Abstract
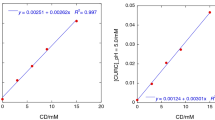
The effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) on solubility, stability and oral bioavailability of curcumin by external factors adjustment, was investigated with an aim of a simple, stable and effective formulation. The phase solubility studies showed the solubility of curcumin increased slightly with increasing pH. However, the apparent stability constant (K S) were found to decrease with increasing pH from 1.29 × 104 M−1 at pH 3.0 to 5.22 × 103 M−1 at pH 7.0. The thermodynamic parameters were calculated for inclusion complex formation in aqueous solution. Interestingly, it could be concluded that the degrees of curcumin stability improved by HPβCD grew with increasing drug–cyclodextrin binding ability. Furthermore, in vivo study not only revealed that the bioavailability of curcumin after oral administration to rats was significantly improved by curcumin/HPβCD inclusion complex, but also showed more dramatic changes in the plasma concentration–time curve (1752.76–866.70 ng mL−1 h) and the peak plasma concentration (370.10–178.11 ng mL−1) of drug by formation of complexes in pH 3–7 solution.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Cyclodextrin
- HPβCD:
-
2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- S 0 :
-
Solubility in a medium in the absence of CD
- K S :
-
Apparent stability constant for the drug–CD interaction
- [C 0]:
-
The initial concentration of drug
- [C t ]:
-
The time-dependent concentration of drug
- ΔH :
-
Values of enthalpy change
- ΔS :
-
Values of entropy change
- ΔG :
-
Variation of Gibbs free energy
- k :
-
Observed first-order rate constant of drug
- k 0 :
-
Observed first-order rate constant of drug in the absence of CD
- k C :
-
Observed first-order rate constant for the inclusion complex
- E a :
-
Activation energy (the amount of energy needed to initiate a chemical process, most often a reaction)
- R.S.D.:
-
Relative standard deviation
- C max :
-
Maximum plasma concentration
- T max :
-
Time required to reach C max
- AUC:
-
Total area under the plasma concentration–time
- AUC(0–24) :
-
Total area under the plasma concentration–time curve from 0 to 24 h
- AUC(0–∞) :
-
Total area under the plasma concentration–time curve from time zero to infinity
References
Araujo, C.A.C., Leon, L.L.: Biological activities of Curcuma longa L. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 96, 723–728 (2001)
Srinivasan, K.: Spices as influencers of body metabolism: an overview of three decades of research. Food Res. Int. 38, 77–86 (2005)
Tayyem, R.R., Heath, D.D., Al-Delaimy, W.K., Rock, C.L.: Curcumin content of turmeric and curry powders. Nutr. Cancer 55, 126–131 (2006)
Aggarwal, B.B., Harikumar, K.B.: Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41, 40–59 (2009)
Sharma, R.A., Steward, W.P., Gescher, A.J.: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of curcumin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 595, 453–470 (2007)
Ireson, C., Orr, S., Jones, D.J.L., Verschoyle, R., Lim, C.K., Luo, J.L., Howells, L., Plummer, S., Jukes, R., Williams, M., Steward, W.P., Gescher, A.: Characterization of metabolites of the chemopreventive agent curcumin in human and rat hepatocytes and in the rat in vivo, and evaluation of their ability to inhibit phorbol ester-induced prostaglandin E-2 production. Cancer Res. 61, 1058–1064 (2001)
Bar-Sela, G., Epelbaum, R., Schaffer, M.: Curcumin as an anti-cancer agent: review of the gap between basic and clinical applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 17, 190–197 (2010)
Somasundaram, S., Edmund, N.A., Moore, D.T., Small, G.W., Shi, Y.Y., Orlowski, R.Z.: Dietary curcumin inhibits chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in models of human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62, 3868–3875 (2002)
Chauhan, D.P.: Chemotherapeutic potential of curcumin for colorectal cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 8, 1695–1706 (2002)
Cohly, H.H.P., Asad, S., Das, S.K., Angel, M.F., Rao, M.: Effect of antioxidant (turmeric, turmerin and curcumin) on human immunodeficiency virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 4, 22–33 (2003)
Balasubramanyam, K., Varier, R.A., Altaf, M., Swaminathan, V., Siddappa, N.B., Ranga, U., Kundu, T.K.: Curcumin, a novel p300/CREB-binding protein-specific inhibitor of acetyltransferase, represses the acetylation of histone/nonhistone proteins and histone acetyltransferase-dependent chromatin transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 51163–51171 (2004)
Egan, M.E., Pearson, M., Weiner, S.A., Rajendran, V., Rubin, D., Glockner-Pagel, J., Canny, S., Du, K., Lukacs, G.L., Caplan, M.J.: Curcumin, a major constituent of turmeric, corrects cystic fibrosis defects. Science 304, 600–602 (2004)
