Abstract
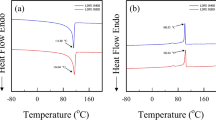
A high-damping thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) composed of chlorinated butyl rubber (CIIR) and polyethylacrylate (PEA) was prepared by using a twin-screw extruder. The effect of extrusion temperature and times on the morphology, rheology and surface of the extrudates was examined and attempts were made to correlate the extrudate surface with the evolution of two-phase morphology and the rheological behavior. CIIR gel content of each extrudate was also analyzed. The result shows that CIIR gel content increases with increasing extrusion temperature or times; furthermore, extrusion at high temperature can produce numerous PEA and CIIR macromolecular radicals, thus chemical links take place between PEA and CIIR molecules. Morphological analysis indicates that phase inversion occurs at a gel content of around 68%, and with increasing extrusion times at high temperature the dispersed particles become larger and the particle edges become blurrier. All CIIR/PEA extrudates show pseudoplastic flow behavior. The extrusion temperature or extrusion times have a significant effect on melt viscosity of the extrudates. Surface analysis exhibits that co-continuous nature of the two-phase morphology results in melt fracture and periodic distortions on the extrudate surface, but with the increasing extrusion temperature or times the surfaces of the extrudates become gradually smooth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holden G, Legge NR, Quirk R, Shroeder HE (1996) Thermoplastic elastomers—a comprehensive review, 2nd edn. Hanser Publishers, Munich, Vienna, New York
Abdou-Sabet S, Puydak RC, Rader CP (1996) Rubber Chem Technol 69(3):476
Anandhan S, De PP, De SK, Bhowmick AK (2003) J Appl Polym Sci 88(8):1976
Wu CG, Zhu YJ, Sun YJ (2000) China Synth Rubber Ind 23(5):270
Cai F, Isayev AI (1993) J Elastomers Plastics 25(1):76
Cai F, Isayev AI (1993) J Elastomers Plastics 25(3):249
Fritz HG, Boelz U, Cai Q (1999) Polym Eng Sci 39(6):1087
Fritz HG (1999) J Macromol Sci Pure Appl Chem 36A(11):1683
Wu CG, Zhu YJ, Sun YJ (2000) China Synth Rubber Ind 23(6):362
Pei LM, Basil DF (2002) Polym Eng Sci 42(10):1976
Agnes V, Philippe C, Alain M (2004) Polym Int 53(5):523
Rudolf JK, Jaap M (1998) Polym Eng Sci 38(1):101
He XR, Huang GS, Zhou H, Jiang LX, Zhao XD (2005) Acta Polym Sin n1:108
Danesi S, Porter RS (1978) Polymer 19(4):448
Snooppy G, Ramamurthy K, Anand JS, Groeninckx G, Varughese KT, Sabu T (1999) Polymer 40(15):4325
Coran AY, Bhowmick AK, Stephens HL (eds) (1988) Handbook of elastomers-development and technology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 10276025)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Pan, Q. & Huang, G. Study on the morphology, rheology and surface of dynamically vulcanized chlorinated butyl rubber/polyethylacrylate extrudates: effect of extrusion temperature and times. J Mater Sci 42, 4494–4501 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0396-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0396-x