Abstract
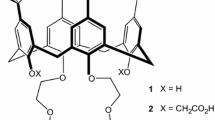
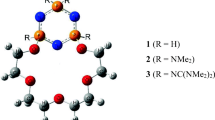
A systematic analysis of the structural, energetic, and thermodynamic factors involved in alkali metal (i.e., Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+) complexation by four calix[4]arene crown-6 ethers in the 1,3-alternate conformation is presented here. The ligands (or hosts) in this work are identical to, or closely related to, the four molecules whose selectivity towards complexing Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+ from aqueous solutions was studied experimentally by Casnati et al. (Tetrahedron 60(36):7869–7876, 2004). By dividing the complexation process into three different contributions, namely, the binding energy of the ion to the crown, the elastic energy of the crown, and the solvation effect, it becomes clear that the primary factor that determines ion selectivity in crown-6-ethers is not the size of the crown, as currently believed. All four crown ethers preferentially complex with the smallest ion (Na+) in the gas phase. In the condensed phase, these crown-6 ethers preferentially complex with the larger ions only because the aqueous solvation energies of the alkali metal ions make it thermodynamically less favorable to extract the smaller ions from aqueous solutions. This suggests that the current understanding of the factors influencing the selectivity of metal ion complexation by crown ethers may be in need of revision.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asfari, M.Z., Böhmer, V., Harrowfield, J., Vicens, J.: Calixarenes 2001. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
Salorinne, K., Nissinen, M.: Calixcrowns: synthesis and properties. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 61(1–2), 11–27 (2008)
Arnaud-Neu, F., Schwing-Weill, M.J., Dozol, J.F.: Calixarenes for nuclear waste treatment. In: Asfari, M.Z., Böhmer, V., Harrowfield, J., Vicens, J. (eds.) Calixarenes 2001, pp. 642–662. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
PUREX Process. http://www.euronuclear.org/info/encyclopedia/p/purex-process.htm. Accessed 1 May 2012
Hill, C., Dozol, J.F., Lamare, V., Rouquette, H., Eymard, S., Tournois, B., Vicens, J., Asfari, Z., Bressot, C., Ungaro, R., Casnati, A.: Nuclear waste treatment by means of supported liquid membranes containing calixcrown compounds. J. Inclusion Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem. 19(1–4), 399–408 (1994)
Casnati, A., Ca, N.D., Sansone, F., Ugozzoli, F., Ungaro, R.: Enlarging the size of calix[4]arene-crowns-6 to improve Cs+/K+ selectivity: a theoretical and experimental study. Tetrahedron 60(36), 7869–7876 (2004)
Golebiowski, J., Lamare, V., Ruiz-López, M.F.: Quantum chemical calculations on alkali metal complexes. In: Asfari, M.Z., Böhmer, V., Harrowfield, J., Vicens, J. (eds.) Calixarenes 2001, pp. 334–345. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
Schatz, J., Backes, A.C., Siehl, H.U.: Geometry and GIAO-DFT chemical shift calculations of calixarene complexes-the inclusion of carbon disulfide in p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2(4), 609–610 (2000)
Hay, B.P., Nicholas, J.B., Feller, D.: Novel binding modes in tetramethoxycalix[4]arene: implications for ligand design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122(41), 10083–10089 (2000)
Çiçek, B., Yildiz, A.: Synthesis, metal ion complexation and computational studies of thio oxocrown ethers. Molecules 16(10), 8670–8683 (2011)
Çiçek, B., Çakir, Ü., Azizoglu, A.: The associations of macrocyclic ethers with cations in 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures; potentiometric Na+ and K+ binding measurements and computational study. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 72(1), 121–125 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10847-011-9949-y
Rozhenko, A.B., Schoeller, W.W., Letzel, M.C., Decker, B., Agena, C., Mattay, J.: Conformational features of calix[4]arenes with alkali metal cations: a quantum chemical investigation with density functional theory. J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem) 732(1–3), 7–20 (2005)
