Abstract
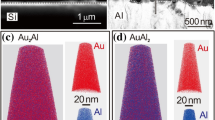
The purpose of this study is to understand the morphological changes that occur during annealing of Al–Au wire-bonds, by analyzing the interface region of annealed model wire-bonded samples between 5N (99.999%) Au wires and Al pads. Due to the small length scale of the intermetallic region at the interface of the bond, the analysis was done using scanning/transmission electron microscopy combined with energy dispersive spectroscopy. Samples were prepared using a dual-beam focused ion beam system. Microstructural characterization showed that during annealing, a Au-rich intermetallic region was formed under the bond and at the periphery of the bond. Two types of failures occurred during annealing: crack formation at the bond periphery due to an increase in volume during intermetallic growth and the formation of stresses; and oxidation of the AlAu4 phase adjacent to the Au ball, which resulted in the formation of continuous cracks between the Au ball and the intermetallic region. The characteristic void-line found inside the intermetallic region played no part in failure that occurred during exposure to elevated temperatures.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harman G (1997) Wire-bonding in microelectronics materials process reliability and yield. McGraw-Hill Publishers, NY
Zhang X, Yan TT (2006) Thin Solid Films 504[1–2]:355
Noolu NJ, Murdeshwar NM, Ely KJ, Lippold JC, Baeslack WA (2004) J Mater Res 19(5):1374
Breach CD, Tok CW, Wulff F, Calpito D (2004) J Mater Sci 39(19):6125
Maiocco L, Smyers D, Kadiyala S, Baker I (1990) Mater Charact 24(4):293
Clatterbaugh GV, Weiner JA, Charles HK (1984) IEEE Trans Compon Hybrids Manufacture Technol 7(4):349
Majni G, Nobili C, Ottaviani G, Costato M, Galli E (1981) J Appl Phys 52(6):4047
Markwitz A, Matz W (1970) Surf Interface Anal 26(9):650
Philofsky E (1970) Solid-State Electron 13(10):1391
Xu C, Sritharan T, Mhaisalkar SG (2007) Scripta Mater 56(6):549
Chang HS, Hsieh KC, Martens T, Yang A (2004) IEEE Trans Compon Pack Technol 27(1):155
Ji H, Li M, Wang C, Bang HS, Bang HS (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 447(1–2):111
Williams DB, Carter BC (1996) Transmission electron microscopy. Plenum, New York
Karpel A, Kaplan WD, Atzmon Z, Gur G (2005) In: Havas D, Levine L (eds) Proceedings of the 2005 international symposium on microelectronics, IMAPS. p 325
Reyntjens S, Puers R (2001) J Micromech Microeng 11(4):287
Karpel A, Gur G, Atzmon Z, Kaplan WD (2007) J Mater Sci, in press. doi 10.1007/s10853-007-1592-z
Bowden P, Brandon DG (1963) J Nuclear Mater 9(3):348
Piao H, McIntyre NS (2001) Surf Interface Anal 31(9):874
Xu C, Breach CD, Sritharan T, Wulff F, Mhaisalkar SG (2004) Thin Solid Films 462–463:357
Villars P (1991) Pearson’s handbook of crystallographic data for intermetallic phases, 2nd ed. vol 1. ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, p 652
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute at the Technion for use of the FIB, and I. Popov for assistance with use of the TEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karpel, A., Gur, G., Atzmon, Z. et al. Microstructural evolution of gold–aluminum wire-bonds. J Mater Sci 42, 2347–2357 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1593-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1593-y