Abstract
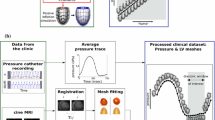
Comparing the deformations of different beating hearts is a challenging operation. As in clinics the impaired condition is often recognized upon (local and global) deformation parameters, the particular nature of heart deformation during one beat can be compared among different individuals in the same ordination space more effectively if initial inter-individual form (shape + size) differences are filtered out. This is even more true if the shape of cardiac trajectory itself is under consideration. This need is satisfied by applying a geometric machinery named “parallel transport” in the field of differential geometry. In recent years several parallel transport methods have been applied to cardiological data acquired via echocardiography, CT scan or magnetic resonance. Concomitantly, some efforts were made for comparing different parallel transport algorithms applied to a variety of toy examples and real deformational data. Here we face the problem of comparing the heavily used LDDMM parallel transport with the recently proposed Riemannian “TPS space” in the context of the deformation of the right ventricle. Using local tensors diagnostics and global energy-based and shape distance-based parameters, we explored the maintenance of original deformations in transported data in four systo-diastolic deformations belonging to one healthy subject and three individuals affected by tetralogy of Fallot, atrial septal defect and pulmonary hypertension. We also do the same in a larger dataset relative to the left ventricle of 82 heathly subjects and 21 patients affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. We also do the same in a larger dataset relative to the left ventricle of 82 heathly subjects and 21 patients affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In particular, we contrasted the TPS space with classic LDDMM and a modified LDDMM able to manage spherical differences. Our results point toward a neat superiority of TPS space over classic LDDMM. The modified LDDMM performs similarly as it maintains better the chosen diagnostics.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao, A., Chandrashekara, R., Sanchez-Ortiz, G.I., Mohiaddin, R., Aljabar, P., Hajnal, J.V., Puri, B.K., Rueckert, D.: Spatial transformation of motion and deformation fields using nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 23(9), 1065–1076 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2004.828681
Alexander, A., McGill, M., Tarasova, A., Ferreira, C., Zurkiya, D.: Scanning the future of medical imaging. J. Am. College Radiol. 16(4), 501–507 (2019)
Glaunes, J., Trouvé, A., Younes, L.: Diffeomorphic Matching of Distributions: A New Approach for Unlabelled Point-sets and Sub-manifolds Matching 2, pp. 712–718 (2004)
Ferraro, A.M., Adar, A., Ghelani, S.J., Sleeper, L.A., Levy, P.T., Rathod, R.H., Marx, G.R., Harrild, D.M.: Speckle tracking echocardiographically-based analysis of ventricular strain in children: an intervendor comparison. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12947-020-00199-x
Piras, P., Torromeo, C., Evangelista, A., Esposito, G., Nardinocchi, P., Teresi, L., Madeo, A., Re, F., Chialastri, C., Schiariti, M., Varano, V., Puddu, P.E.: Non-invasive prediction of genotype positive-phenotype negative in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by 3d modern shape analysis. Exp. Physiol. 104(11), 1688–1700 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1113/EP087551
Esposito, G., Piras, P., Evangelista, A., Nuzzi, V., Nardinocchi, P., Pannarale, G., Torromeo, C., Puddu, P.E.: Improving performance of 3d speckle tracking in arterial hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by using novel strain parameters. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43855-7
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B.E., Setio, A.A.A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M., van der Laak, J.A.W.M., van Ginneken, B., Sánchez, C.I.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005
Moceri, P., Duchateau, N., Gillon, S., Jaunay, L., Baudouy, D., Squara, F., Ferrari, E., Sermesant, M.: Three-dimensional right ventricular shape and strain in congenital heart disease patients with right ventricular chronic volume loading. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 22(10), 1174–1181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeaa189
Piras, P., Torromeo, C., Evangelista, A., Gabriele, S., Esposito, G., Nardinocchi, P., Teresi, L., Madeo, A., Schiariti, M., Varano, V., Puddu, P.E.: Homeostatic left heart integration and disintegration links atrio-ventricular covariation’s dyshomeostasis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06189-w
Piras, P., Evangelista, A., Gabriele, S., Nardinocchi, P., Teresi, L., Torromeo, C., Schiariti, M., Varano, V., Puddu, P.E.: 4d-analysis of left ventricular heart cycle using procrustes motion analysis. PloS ONE 9(1), 86896 (2014)
Arsigny, V., Fillard, P., Pennec, X., Ayache, N.: Geometric means in a novel vector space structure on symmetric positive-definite matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 29(1), 328–347 (2006)
Filiard, P., Pennec, X., Arsigny, V., Ayache, N.: Clinical DT-MRI estimation, smoothing, and fiber tracking with log-Euclidean metrics. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 26(11), 1472–1482 (2007)
Miller, M.I., Qiu, A.: The emerging discipline of computational functional anatomy. Neuroimage 45(1), 16–39 (2009)
Hartman, E., Sukurdeep, Y., Klassen, E., Charon, N., Bauer, M.: Elastic shape analysis of surfaces with second-order Sobolev metrics: a comprehensive numerical framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 131(5), 1183–1209 (2023)
Madeo, A., Piras, P., Re, F., Gabriele, S., Nardinocchi, P., Teresi, L., Torromeo, C., Chialastri, C., Schiariti, M., Giura, G., et al.: A new 4d trajectory-based approach unveils abnormal lv revolution dynamics in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PloS ONE 10(4), 0122376 (2015)
Piras, P., Profico, A., Pandolfi, L., Raia, P., Di Vincenzo, F., Mondanaro, A., Castiglione, S., Varano, V.: Current options for visualization of local deformation in modern shape analysis applied to paleobiological case studies. Front. Earth Sci. 8, 66 (2020)
