Abstract
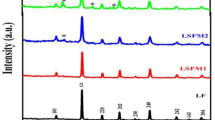
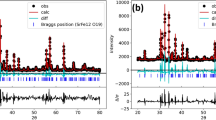
Rare earth (RE) and manganese-modified lead titanate ceramics were studied concerning the presence of two peaks in the temperature dependence of the dielectric permittivity. An eventual incorporation of the RE into A-site and/or B-site in the perovskite structure and the oxygen migration were considered as causes of the observed phenomenon. The structural analysis showed that at least a small amount of Ti4+ could be substituted by the RE ions. It was considered from the pyroelectric and electrical conductivity results that, even when an eventual incorporation of the RE into the A-site and/or B-site of the structure could be possible, both peaks could not be associated with paraelectric–ferroelectric (PE-FE) phase transitions. The observed peak at lower temperatures has been associated with the PE-FE phase transitions, whereas the hopping of oxygen vacancies has been considered as the cause for the dielectric anomaly observed at higher temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rossetti GA, Cross LE, Cline JP (1999) J Mater Sci 30:24. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352127
Ito Y, Takeuchi H, Nagatsuma N, Jyomura S, Ashida S (1981) J Appl Phys 52:3223
Ichinose N (1985) Am Ceram Soc Bull 64:1581
Pérez-Martínez O, Calderón F, Pentón A, Suaste E, Rivera M, Leccabue F, Boccelli G, Watts E (1995) Rev Mex Fis 41:85
Pérez-Martínez O, Saniger JM, Peláiz-Barranco A, Calderón-Piñar F (1999) J Mater Res 14:3083
Pérez-Martínez O, Saniger JM, Torres-García E, Flores JO, Calderón-Piñar F, Llópiz JC, Peláiz-Barranco A (1997) J Mat Sci Lett 16:1161
Ch Ang, Yu Z, Cross LE (2000) Phys Rev B 62:228
Johnson DW, Cross LE, Hummel FA (1970) J Appl Phys 41:2828
Stumpe R, Wagner D, Bauerle D (1983) Phys Stat Sol A 75:143
Bidault O, Goux P, Kchikech M, Belkaomi M, Maglione M (1994) Phys Rev B 49:7868
Kang BS, Choi SK, Park CH (2003) J Appl Phys 94:1904
Peláiz-Barranco A, Guerra JDS, López-Noda R, Araújo EB (2008) J Phys D Appl Phys 41:215503
Takeuchi H, Jhomura S, Nakaya P, Ishikawa Y (1983) Jpn J Appl Phys 22:166
Takeuchi H, Jhomura S, Nakaya P (1985) Jpn J Appl Phys 24:36
Tura V, Mitoseriu L, Papusoi C, Osaka T, Okuyama M (1998) J Electroceram 2:163
Kinoshita K, Yamaji A (1976) J Appl Phys 47:371
Frey MH, Payne DA (1996) Phys Rev B 54:3158
Arlt G (1990) J Mater Sci 25:2655. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584864
Zhong WL, Wang YG, Zhang PL (1994) Phys Lett A 189:121
Lines ME, Glass AM (1977) Principles and applications of ferroelectrics and related materials. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Strukov BA, Levanyuk AP (1998) Ferroelectric phenomena in crystal. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Xu Y (1991) Ferroelectric materials and their applications. Elsevier Science Publishers, Netherlands
Cotton FA, Wilkinson G, Wilkinson CA, Bochmann M (1999) Advanced inorganic chemistry. Wiley, New York
Halliyal A (1987) Am Ceram Soc Bull 66:671
Ramírez-Rosales D, Zamorano-Ulloa R, Pérez-Martínez O (2001) Solid State Comm 118:371
Saiful-Islam M (2000) J Mater Chem 10:1027
Jiménez B, Vicente JM (1998) J Phys D Appl Phys 31:446
Lang SB (1974) Ferroelectrics 7:231
Berlincourt D (1956) IRE Trans Ultrason Eng 4:53
Jaffe H (1958) J Am Ceram Soc 41:494
Berlincourt D, Crolik C, Jaffe H (1960) Proc IRE 48:220
Blood HL, Levine S, Roberts NH (1956) J Appl Phys 27:660
Northrip JW (1960) J Appl Phys 31:2293
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Third World Academy of Sciences (RG/PHYS/LA No. 99-050, No. 02-225, No. 05-043) and FAPESP Brazilian agency (Proc. No. 06/60013-5) for financial support, and ICTP for financial support of Latin-American Network of Ferroelectric Materials (NET-43). Dr. Peláiz-Barranco wishes to thank Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for financial support. Dr. Calderón-Piñar wishes to thank the ICTP program for Training and Research in Italian laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peláiz-Barranco, A., Guerra, J.D.S., Calderón-Piñar, F. et al. Dielectric response features and oxygen migration on rare earth modified lead titanate ferroelectric ceramics. J Mater Sci 44, 204–211 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3100-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3100-5