Abstract
The tetraazamacrocycle crown ether (cyclen) containing two pyridine subunits was prepared by a modified procedure and the interaction of its metal complexes with DNA was studied by agarose gel electrophoresis analysis. The results indicate that the Cu2+ complex as nuclease model can promote the hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond of supercoiled DNA. The rate of degradation of the supercoiled DNA (form I) to nicked DNA (form II) obtained at physiological condition in the presence of 2.14 mM Cu2+ complex is 2.31 × 10–3 min−1. The dependence of the rate of supercoiled DNA cleavage from the complex concentration shows an unusual profile and a hydrolytic cleaving mechanism of two monometallic complexes through cooperation from two-point binding to DNA is proposed.
Graphical abstract
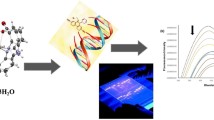
DNA cleavage promoted by metal complex of cyclen containing pyridine subunit
Ying Li, Xiao-Min Lu, Xin Sheng, Guo-Yuan Lu*, Ying Shao and Qiang Xu*
The copper complex of tetraazamacrocycle crown ether (cyclen) containing two pyridine subunits can promote the hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond of supercoiled DNA and a hydrolytic mechanism of two
monometallic complexes through cooperation from two-point binding to DNA is proposed. 









Similar content being viewed by others
References
(a) Liu, C., Wang, M., Zhang, T., Sun, H.: DNA hydrolysis promoted by di- and multi-nuclear metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 248, 147–168 (2004), (b) Burer, R.M.: Cleavage of nucleic acids by bleomycin. Chem. Rev. 98, 1153–1169 (1998), (c) Pogozelski, W.K., Tullius, T.D.: Oxidative Strand Scission of Nucleic Acids: Routes Initiated by Hydrogen Abstraction from the Sugar Moiety. Chem. Rev. 98, 1089–1108 (1998), (d) Armitage, B.: Photocleavage of nucleic acids. Chem. Rev. 98, 1171–1200 (1998), (e) McMillin, D., McNett, K.M.: Photoprocesses of copper complexes that bind to DNA. Chem. Rev. 98, 1201–1220 (1998), (f) David, S.S., Williams, S.D.: Chemistry of glycosylases and endonucleases involved in base-excision repair. Chem. Rev. 98, 1221–1262 (1998), (g) Rajski, S.R., Williams, R.M.: DNA crosslinking agents as antitumor drugs. Chem. Rev. 98, 2723–2796 (1998), (h) Hegg, E.L., Burstyn, J.N.: Toward the development of metal-based synthetic nucleases and peptidases: a rationale and progress report in applying the principles of coordination chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 173, 133–165 (1998), (i) Cowan, J.A.: Chemical nucleases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 634–642 (2001), (j) Morrow, J.R., Iranzo, O.: Synthetic metallonucleases for RNA cleavage. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 8, 192–200 (2004), (k) Chen, C-A., Cowan, J.A.: In vivo cleavage of a target RNA by copper kanamycin A. Direct observation by a fluorescence assay. Chem. Commun. 196–197 (2002), (l) Baker, B.F., Lot, S.S., Kringel, J., Cheng-Flournoy, S., Villiet, P., Sasmor, H.M., Siwkowski, A.M., Chappell, L.L., Morrow, J.R.: Oligonucleotide-europium complex conjugate designed to cleave the 5′ cap structure of the ICAM-1 transcript potentiates antisense activity in cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 1547–1551 (1999), (m) Perreault, D.M., Anslyn, E.V.: Unifying the current data on the mechanism of cleavage-transesterification of RNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36, 432–450 (1997)
