Abstract
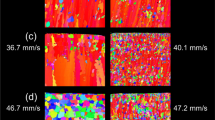
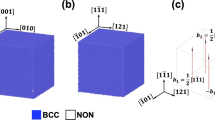
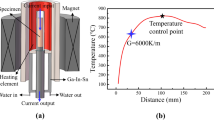
Solid–liquid interface morphologies of a nickel-base single crystal superalloy AM3 were investigated under high thermal gradient. The critical velocities of planar–cellular and cellular–dendritic transition were greatly increased by high thermal gradients. A high thermal gradient was of great benefit to dendrite refinement. Experimental results showed that the primary and secondary dendrite arm spacings decreased with increasing cooling rate. As expected, the segregation of elements was suppressed and the size of the gamma prime (γ′) phase decreased significantly with increasing withdrawal rates. The shape of γ′ in interdendritic region kept cuboidal at higher withdrawal rate. It was found that the withdrawal rates had little influence on the crystallographic orientation in high thermal gradient directional solidification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durand-Charre M (1998) The microstructure of superalloys. CRC Press, Boca Raton
D’Souza N, Ardakani MG, Mclean M, Shollock BA (2000) Metall Mater Trans A 31:2877
Kumar A, Dutta P (2009) J Mater Sci 44:3952. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3539-z
Madison J, Spowart JE, Rowenhorst DJ, Pollock TM (2008) JOM 60:26
Tang JJ, Xue X (2009) J Mater Sci 44:745. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3157-1
Kurz W, Fisher DJ (1981) Acta Metall 29:11
Trivedi R (1984) Metall Trans A 15:977
Hunt JD, Lu S-Z (1996) Metall Mater Trans A 27:611
Hosch T, England LG, Napolitano RE (2009) J Mater Sci 44:4892. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3747-6
Clemens ML, Price A, Bellows RS (2003) JOM 55:27
Elliott AJ, Tin S, King WT, Huang S-C, Gigliotti MFX, Pollock TM (2004) Metall Mater Trans A 35:3221
Fu HZ, Geng XG (2001) Sci Technol Adv Mater 2:197
Liu L, Huang TW, Zhang J, Fu HZ (2007) Mater Lett 61:227
Caron P, Ohta Y, Nakagawa YG, Khan T (1988) In: Duhl DN et al (eds) Superalloys 1988. The Metallurgical Society, Warrendale, PA, p 215
Gunturi SSK, MacLachlan DW, Knowles DW (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 289:289
Carter P, Cox DC, Gandin CA, Reed RC (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 280:233
Ganesan S, Chan CL, Poirier DR (1992) Mater Sci Eng A 151:97
Gündüz M, Çadırlı E (2002) Mater Sci Eng A 327:167
Guo ZQ, Fu T, Fu HZ (2000) Mater Charact 44:431
Caldwell EC, Fela FJ, Fuchs GE (2004) JOM 56:44
Liu L, Zhang J, Huang TW, Fu HZ (2005) Mater Sci Forum 475–479:665
Guo XP, Fu HZ, Sun JH (1997) Metall Mater Trans A 28:997
Ma D, Sahm P (1998) Metall Mater Trans A 29:1113
Du W (1998) Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University (in Chinese)
Li L, Overfelt RA (2002) J Mater Sci 37:3521. doi:10.1023/A:1016527509815
Vijayakumar M, Tewari SN, Lee JE, Curreri PA (1991) Mater Sci Eng A 132:195
Quested PN, McLean M (1980) In: Kirman I et al (eds) Conference on solidification technology in the foundry and cast house. The Metals Society, London, p 586
Kermanpur A, Varahraam N, Engilehei E, Mohammadzadeh M, Davami P (2000) Mater Sci Technol 16:579
Wilson BC, Cutler ER, Fuchs GE (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 479:256
Xiao JM (1987) Alloy phase and phase transformation. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Esaka H, Daimon H, Natsume Y, Ohsasa K, Tamura M (2002) Mater Trans 43:1312
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50771081) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB605202) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Liu, L., Yu, Z. et al. Influence of directional solidification variables on the microstructure and crystal orientation of AM3 under high thermal gradient. J Mater Sci 45, 6101–6107 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4696-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4696-9