Zeitlin, P.: Can curcumin cure cystic fibrosis? New Engl. J. Med. 351, 606–608 (2004)
Begum, A.N., Jones, M.R., Lim, G.P., Morihara, T., Kim, P., Heath, D.D., Rock, C.L., Pruitt, M.A., Yang, F.S., Hudspeth, B., Hu, S.X., Faull, K.F., Teter, B., Cole, G.M., Frautschy, S.A.: Curcumin structure-function, bioavailability, and efficacy in models of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease Frautschy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326, 196–208 (2008)
Ortiz-Ortiz, M.A., Moran, J.M., Ruiz-Mesa, L.M., Niso-Santano, M., Bravo-SanPedro, J.M., Gomez-Sanchez, R., Gonzalez-Polo, R.A., Fuentes, J.M.: Curcumin exposure induces expression of the Parkinson’s disease-associated leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in rat mesencephalic cells. Neurosci. Lett. 468, 120–124 (2010)
Anand, P., Kunnumakkara, A.B., Newman, R.A., Aggarwal, B.B.: Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol. Pharmacol. 4, 807–818 (2007)
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaccutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007)
Choi, H.S., Takahashi, A., Ooya, T., Yui, N.: Structural role of guest molecules in rapid and sensitive supramolecular assembling system based on β-cyclodextrin-conjugated poly(epsilon-lysine). Macromolecules 37, 10036–10041 (2004)
Davis, M.E., Brewster, M.E.: Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 1023–1035 (2004)
Yang, B., Yang, L.J., Lin, J., Chen, Y., Liu, Y.: Binding behaviors of scutellarin with α-, β-, γ-cyclodextrins and their derivatives. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 64, 149–155 (2009)
Liu, Y., Chen, G.S., Chen, Y., Zhang, N., Chen, J., Zhao, Y.L.: Bundle-shaped cyclodextrin-Tb nano-supramolecular assembly mediated by C-60. Nano Lett. 6, 2196–2200 (2006)
Loftsson, T., Duchene, D.: Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 329, 1–11 (2007)
Loftsson, T., Hreinsdottir, D., Másson, M.: Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 302, 18–28 (2005)
Agueros, M., Ruiz-Gaton, L., Vauthier, C., Bouchemal, K., Espuelas, S., Ponchel, G., Irache, J.M.: Combined hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and poly(anhydride) nanoparticles improve the oral permeability of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 38, 405–413 (2009)
Muraoka, A., Tokumura, T., Machida, Y.: Evaluation of the bioavailability of flurbiprofen and its β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in four different doses upon oral administration to rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 58, 667–671 (2004)
Buchanan, C.M., Buchanan, N.L., Edgar, K.J., Little, J.L., Ramsey, M.G., Ruble, K.M., Wacher, V.J., Wernpe, M.F.: Pharmacokinetics of saquinavir after intravenous and oral dosing of saquinavir: hydroxybutenyl-β-cyclodextrin formulations. Biomacromolecules 9, 305–313 (2008)
Cappello, B., Carmignani, C., Iervolino, M., La Rotonda, M.I., Saettone, M.F.: Solubilization of tropicamide by hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and water-soluble polymers: in vitro/in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 213, 75–81 (2001)
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.E.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1017–1025 (1996)
Hegge, A.B., Schuller, R.B., Kristensen, S., Tønnesen, H.H.: In vitro release of curcumin from vehicles containing alginate and cyclodextrin. Studies of curcumin and curcuminoides. XXXIII. Pharmazie 63, 585–592 (2008)
Marcolino, V.A., Zanin, G.M., Durrant, L.R., Benassi, M.D.T., Matioli, G.: Interaction of curcumin and bixin with β-cyclodextrin: complexation methods, stability, and applications in food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(7), 3348–3357 (2011)
Tang, B., Ma, L., Wang, H.Y., Zhang, G.Y.: Study on the supramolecular interaction of curcumin and β-cyclodextrin by spectrophotometry and its analytical application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 1355–1361 (2002)
Qi, A.D., Li, L., Liu, Y.: The binding ability and inclusion complexation behavior of curcumin with natural α-, β-, γ-cyclodextrins and organoselenium-bridged bis (β-cyclodextrin)s. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 12(1), 15–20 (2003)
Singh, R., Tønnesen, H.H., Vogensen, S.B., Loftsson, T., Másson, M.: Studies of curcumin and curcuminoids. XXXVI. The stoichiometry and complexation constants of cyclodextrin complexes as determined by the phase-solubility method and UV–Vis titration. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 66, 335–348 (2010)
Swaroop, S., Mishra, B., Priyadarsini, K.I.: Studies on β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex of curcumin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India B Biol. Sci. 77(3), 205–211 (2007)
Baglole, K.N., Boland, P.G., Wagner, B.D.: Fluorescence enhancement of curcumin upon inclusion into parent and modified cyclodextrins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 173, 230–237 (2005)