(a) Feng, G., Mareque-Rivas, J.C., Torres Martin de Rosales, R., Williams, N.H.: A highly reactive mononuclear Zn(II) complex for phosphodiester cleavage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 13470–13471 (2005), (b) Branum, M.E., Tipton, A.K., Zhu, S., Que L. Jr.: Double-strand hydrolysis of plasmid DNA by dicerium complexes at 37 degrees C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 1898–1904 (2001), (c) Komiyama, M., Kina, S., Matsumura, K., Sumaoka, J., Tobey, S., Lynch, V.M., Anslyn, E.: Trinuclear copper(II) complex showing high selectivity for the hydrolysis of 2′-5′ over 3′-5′ for UpU and 3′-5′ over 2′-5′ for ApA ribonucleotides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 13731–13736 (2002), (d) Kuzuya, A., Mizoguchi, R., Morisawa, F., Machida, K., Komiyama, M.: Metal ion-induced site-selective RNA hydrolysis by use of acridine-bearing oligonucleotide as cofactor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 6887–6894 (2002), (e) Scheffer, U., Strick, A., Ludwig, V., Peter, S., Kalden, E., Göbel, M. W.: Metal-free catalysts for the hydrolysis of RNA derived from guanidines, 2-aminopyridines, and 2-aminobenzimidazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2211–2217 (2005), (f) Sissi, C., Mancin, F., Gatos, M., Palumbo, M., Tecilla, P., Tonellato, U.: Efficient plasmid DNA cleavage by a mononuclear copper(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. 44, 2310–2317 (2005), (g) Iranzo, O., Elmer, T., Richard, J.P., Morrow, J.R.: Cooperativity between metal ions in the cleavage of phosphate diesters and RNA by dinuclear Zn(II) catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 42, 7737–7746 (2003), (h) Rossi, L.M., Neves, A., Bortoluzzi, A.J., Hörner, R., Szpoganicz, B., Terenzi, H., Mangrich, A.S., Pereira-Maia, E., Castellano, E.E., Haase, W.: Synthesis, structure and properties of unsymmetrical-alkoxo-dicopper(II) complexes: biological relevance to phosphodiester and DNA cleavage and cytotoxic activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 358, 1807–1822 (2005), (i) Yang, M-Y., Richard, J.P., Morrow, J.R.: Substrate specificity for catalysis of phosphodiester cleavage by a dinuclear Zn(II) complex. Chem. Commun. 2832–2833 (2003), (j) Feng, G., Mareque-Rivas, J.C., Williams, N.H.: Comparing a mononuclear Zn(II) complex with hydrogen bond donors with a dinuclear Zn(II) complex for catalyzing phosphate ester cleavage. Chem. Commun. 1845–1847 (2006), (k) Kondo, S., Shinbo, K., Yamaguchi, T., Yoshida, K., Yano, Y.: Cooperativity of binuclear Zn(II) complexes of bisimidazolyl ligands in the hydrolysis of bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) phosphate in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 128–131 (2001), (l) Baldini M., Belicchi-Ferrari, M., Bisceglie, F., Capacchi, S., Pelosi, G., Tarasconi, P.: Zinc complexes with cyclic derivatives of ketoglutaric acid thiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, X-ray structures and DNA interactions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 1504–1513 (2005), (m) Erkkila, K.E., Odom, D.T., Barton, J.K.: Recognition and reaction of metallointercalators with DNA. Chem. Rev. 99, 2777–2796 (1999), (n) Shao, Y., Zhang, J., Tu, C., Dai, C., Xu, Q., Guo, Z.: Steric effect on the nuclease activity of Cu(II) complexes with aminoquinoline derivatives. J. Inorg. Biochem. 99, 1490–1496 (2005), (o) Ren, R., Yang, P., Zheng, W., Hua, Z.: A simple copper(II)-L-histidine system for efficient hydrolytic cleavage of DNA. Inorg. Chem. 39, 5454–5463 (2000), (p) Zhu, L., dos Santos, O., Koo, C.W., Rybstein, M., Pape, L., Canary, J.W.: Geometry-dependent phosphodiester hydrolysis catalyzed by binuclear copper complexes. Inorg. Chem. 42, 7912–7920 (2003), (q) Feng, G., Mareque-Rivas, J.C., Williams, N.H.: Bioinorganic models for the catalytic cooperation of metal ions and functional groups in nuclease and peptidase enzymes. Chem. Commun. 1845–1847 (2006), (r) Metzler-Nolte, N., Klein, C., Weyhermüller, T., Hrubanova, S., Happel, C.M., Kirin, S.I.: Synthesis, structure and comparison of the DNA cleavage ability of metal complexes M(II)L with the N-(2-hydroxyethoxyethyl)-bis(2-picolyl)amine ligand L (M = Co, Ni, Cu and Zn). Dalton Trans. 1201–1207 (2004), (s) Krämer, R.: Bioinorganic models for the catalytic cooperation of metal ions and functional groups in nuclease and peptidase enzymes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 182, 243–261 (1999)