Ilchenko, N.N., Kuchma, O.V., Zub, Y.L., Leszczynski, J.: Cesium cation complexation by 25,27-dihydroxycalix[4]arene-crown-6: computational study. J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem) 815(1–3), 83–86 (2007)
Wipff, G.: Molecular dynamics of cation complexation and extraction. In: Asfari, M.Z., Böhmer, V., Harrowfield, J., Vicens, J. (eds.) Calixarenes 2001, pp. 312–333. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
Sieffert, N., Chaumont, A., Wipff, G.: Importance of the liquid–liquid interface in assisted ion extraction: new molecular dynamics studies of cesium picrate extraction by a calix[4]arene. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(24), 10610–10622 (2009)
Sieffert, N., Wipff, G.: Alkali cation extraction by calix[4]crown-6 to room-temperature ionic liquids. The effect of solvent anion and humidity investigated by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. A 110(3), 1106–1117 (2006)
Sieffert, N., Wipff, G.: Comparing an ionic liquid to a molecular solvent in the cesium cation extraction by a calixarene: a molecular dynamics study of the aqueous interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(39), 19497–19506 (2006)
Sieffert, N., Wipff, G.: The effect of a solvent modifier in the cesium extraction by a calix[4]arene: a molecular dynamics study of the oil phase and the oil–water interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9(28), 3763–3775 (2007)
Becke, A.D.: A new mixing of Hartree–Fock and local density-functional theories. J. Chem. Phys. 98(2), 1372–1377 (1993)
Perdew, J.P.: Unified theory of exchange and correlation beyond the local density approximation. In: Ziesche, P., Esching, H. (eds.) Electronic structure of solids ‘91. Akademic Verlag, Berlin (1991)
Perdew, J.P., Wang, Y.: Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy. Phys. Rev. B 45(23), 13244–13249 (1992)
Schaefer, H.F.: Methods of electronic structure theory. Springer, New York (1977)
Hay, P.J., Wadt, W.R.: Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 82(1), 270–283 (1985)
Wadt, W.R., Hay, P.J.: Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for main group elements Na to Bi. J. Chem. Phys. 82(1), 284–298 (1985)
Hay, P.J., Wadt, W.R.: Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for K to Au including the outermost core orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 82(1), 299–310 (1985)
Weigend, F., Ahlrichs, R.: Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7(18), 3297–3305 (2005)
Dunning Jr, T.H.: Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 90(2), 1007–1023 (1989)
Kendall, R.A., Dunning Jr, T.H., Harrison, R.J.: Electron affinities of the first-row atoms revisited. Systematic basis sets and wave functions. J. Chem. Phys. 96(9), 6796–6806 (1992)
Boys, S.F., Bernardi, F.: The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 19(4), 553–566 (1970)
Tomasi, J., Mennucci, B., Cammi, R.: Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models. Chem. Rev. 105(8), 2999–3093 (2005)
Frisch, M.J., Trucks, G.W., Schlegel, H.B., Scuseria, G.E., Robb, M.A., Cheeseman, J.R., Scalmani, G., Barone, V., Mennucci, B., Petersson, G.A., Nakatsuji, H., Caricato, M., Li, X., Hratchian, H.P., Izmaylov, A.F., Bloino, J., Zheng, G., Sonnenberg, J.L., Hada, M., Ehara, M., Toyota, K., Fukuda, R., Hasegawa, J., Ishida, M., Nakajima, T., Honda, Y., Kitao, O., Nakai, H., Vreven, T., Montgomery, Jr., J.A., Peralta, J.E., Ogliaro, F., Bearpark, M., Heyd, J.J., Brothers, E., Kudin, K.N., Staroverov, V.N., Kobayashi, R., Normand, J., Raghavachari, K., Rendell, A., Burant, J.C., Iyengar, S.S., Tomasi, J., Cossi, M., Rega, N., Millam, N.J., Klene, M., Knox, J.E., Cross, J.B., Bakken, V., Adamo, C., Jaramillo, J., Gomperts, R., Stratmann, R.E., Yazyev, O., Austin, A.J., Cammi, R., Pomelli, C., Ochterski, J.W., Martin, R.L., Morokuma, K., Zakrzewski, V.G., Voth, G.A., Salvador, P., Dannenberg, J.J., Dapprich, S., Daniels, A.D., Farkas, Ö., Foresman, J.B., Ortiz, J.V., Cioslowski, J., Fox, D.J.: Gaussian 09, Rev. A.1. In., p. Gaussian 09. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, (2009)
