eng B96:221
Sun W, Li J (2006) Mater Lett 60:1599
Ho IC, Fu SL (1990) J Mater Sci 25:4699. doi:10.1007/BF01129927
Asiaie R, Zhu W, Akbar SA, Dutta PK (1996) Chem Mater 8:226
Fathi Z, Ahmed I, Simmons JH, Clark DE, Lodding AR (1991) Microwaves: theory and application in materials processing. In: Clark DE, Gac FD, Sutton WH (eds) Ceram Transactions, vol 21, p 623
Hassine JGP, Hassine NA, Cross TE (1995) J Mater Sci 30:5389. doi:10.1007/BF00351548
Rybakov KI, Semenov VE (1994) Phys Rev B 49:64
Rybakov KI, Semenov VE (1995) Phys Rev B 52:3032
Hanxing L, Yongwei L, Hanlin Z, Shixi O (1997) Sci China Ser A 40:843
Zhang H, Ouyang S, Liu H, Li Y (1996) Microwave processing of materials V. In: Iskander MK, Kiggans JO, Bolomey JC (eds) Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, vol 430, p 447
Vaidhyanathan B, Singh AP, Agrawal DK, Shrout TR, Roy R (2001) J Am Ceram Soc 84:1197
Vaidhyanathan B, Binner JGP (2006) J Mater Sci 41:5954. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0260-z
Vaidhyanathan B, Raizada P, Rao KJ (1997) J Mater Sci Lett 16:2022
Willert-Porada M, Bartusch W, Dhupia G, Müller G, Nagel A, Wötting G (2000) In: Müller G (ed) Ceramics-processing, reliability, tribology and wear. Euromat 12:87. Wiley-VCH, Berlin
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the EPSRC/TSB of the United Kingdom for the research funding and one of the authors (VV) thank the Science Faculty Fellowship Fund of the Loughborough University for her PhD scholarship. Thanks are also due to Dr. George A Dimitrakis of the Nottingham University, UK for timely help with the high frequency dielectric measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinothini, V., Vaidhyanathan, B. & Binner, J. Microwave assisted synthesis of barium zirconium titanate nanopowders. J Mater Sci 46, 2155–2161 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5052-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5052-9