(a) Boseggia, E., Gatos, M., Lucatello, L., Mancin, F., Moro, S., Palumbo, M., Sissi, C., Tecilla, P., Tonellato, U., Zagotto, G.: Toward efficient Zn(II)-based artificial nucleases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 4543–4549 (2004), (b) Iranzo, O., Kovalevsky, A.Y., Morrow, J.R., Richard, J.P.: Physical and kinetic analysis of the cooperative role of metal ions in catalysis of phosphodiester cleavage by a dinuclear Zn(II) complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(7), 1988–1993 (2003), (c) Williams, N.H., Lebuis, A.M., Chin, J.: A structural and functional model of dinuclear metallophosphatases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 3341–3348 (1999), (d) Kikuta, E., Murata, M., Katsube, N., Koike, T; Kimura, E.: Novel recognition of thymine base in double-stranded DNA by zinc(II)-macrocyclic tetraamine complexes appended with aromatic groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 5426–5436 (1999), (e) Sissi, C., Rossi, P., Felluga, F., Formaggio, F; Palumbo, M; Tecilla, P., Toniolo, C., Scrimin, P.: Dinuclear Zn(2+) complexes of synthetic heptapeptides as artificial nucleases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 3169–3170 (2001), (f) Kimura, E., Kodama, Y., Koike, T., Shiro, M.: Phosphodiester hydrolysis by a new zinc(II) macrocyclic tetraamine complex with an alcohol pendant: Elucidation of the roles of Ser-102 and zinc(II) in alkaline phosphatase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 8304–8311 (1995), (g) Young, M.J., Chin, J.: Dinuclear copper(II) complex that hydrolyzes RNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 10577–10578 (1995), (h) Bencini, A., Berni, E., Bianchi, A., Giorgi, C., Valtancoli, B., Chand, D.K., Schneider, H.-J.: Proton and Cu(II) binding to tren-based tris-macrocycles. Affinity towards nucleic acids and nuclease activity. Dalton Trans. (5), 793–800 (2003), (i) Kim, J.H.: Selective hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl phosphate by a dinuclear Cu(II) complex. Chem. Lett. 156–157 (2000) (j) Chand, D.K., Schneider, H.-J., Bencini, A., Bianchi, A., Giorgi, C., Ciattini, S., Valtancoli, B.: Supramolecular chemistry, part 99. Affinity and nuclease activity of macrocyclic polyamines and their CuII complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 6(21), 4001–4008 (2000), (k) Williams, N.H., Wyman, P.: Phosphate diester hydrolysis within a highly reactive dinuclear cobalt(III) complex. Ligand effect on reactivity, transition state and dissociation. J Chem. Soc. Perk Trans 2(11), 2068–2073 (2001), (l) McCue, K.P., Morrow, J.R.: Hydrolysis of a model for the 5′-cap of mRNA by dinuclear copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes. Rapid hydrolysis by four copper(II) ions. Inorg. Chem. 38, 6136–6142 (1999), (m) Jeung ,C.S., Kim, C.H., Min, K., Suh, S.W., Suh, J.: Hydrolysis of plasmid DNA catalyzed by Co(III) complex of cyclen attached to polystyrene. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 2401–2404 (2001), (n) Kikuta, E., Matsubara, R., Katsube, N., Koike, T., Kimura, E.: Selective recognition of consecutive G sequence in double-stranded DNA by a zinc(II)-macrocyclic tetraamine complex appended with an anthraquinone.J. Inorg. Biochem. 82, 239–249 (2000), (o) Ragunathan K.G., Schneider, H.J.: Supramolecular chemistry. 51. Complexes from polyazacyclophanes, fluorescence indicators, and metal cations - an example of allosterism through ring contraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 35, 1219–1221 (1995), (p) Rammo, J., Hettich, R., Roigk, A., Schneider, H.J.: Catalysis of DNA cleavage by lanthanide complexes with nucleophilic or intercalating ligands and their kinetic characterization. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 105–107 (1996), (q) Fry, F.H., Fischmann, A.J., Belousoff, M.J., Spiccia, L., Brügger, J.: Kinetics and mechanism of hydrolysis of a model phosphate diester by [Cu(Me3tacn)(OH2)2]2+ (Me3tacn = 1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane). Inorg. Chem. 44, 941–950 (2005), (r) Peng, W., Liu, P.-Y., Jiang, N., Lin, H.-H., Zhang, G.L., Liu, Y., Yu, X.-Q.: Dinuclear macrocyclic polyamine zinc(II) complexes linked with flexible spacers: Synthesis, characterization, and DNA cleavage. Bioorg. Chem. 33, 374–385 (2005)