Piras, P., Torromeo, C., Re, F., Evangelista, A., Gabriele, S., Esposito, G., Nardinocchi, P., Teresi, L., Madeo, A., Chialastri, C., Schiariti, M., Varano, V., Uguccioni, M., Puddu, P.E.: Left atrial trajectory impairment in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disclosed by geometric morphometrics and parallel transport. Sci. Rep. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34906
Buckley, P.F., Dean, D., Bookstein, F.L., Friedman, L., Kwon, D., Lewin, J.S., Kamath, J., Lys, C.: Three-dimensional magnetic resonance-based morphometrics and ventricular dysmorphology in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 45(1), 62–67 (1999)
Piras, P., Sansalone, G., Teresi, L., Moscato, M., Profico, A., Eng, R., Cox, T.C., Loy, A., Colange, lP., Kotsakis, T.: Digging adaptation in insectivorous subterranean eutherians. The enigma of mesoscalops montanensis unveiled by geometric morphometrics and finite element analysis. J. Morphol. 276(10), 1157–1171 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmor.20405
Varano, V., Gabriele, S., Teresi, L., Dryden, I.L., Puddu, P.E., Torromeo, C., Piras, P.: The TPS direct transport: a new method for transporting deformations in the size-and-shape space. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 124(3), 384–408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-017-1031-9
Durrleman, S., Prastawa, M., Charon, N., Korenberg, J.R., Joshi, S., Gerig, G., Trouvé, A.: Morphometry of anatomical shape complexes with dense deformations and sparse parameters. NeuroImage 101, 35–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.06.043
Joshi, S.C., Miller, M.I.: Landmark matching via large deformation diffeomorphisms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(8), 1357–1370 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.855431
Piras, P., Varano, V., Louis, M., Profico, A., Durrleman, S., Charlier, B., Milicchio, F., Teresi, L.: Transporting deformations of face emotions in the shape spaces: a comparison of different approaches. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 63(7), 875–893 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-021-01030-6
Guigui, N., Moceri, P., Sermesant, M., Pennec, X.: Cardiac motion modeling with parallel transport and shape splines. In: ISBI 2021—IEEE18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 1394–1397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI48211.2021.9433887
Guigui, N., Pennec, X.: Parallel transport, a central tool in geometric statistics for computational anatomy: application to cardiac motion modeling. In: Geometry and Statistics. Handbook of Statistics, vol. 46. Elsevier (2022)
Varano, V., Piras, P., Gabriele, S., Teresi, L., Nardinocchi, P., Dryden, I.L., Torromeo, C., Puddu, P.E.: The decomposition of deformation: new metrics to enhance shape analysis in medical imaging. Med. Image Anal. 46, 35–56 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2018.02.005
Varano, V., Piras, P., Gabriele, S., Teresi, L., Nardinocchi, P., Dryden, I.L., Torromeo, C., Schiariti, M., Puddu, P.E.: Local and global energies for shape analysis in medical imaging. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.3252
Guigui, N.: Computational methods for statistical estimation on Riemannian manifolds and application to the study of the cardiac deformations. Theses, Université Côte d’Azur (November 2021). https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-03563980
Micheli, M., Glaunès, J.A.: Matrix-valued kernels for shape deformation analysis. Geom. Imaging Comput. 1(1), 57–139 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4310/GIC.2014.v1.n1.a2
Louis, M., Bône, A., Charlier, B., Durrleman, S., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Parallel transport in shape analysis: a scalable numerical scheme. In: International Conference on Geometric Science of Information, pp. 29–37 (2017). Springer
Lorenzi, M., Pennec, X.: Efficient parallel transport of deformations in time series of images: from Schild to pole ladder. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 50(1), 5–17 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-013-0470-3
Guigui, N., Pennec, X.: Numerical accuracy of ladder schemes for parallel transport on manifolds. Found. Comput. Math. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10208-021-09515-x
Niethammer, M., Vialard, F.-X.: Riemannian metrics for statistics on shapes : Parallel transport and scale invariance. In: Proceedings of the 4th MICCAI Workshop on Mathematical Foundations of Computational Anatomy (MFCA) (2013)
Varano, V., Piras, P., Teresi, L., Gabriele, S., Dryden, I.L., Nardinocchi, P., Evangelista, A., Torromeo, C., Puddu, P.E.: A threefold deformation decomposition in shape analysis for medical imaging: spherical, deviatoric and non affine components. Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol. 27, pp. 1125–1134 (2018)
Gabriele, S., Nardinocchi, P., Varano, V.: Evaluation of the strain-line patterns in a human left ventricle: a simulation study. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 18(7), 790–798 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2013.847094
Evangelista, A., Gabriele, S., Nardinocchi, P., Piras, P., Puddu, P., Teresi, L., Torromeo, C., Varano, V.: Non-invasive assessment of functional strain lines in the real human left ventricle via speckle tracking echocardiography. J. Biomech. 48(3), 465–471 (2015)
Bookstein, F.L.: Principal warps: Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(6), 567–585 (1989)
Lafarge, T., Pateiro-Lopez, B.: Alphashape3d: implementation of the 3D alpha-shape for the reconstruction of 3D sets from a point cloud. (2023). R package version 1.3.2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=alphashape3d
Acknowledgements
We really thank Pamela Moceri and Nicolas Duchateau for collecting and curating the right ventricle data as well as for their kindness in sharing part of their data. We also thank Concetta Torromeo and Paolo Emilio Puddu for sharing the left ventricle dataset.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Piras, P., Guigui, N. & Varano, V. Comparison of Different Parallel Transport Methods for the Study of Deformations in 3D Cardiac Data. J Math Imaging Vis 66, 393–415 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-024-01186-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-024-01186-x