Floris, F., Tomasi, J.: Evaluation of the dispersion contribution to the solvation energy. A simple computational model in the continuum approximation. J. Comput. Chem. 10(5), 616–627 (1989)
Floris, F.M., Tomasi, J., Ahuir, J.L.P.: Dispersion and repulsion contributions to the solvation energy: refinements to a simple computational model in the continuum approximation. J. Comput. Chem. 12(7), 784–791 (1991)
Pierotti, R.A.: A scaled particle theory of aqueous and nonaqueous solutions. Chem. Rev. 76(6), 717–726 (1976)
Thompson, J.D., Cramer, C.J., Truhlar, D.G.: Predicting aqueous solubilities from aqueous free energies of solvation and experimental or calculated vapor pressures of pure substances. J. Chem. Phys. 119(3), 1661–1670 (2003)
Pratt, L.M., Trần, P.T.T., Nguỹên, N.V., Ramachandran, B.: Cyclopropanation reactions of halomethyllithium carbenoids: a computational study of the effects of aggregation and solvation. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 82(9), 1107–1125 (2009)
Helgeson, R.C., Weisman, G.R., Toner, J.L., Tarnowski, T.L., Chao, Y., Mayer, J.M., Cram, D.J.: Host–guest complexation. 18. Effects on cation binding of convergent ligand sites appended to macrocyclic polyethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101(17), 4928–4941 (1979)
Casnati, A., Pochini, A., Ungaro, R., Ugozzoli, F., Arnaud, F., Fanni, S., Schwing, M.J., Egberink, R.J.M., De Jong, F., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Synthesis, complexation, and membrane transport studies of 1,3-alternate calix[4]arene-crown-6 conformers: a new class of cesium selective ionophores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117(10), 2767–2777 (1995)
Casnati, A., Sansone, F., Dozol, J.F., Rouquette, H., Arnaud-Neu, F., Byrne, D., Fuangswasdi, S., Schwing-Weill, M.J., Ungaro, R.: New calix[4]arene-monobenzo-and -dibenzo-crown-6 as cesium selective ionophores in the radioactive waste treatment: synthesis, complexation and extraction properties. J. Incl. Phenom. 41(1–4), 193–200 (2001)
Singh, U.C., Kollman, P.A.: An approach to computing electrostatic charges for molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 5(2), 129–145 (1984)
Besler, B.H., Merz, K.M., Kollman, P.A.: Atomic charges derived from semiempirical methods. J. Comput. Chem. 11(4), 431–439 (1990)
More, M.B., Ray, D., Armentrout, P.B.: Intrinsic affinities of alkali cations for 15-crown-5 and 18-crown-6: bond dissociation energies of gas-phase M +-crown ether complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121(2), 417–423 (1999)
Ma, J.C., Dougherty, D.A.: The cation-π interaction. Chem. Rev. 97(5), 1303–1324 (1997)
Kelly, C.P., Cramer, C.J., Truhlar, D.G.: Aqueous solvation free energies of ions and ion-water clusters based on an accurate value for the absolute aqueous solvation free energy of the proton. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(32), 16066–16081 (2006)
Tissandier, M.D., Cowen, K.A., Feng, W.Y., Gundlach, E., Cohen, M.H., Earhart, A.D., Coe, J.V., Tuttle Jr, T.R.: The proton’s absolute aqueous enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of solvation from cluster-ion solvation data. J. Phys. Chem. A 102(40), 7787–7794 (1998)
Fawcett, W.R.: Thermodynamic parameters for the solvation of monatomic ions in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 103(50), 11181–11185 (1999)
Acknowledgments
This work was done with the help of generous grants of computer time on the supercomputers of the Louisiana Optical Network Initiative (LONI). BRR is grateful to Professor Naresh Patwari for very helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramachandran, B.R., Baker, S.D., Suravajhula, G. et al. Selective complexation of alkali metal ions using crown ethers derived from calix[4]arenes: a computational investigation of the structural and energetic factors. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 75, 185–195 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-012-0160-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-012-0160-6