(a) Michaelis, K., Kalesse, M.: Selective cleavage of the HIV-1 TAR-RNA with a peptide-cyclen conjugate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38, 2243–2245 (1999), (b) Parker, L.L., Lacy, S.M., Farrugia, L.J., Evans, C., Robins, D.J., O’Hare, C.C., Hartley, J.A., Jaffar, M., Stratford, I.J.: A novel design strategy for stable metal complexes of nitrogen mustards as bioreductive prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 47, 5683–5689 (2004), (c) Parker, L.L., Anderson, F.M., O’Hare, C.C., Lacy, S.M., Bingham, J.P., Robins, D.J., Hartley, J.A.: Synthesis of novel DNA cross-linking antitumour agents based on polyazamacrocycles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13, 2389–2395 (2005), (d) Liang, F., Wang, P., Zhou, X., Li, T., Li, Z., Lin, H., Gao, D., Zheng, C., Wu, C.: Nickel(II) and cobalt(II) complexes of hydroxyl-substituted triazamacrocyclic ligand as potential antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 1901–1904 (2004), (e) Liang, X.-Y., Sadler, P.J.: Cyclam complexes and their applications in medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 33, 246–266 (2004), (f) De Clercq, E.: Timeline: The bicyclam AMD3100 story. Nat. Res. Drug. Disc. 2, 581–587 (2003), (g) Jang, Y.H., Blanco, M., Dasgupta, S., Keire, D.A., Shively, J.E., Goddard, W.A.: Mechanism and energetics for complexation of 90Y with 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic Acid (DOTA), a model for cancer radioimmunotherapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 6142–6151 (1999), (h) Fichna, J., Janecka, A.: Synthesis of target-specific radiolabeled peptides for diagnostic imaging. Bioconjugate Chem. 14, 3–17 (2003)
(a) Kim, W.D., Hrncir, D.C., Kiefer, G.E., Sherry, A.D.: Synthesis, crystal structure, and potentiometry of pyridine-containing tetraaza macrocyclic ligands with acetate pendant arms. Inorg. Chem. 34, 2225–2232 (1995), (b) Marchand, A.P., Chong, H.-S., Alihodžić, S., Watson, W.H., Bodige, S.G.: Synthesis and alkali metal picrate extraction capabilities of novel, cage-functionalized, pyridine containing crown ethers and cryptands. Tetrahedron, 55, 9687–9696 (1999), (c) Koch, W.O., Kaiser, J.T., Krüger, H.-J.: First structural characterization of an eight-coordinate cobalt(II) complex containing five-membered chelate rings: Evidence for d-orbital-stabilization energy favoring eight-over six-coordination at cobalt(II) ions. Chem. Commun. 22, 2237–2238 (1997), (d) Koch, W.O., Barbieri, A., Grodzicki, M., Schünemann, V., Trautwein, A.X., Krüger, H.-J.: Eight-coordinate iron(II) and iron(III) ions in complexes with distorted dodecahedral FeN8 environments: synthesis and structures of bis(2,11-diaza[3.3](2,6)pyridinophane)iron complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 35, 422–424 (1996)
Bottino , F., Di Grazia, M., Finocchiaro, P., Fronczek, F.R., Mamo A., Pappalardo, S.: Reaction of tosylamide monosodium salt with bis(halomethyl) compounds: an easy entry to symmetrical N-tosyl aza macrocycles. J. Org. Chem. 53, 3521–3529 (1988)
(a) Dai, W.-M., Fong, K.C., Lau, C.W., Zhou, L., Hamaguchi, W., Nishimoto, S.: Synthesis and DNA cleavage study of a 10-membered ring enediyne formed via allylic rearrangement. J. Org. Chem. 64, 682–683 (1999), (b) Basile, L.A., Raphael, A.L., Barton, J.K.: Metal-activated hydrolytic cleavage of DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109, 7550–7551 (1987), (c) Branum, M.E., Tipton, A.K., Zhu, S., Que, L. Jr.: Double-strand hydrolysis of plasmid DNA by dicerium complexes at 37 degrees C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 1898–1904 (2001), (d) Takeda, N., Shibata, M., Tajima, N., Hirao, K., Komiyama, M.: Kinetic and theoretical studies on the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of DNA. J. Org. Chem. 65, 4391–4396 (2000)
