Abstract
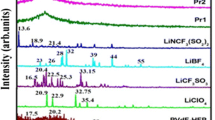
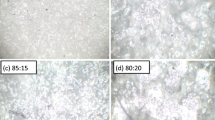
A composite polymer electrolyte film was prepared by dissolving polyethylene glycol (PEG) with different molecular weight in acetonitrile, and vapor-induced response behavior was investigated upon exposure to various chemical environments. The effect of lithium concentrations on ionic conductivity and response was discussed. The surface microporous structures and vapor sensitive conductivity of the films in the case of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) were examined with the PVDF content changed. The crystalline and micro-phase isolation behavior were characterized by a differential scanning calorimeter, an environmental scanning electron microscope, a polarization microscope and a wide-angle X-ray diffraction. The experimental results indicated that PEG/Li+ salt composite films exhibited preferential responsive characteristics. The responsivities to ethanoic acid, chloroform, and acetone vapors were enhanced with molecular weight of PEG increased. The conductivity was increased at a higher lithium salt concentration, and also enhanced with PEG content increased, while the responsivities decreased. The formation of microporous structures on the surface of the mixed PEG/PVDF composite films enlarged their specific area and strikingly improved the responsive performances. The changes in conduction behavior were explained from the viewpoint of the swelling and free volume theories as well as a hydrogen bond interaction, combined with the structural and morphological analyses. The introduction of an ionogenic matter also has an important effect on ionic conductivity and responsiveness.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Polymer 14:589
Meyer WH (1998) Adv Mater 10:439
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Nature 414:359
Amand MB, Chabagno JM, Duclot MJ (1979) Fast ion transport in solids electrodes and electrolytes. North-Holland Amsterdam, New York, p 131
Kim YW, Lee W, Choi BK (2000) Electrochimica Acta 45:147
Zhou H, Gu N, Dong S (1998) J Electroanal Chem 441:153
Dong S, Gu N, Zhou H (1998) J Electroanal Chem 441:95
Qian XM, Gu NY, Cheng ZL (2001) Electroanal Acta 46:1829
Yu WX, Yong SW, Guo GR (1994) Chin J National Uni Defense Technol 16:1
Zhao ZC, Liu K, Zheng H (2005) Instrument Techn Sens 3:1
Xia Y, Lu YL, Sun LC (2005) Comput Eng Sci 27:25
Li J, Xi JY, Song Q, Tang XZ (2005) Chin Sci Bull 3:305
Kumar GG, Kim P, Nahm K, Elizabeth RN (2007) J Membr Sci 303:126
Hilal N, Ogunbiyi OO, Miles NJ, Nigmatullin R (2005) Sep Sci Technol 40:1957
Xu Z, Li L, Wu F, Tan S, Zhang Z (2005) J Membr Sci 255:125
Kim JW, Ji KS, Lee JP, Park JW (2003) J Power Sources 119–121:415
Ahn JH, Wang GX, Liu HK, Dou SX (2003) J Power Sources 119–121:422
Liang XH, Guo YQ, Gu LZ, Ding EY (1995) Macromolecules 28:6551
Chen QC, Deng HY, Ma YM (2002) Chin Surfactant Detergent Cosmet 32:2
Gu NY, Qian XM, Cheng ZL, Jiang JG, Yang XR, Dong SJ (2001) Chem Res Chin Univ 22:1403
Rodgers PA (1993) J Appl Polym Sci 50:2075
Luo YL, Wang GC, Zhang BY, Zhang ZP (1998) European Polym J 34:1221
Liu YX, Luo YL (2006) Mater Res Innov 10:52
Luo J, Wang P, Li J, Xie X, Fan C, He C, Zhong Y (2006) J Bionic Eng 23:125
Zhao WY, Wang YJ (2003) Functional polymer materials chemistry, 2nd edn. Chem Ind Press, Beijing, p 53
Nishio K, Tsuchiya T (2001) Sol Energ Mat Sol C 68:295
Bonino F, Croce F, Panero S (1994) Solid State Ionics 70–71:654
Ikeda Y, Hiraoka T, Ohta S (2004) Solid State Ionics 175:261
Chen J, Tsubokawa N (2000) Poly Adv Tech 11:101
Tsubokawa N, Yukio S, Okazaki M (1999) Poly Bull 42:425
Saito Y, Kataoka H, Stephan AM (2001) Macromolecules 34:6955
Carvalho LM, Guegan P, Cheradame H, Gomes AS (2000) Eur Polym J 36:401
Usami H, Takagi K, Sawaki Y (1992) J Chem Soc: Faraday Trans 88:77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Wang, S. & Li, Z. Characterization, microstructure, and gas sensitive response behavior of PEG/lithium salt polymer electrolyte films. J Mater Sci 43, 174–184 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2125-5