Abstract
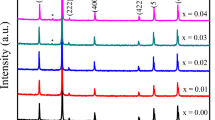
Mn0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite synthesized by coprecipitation method is investigated in the present work. D.C. resistivity is studied as a function of temperature and values upto 102 times greater than those for samples prepared by the conventional ceramic method are observed. It is found that resistivity decreases with increase in temperature. The initial permeability values are high as compared to those prepared by soft chemical route. Initial permeability is found to increase with increase in temperature. At a certain temperature, called the Curie temperature, it attained a maximum value, after which the initial permeability is found to decrease. Even at nanolevel, appreciable value of initial permeability is obtained. The particle size is calculated using Scherrer equation for Lorentzian peak, which comes out between 9 nm and 19 nm. Possible mechanisms contributing to these processes have been discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh M, Sud SP (2000) Mod Phys Lett 14:531
Singh M, Chauhan BS (2000) Int Mod Phys B 14:1593
Rosales MI, Amano E, Cuautle MP, Valenzuela R (1997) Mater Sci Eng B 49:221
Thakur A, Singh M (2003) Ceramic Int 29:505
Thakur A, Mathur P, Singh M (2007) J Phys Chem Solids 68:378
Verma A, Goel TC, Mendiratta RG, Alam MI (1999) Mater Sci Eng B 60:156
Verma A, Goel TC, Mendiratta RG (2000) Mater Sci Technol 16:712
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addison Wesley Reading, MA
Caizer C, Stefanescu M (2003) Physica B 327:129
Singh M (1996) Ph.D. thesis, Himachal Pradesh University, Shimla, India
Rado GT, Wright RW, Emerson WH (1960) Phys Rev 80:273
Rado GT, Wright RW, Emerson WH, Terris A (1952) Phys Rev 88:909
Rado GT (1953) Rev Mod Phys 25:81
Snoek JL (1947) New developments in ferromagnetic materials. Elsevier Publishing, New York
Gieraltowski J, Globus A (1977) IEEE Trans Magn 13:1359
Globus A (1977) Proc J Phys Colloq 38:C1
Soohoo RF (1960) Theory and application of ferrites. Prentice-Hall, USA
Yue Z, Zhou J, Wang X, Gui Z, Li L (2001) J Mater Sci Lett 20:1327
Iwauchie K (1971) Jap J Appl Phys 10:1520
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathur, P., Thakur, A. & Singh, M. Low temperature processing of Mn–Zn nanoferrites. J Mater Sci 42, 8189–8192 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1690-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1690-y