(a) Deck, K.M., Tseng, T.A., Burstyn, J.N.: Triisopropyltriazacyclononane copper(II): An efficient phosphodiester hydrolysis catalyst and DNA cleavage agent. Inorg. Chem. 41, 669–677 (2002), (b) Shi, S., Liu, J., Li, J., Zheng, K.C., Tan, C.P., Chen, L.M., Ji, L.N.: Electronic effect of different positions of the -NO2 group on the DNA-intercalator of chiral complexes [Ru(bpy)2L]2+ (L = o-npip, m-npip and p-npip). Dalton Trans. 2038–2046 (2005)
(a) Hegg, E.L., Burtyn, J.N.: Copper(II) macrocycles cleave single-stranded and double-stranded DNA under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Inorg. Chem. 35, 7474–7481 (1996), (b) Itoh, T., Hisada, H., Sumiya, T., Hosono, M., Usui, Y., Fujin, Y.: Hydrolytic cleavage of DNA by a novel copper(II) complex with cis,cis-1,3,5-triaminocyclohexane. Chem. Commun. 677–678 (1997), (c) Sreedhara, A., Cowan, J.A.: Efficient catalytic cleavage of DNA mediated by metalloaminoglycosides. Chem. Commun. 1737–1738 (1997)
(a) Sigman, D.S., Mazumder, A., Perrin, D.M.: Chemical nucleases. Chem. Rev. 93, 2295–2316v (1993), (b) Westheimer, F.H.: Why nature chose phosphates. Science 235, 1173–1178 (1987)
(a) Subramanian, M., Shadakshari, U., Chattopadhyay, S.: A mechanistic study on the nuclease activities of some hydroxystilbenes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 1231–1237 (2004), (b) Song, Y.-F., Yang, P.: Synthesis, DNA scission chemistry, and an investigation of the reactive oxygen species of two 2,6-dimethoxyhydroquinone-3-mercaptoacetic acid-peptide conjugates. Aus. J. Chem. 54, 253–259 (2001), (c) Scarpellini, M., Neves, A., Horner, R., Bortoluzzi, A.J., Szpoganics, B., Zucco, C., Nome Silva, R.A., Drago, V., Mangrich, A.S., Ortiz, W.A., Passos, W.A., de Oliveira, M.C.B., Terenzi, H.: Phosphate diester hydrolysis and DNA damage promoted by new cis-aqua/hydroxy copper(II) complexes containing tridentate imidazole-rich ligands. Inorg. Chem. 42, 8353–8365 (2003)
Molenveld , P., Engbersen, J.F.J., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Dinuclear metallo-phosphodiesterase models: application of calix[4]arenes as molecular scaffolds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 29, 75–86 (2000)
(a) Selmeczi, K., Giorgi, M., Speier, G., Farkas, E., Reglier, M.: Mono- versus binuclear copper(II) complexes in phosphodiester hydrolysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1022–1031 (2006), (b) Rossi, L.M., Neves, A., Hörner, R., Terenzi, H., Szpoganicz, B., Sugai, J.: Hydrolytic activity of a dinuclear copper(II,II) complex in phosphate diester and DNA cleavage. Inorgan. Chim. Acta 337, 366–370 (2002), (c) Rossi, L.M., Neves, A., Bortoluzzi, A.J., Hörner, R., Szpoganicz, B., Terenzi, H., Mangrich, A.S., Pereira-Maia, E., Castellano, E.E., Haase, W.: Synthesis, structure and properties of unsymmetrical-alkoxo-dicopper(II) complexes: biological relevance to phosphodiester and DNA cleavage and cytotoxic activity. Inorganica Chimica Acta 358, 1807–1822 (2005), (d) Reddy, P.A., Nethaji, M., Chakravarty, A.R.: Hydrolytic cleavage of DNA by ternary amino acid Schiff base copper(II) complexes having planar heterocyclic ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1440–1446 (2004)
Reed , R., Holmes, D., Weyers, J., Jones, A.: Practical skills in biomolecular sciences, Addison-Wesley, Boston, (2001) 8–33
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Science Foundation (Grant. No. 20372032) of China and the Analytical Foundation of Nanjing University are deeply acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lu, XM., Sheng, X. et al. DNA cleavage promoted by Cu2+ complex of cyclen containing pyridine subunit. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 59, 91–98 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-007-9299-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-007-9299-y