Abstract
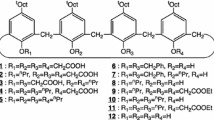
The proton di-ionizable p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-1,2-crown-3 in cone and 1,2-alternate conformations and the p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-1,2-thiacrown-3 in cone conformation were synthesized and the competitive solvent extractions of alkali and alkaline earth metal cations were studied using such nano-baskets. The novelty of this study is investigation of three binding units of calixarene’s bowl, crown ether’s ring and electron-donor ionizable moieties in a unique scaffold. The calixarene’s bowl, crown ether’s ring and electron-donor ionizable moieties were selected base upon their complexation ability to show equal binding tendency towards the cations. The objective of this study is to assess the extraction efficiency, selectivity and pH1/2 of such complexes. The result of solvent extraction experiments indicated that these compounds were effective extractants towards alkali and alkaline earth metals. Their selectivity was influenced by the acidity of solution and the conformation of calixcrowns. p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-1,2-crown-3 diacid in cone conformation was highly selective to Na+ and p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-1,2-thiacrown-3 diacid in cone conformation was highly selective to Ba2+ in acidic and basic solutions, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K., Dalali, N.: Analytical applications of calixarenes from 2005 up-to-date. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 69(1–2), 1–55 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10847-010-9848-7
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K., Dalali, N.: Molecule and ion recognition of nano-baskets of calixarenes since 2005. J. Coord. Chem. 64(5), 743–794 (2011). doi:10.1080/00958972.2011.555538
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K., Dallali, N.: A review of calixarene applications in nuclear industries. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 287(3), 921–934 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10967-010-0881-1
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K., Dalali, N.: Applications of nano-baskets of calixarenes in chromatography. Chromatographia 73(9–10), 829–847 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10337-011-1954-1
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K.: Advances in binding ability and extractive applications of nano-baskets of calixarene. Asian J. Chem. 23(11), 4717–4734 (2011)
Salorinne, K., Nissinen, M.: Calixcrowns: synthesis and properties. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 61(1–2), 11–27 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10847-008-9411-y
Kim, J.S., Vicens, J.: Progress of calixcrowns chemistry. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 63(1–2), 189–193 (2009). doi:10.1007/s10847-008-9503-8
Tu, C., Surowiec, K., Bartsch, R.A.: Novel calix[4]arene-thiacrown ether for selective and efficient extraction of Ba(II), Pb(II), and Hg(II). J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 58(3–4), 361–366 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10847-006-9283-y
Tu, C., Surowiec, K., Gega, J., Purkiss, D.W., Bartsch, R.A.: Di-ionizable calix[4]arene-1, 2-crown-5 and -crown-6 ethers in cone conformations: synthesis and divalent metal ion extraction. Tetrahedron 64(7), 1187–1196 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.tet.2007.11.065
Yang, Y., Arora, G., Fernandez, F.A., Crawford, J.D., Surowiec, K., Lee, E.K., Bartsch, R.A.: Lower-rim versus upper-rim functionalization in di-ionizable calix[4]arene-crown-5 isomers. Synthesis and divalent metal ion extraction. Tetrahedron 67(7), 1389–1397 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.tet.2010.12.006
van Leeuwen, F.W.B., Beijleveld, H., Miermans, C.J.H., Huskens, J., Verboom, W., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Ionizable (thia)calix[4]crowns as highly selective 226Ra2+ ionophores. Anal. Chem. 77(14), 4611–4617 (2005). doi:10.1021/ac050524n
Lamare, V., Dozol, J.F., Ugozzoli, F., Casnati, A., Ungaro, R.: X-ray crystal structures and molecular modelling studies of calix[4]dibenzocrowns-6 and their alkali metal cation complexes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1998(8), 1559–1568 (1998). doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0690(199808)1998:8
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K.: Competitive solvent extraction of alkaline earth metals by ionizable nano-baskets of calixarene. Supramol. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1080/10610278.2011.605452
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K.: Solvent extraction of alkali metals by conformers of di-ionizable calix[4]arenes. J. Coord. Chem. (2011) (in press)
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K.: Effect of crown size and upper moieties in nano-baskets of diacid calix[4]arene-1,2-crowns-3,4,5,6 on the extraction of s-block metals. J. Coord. Chem. 64(17), 3081–3091 (2011). doi:10.1080/00958972.2011.613462
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K.: Medical applications of nano-baskets. J. Coord. Chem. 64(18), 3189–3204 (2011). doi:10.1080/00958972.2011.616930
Ungaro, R., Pochini, A., Andreetti, G.D.: New ionizable ligands from p. t-butylcalix [4] arene. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2(1–2), 199–206 (1984). doi:10.1007/BF00663257
Vicens, J.: Applied and fundamental research: their mutual stimulation in the real world of chemistry–developing calix bis crowns for nuclear waste treatment. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 55(1–2), 193–196 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10847-005-9021-x
Yang, Y., Cao, X., Surowiec, K., Bartsch, R.A.: Calix[4]arene-thiacrown-5 di(carboxylic acid) regioisomers as metal ion extractants. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 66(1–2), 163–169 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10847-009-9675-x
Xia, Y.X., Zhou, H.H., Yin, Y., Qiu, N., Luo, J., Xiang, G.Y.: Intramolecular cyclization strategy: synthesis of 1,3- and 1,2-calix[4]crown-7 and calix[4]crown-9 cone conformers. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 68(3–4), 423–429 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10847-010-9802-8
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Islamic Azad University (Shahreza branch) and Iran Nanotechnology Initiative Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari, B., Pourabdollah, K. Binding and extraction of alkali and alkaline earth metals by nano-baskets of calix[4]arene-1,2-crown-3. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 73, 269–277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0052-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0052-1