Abstract
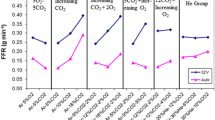
Gas tungsten arc (GTA) welding with deep penetration for high efficiency has long been of concern in industry. Experimental results showed that the small addition of carbon dioxide to the argon shielding gas produces an increase in the weld metal oxygen content, which is one of the compositional variables that strongly influence the Marangoni convection on the pool surface and ultimately change the weld pool shape. An inward Marangoni convection on the weld pool occurs, and hence a narrow and deep weld pool forms when the weld metal oxygen content is over the critical value of 100 ppm. When lower than this value, the weld shape becomes wide and shallow. A heavy oxide layer forms in the periphery area on the pool surface when the CO2 concentration in the shielding gas is over 0.6%. This continuous heavy oxide layer becomes a barrier for oxygen absorption into the molten pool, and also changes the convection mode on the pool surface. A higher welding speed decreases the heat input and temperature gradient on the pool surface, which weakens the Marangoni convection on the liquid surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. C. LUGWIG, Weld. Res. Suppl. 36 (1957) 335s.
B. E. PATON, Avtom. Svarka. 6 (1974) 1.
W. S. BENNETT and G. S. MILLS, Weld. J. 53 (1974) 548s.
W. F. SAVAGE, E. F. NIPPES and G. M. GOODWIN, Weld. J. 56 (1977) 126s.
C. R. HEIPLE and J. R. ROPER, Weld. J. 60 (1981) 143s.
Y. TAKEUCHI, R. TAKAGI and T. SHINODA, Weld. J. 71 (1992) 283s.
M. TANAKA, T. SHIMIZU, H. TERASAKI, M. USHIO, F. KOSHI-ISHI and C. L. YANG, Sci. Tech. Weld. Join. 5 (2000) 397.
P. J. MODENESI, E. R. APOLINARIO and I. M. PEREIRA, J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 99 (2000) 260.
M. KUO, Z. SUN and D. PAN, Sci. Tech. Weld. Join. 6 (2001) 17.
D. FAN, R. ZHANG, Y. GU and M. USHIO, Trans. JWRI. 30 (2001) 35.
D. S. HOWSE and W. LUCAS, Sci. Tech. Weld. Join. 5 (2000) 189.
C. R. HEIPLE and J. R. ROPER, Weld. J. 61 (1982) 97s.
P. C. J. ANDERSON and R. WIKTOROWICZ, Weld. Met. Fabri. 64 (1996) 108.
W. LUCAS and D. HOWSE, Weld. Met. Fabri. 64 (1996) 11.
D. D. SCHWEMMER, D. L. OLSON and D. L. WILLIAMSON, Weld. J. 58 (1979) 153s.
F. LIU, S. LIN, C. YANG and L. WU, Trans. China Weld. Inst. 23 (2002) 1.
T. PASKELL, C. LUNDIN and H. CASTNER, Weld. J. 76 (1997) 57.
F. LIU, S. LIN, C. YANG and L. WU, Trans. China Weld. Inst. 23 (2002) 5.
Y. WANG and H. L. TSAI, Metall. Mater. Trans. 32B (2001) 501.
S. P. LU, H. FUJII, H. SUGIYAMA and K. NOGI, Metall. Mater. Trans. 34A (2003) 1901.
N. N. BAD’YANOV, Avtom. Svarka. 1 (1975) 75.
C. R. HEIPLE and P. BURGARDT, Weld. J. 64 (1985) 159s.
S. P. LU, H. FUJII, H. SUGIYAMA, M. TANAKA and K. NOGI, ISIJ. Int. 43 (2003) 1590.
S. M. GUREVICH and V. N. ZAMKOV, Avtom. Syarka. 12 (1966) 13.
A. PAUL and T. DEBROY, Metall Trans. 19B (1988) 851.
T. ZACHARIA, S. A. DAVID, J. M. VITEK and T. DEBROY, Weld J. 68 (1989) 499s.
T. ZACHARIA, S. A. DAVID, J. M. VITEK and T. DEBROY, Weld J. 68 (1989) 510s.
H. TAIMATSU, K. NOGI and K. OGINO, J. High. Temp. Soc. 18 (1992) 14.
S. P. LU, H. FUJII, H. SUGIYAMA, M. TANAKA and K. NOGI, Mater. Trans. 43 (2002) 2926.
T. KUWANA and Y. SATO, Trans. Japan Weld. Soc. 17 (1986) 124.
T. KUWANA and Y. SATO, Trans. Japan Weld. Soc. 7 (1989) 43.
T. KUWANA and Y. SATO, Trans. Japan Weld. Soc. 7 (1989) 49.
Y. SATO and T. KUWANA, ISIJ Int. 35 (1995) 1162.
M. J. MCNALLAN and T. DEBROY, Metall. Trans. 22B (1991) 557.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanping, L., Hidetoshi, F. & Kiyoshi, N. Effects of CO2 shielding gas additions and welding speed on GTA weld shape. J Mater Sci 40, 2481–2485 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-1979-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-1979-7