Tønnesen, H.H., Másson, M., Loftsson, T.: Studies of curcumin and curcuminoids. XXVII. Cyclodextrin complexation: solubility, chemical and photochemical stability. Int. J. Pharm. 244, 127–135 (2002)
Tomren, M.A., Másson, M., Loftsson, T., Tønnesen, H.H.: Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids XXXI. Symmetric and asymmetric curcuminoids: stability, activity and complexation with cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 338, 27–34 (2007)
Yadav, V.R., Suresh, S., Devi, K., Yadav, S.: Effect of cyclodextrin complexation of curcumin on its solubility and antiangiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity in rat colitis model. AAPS PharmSciTech 10(3), 752–762 (2009)
Yallapu, M.M., Jaggi, M., Chauhan, S.C.: β-Cyclodextrin-curcumin self-assembly enhances curcumin delivery in prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 79(1), 113–125 (2010)
Gould, S., Scott, R.C.: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): a toxicology review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 43, 1451–1459 (2005)
Stella, V.J., Rao, V.M., Zannou, E.A., Zia, V.: Mechanisms of drug release from cyclodextrin complexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 36, 3–16 (1999)
Sanghvi, R., Mogalian, E., Machatha, S.G., Narazaki, R., Karlage, K.L., Jain, P., Tabibi, S.E., Glaze, E., Myrdal, P.B., Yalkowsky, S.H.: Preformulation and pharmacokinetic studies on antalarmin: a novel stress inhibitor. J. Pharm. Sci. 98, 205–214 (2009)
Tommasini, S., Calabro, M.L., Raneri, D., Ficarra, P., Ficarra, R.: Combined effect of pH and polysorbates with cyclodextrins on solubilization of naringenin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36, 327–333 (2004)
Pathak, S.M., Musmade, P., Dengle, S., Karthik, A., Bhat, K., Udupa, N.: Enhanced oral absorption of saquinavir with methyl-β-cyclodextrin-preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 41, 440–451 (2010)
Holvoet, C., Plaizier-Vercammen, J., Vander Heyden, Y., Gabriels, M., Camu, F.: Preparation and in vitro release rate of fentanyl-cyclodextrin complexes for prolonged action in epidural analgesia. Int. J. Pharm. 265, 13–26 (2003)
Wu, Z.M., Tucker, I.G., Razzak, M., McSporran, K., Medlicott, N.J.: Tissue compatibility and pharmacokinetics of three potential subcutaneous injectables for low-pH drug solutions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 62, 873–882 (2010)
Han, H.K., Choi, H.K.: Improved absorption of meloxicam via salt formation with ethanolamines. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 65, 99–103 (2007)
Jerry, N., Anitha, Y., Sharma, C.P., Sony, P.: In vivo absorption studies of insulin from an oral delivery system. Drug Deliv. 8, 19–23 (2001)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Loftsson, T., Másson, M., Brewster, M.E.: Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 1091–1099 (2004)
Tommasini, S., Raneri, D., Ficarra, R., Calabro, M.L., Stancanelli, R., Ficarra, P.: Improvement in solubility and dissolution rate of flavonoids by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 35, 379–387 (2004)
Wang, Y.J., Pan, M.H., Cheng, A.L., Lin, L.I., Ho, Y.S., Hsieh, C.Y., Lin, J.K.: Stability of curcumin in buffer solutions and characterization of its degradation products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 15, 1867–1876 (1997)
Feng, S.G., Qin, G.Y., Liu, H.X., Jiang, Z.H., Liang, J.M., Qiu, F.: Isolation and identification of degradation products of curcumin and study of stability of curcumin. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 26(5), 361–365 (2009)
Tønnesen, H.H., Karlsen, J.: Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. V. Alkaline degradation of curcumin. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 180, 132–134 (1985)
Holder, G.M., Plummer, J.L., Ryan, A.J.: The metabolism and excretion of curcumin (1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) in the rat. Xenobiotica 8(12), 761–768 (1978)
Ravindranath, V., Chandrasekhara, N.: Absorption and tissue distribution of curcumin in rats. Toxicology 16(3), 259–265 (1980)
Arun, R., Ashok Kumar, C.K., Sravanthi, V.V.N.S.S.: Cyclodextrins as drug carrier molecule: a review. Sci. Pharm. 76, 567–598 (2008)
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Tianjin Science and Technology Development Fund for Colleges and Universities (20090223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, HZ., Fang, L., Zhu, L. et al. Effect of external factors on the curcumin/2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: in vitro and in vivo study. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 73, 423–433 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0080-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0080-x