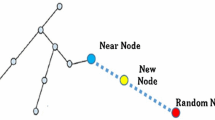
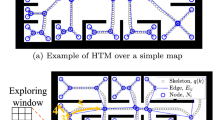
Abstract
This paper presents a faster RRT-based path planning approach for regular 2-dimensional (2D) building environments. To minimize the planning time, we adopt the idea of biasing the RRT tree-growth in more focused ways. We propose to calculate the skeleton of the 2D environment first, then connect a geometrical path on the skeleton, and grow the RRT tree via the seeds generated locally along this path. We conduct batched simulations to find the universal parameters in manipulating the seeds generation. We show that the proposed skeleton-biased locally-seeded RRT (skilled-RRT) is faster than the other baseline planners (RRT, RRT*, A*-RRT, Theta*-RRT, and MARRT) through experimental tests using different vehicles in different 2D building environments. Given mild assumptions of the 2D environments, we prove that the proposed approach is probabilistically complete. We also present an application of the skilled-RRT for unmanned ground vehicle. Compared to the other baseline algorithms (Theta*-RRT and MARRT), we show the applicability and fast planning of the skilled-RRT in real environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguinaga, I., Borro, D., Matey, L.: Parallel rrt-based path planning for selective disassembly planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 36(11-12), 1221–1233 (2008)
Alterovitz, R., Patil, S., Derbakova, A.: Rapidly-exploring roadmaps: Weighing exploration vs. refinement in optimal motion planning 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 3706–3712 (2011)
Arslan, O., Tsiotras, P.: Dynamic programming guided exploration for sampling-based motion planning algorithms 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 4819–4826 (2015)
Bekris, K., Kavraki, L.: Informed and probabilistically complete search for motion planning under differential constraints First International Symposium on Search Techniques in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (STAIR), Chicago, IL (2008)
Brunner, M., Brüggemann, B, Schulz, D.: Hierarchical rough terrain motion planning using an optimal sampling-based method 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 5539–5544 (2013)
Choudhury, S., Gammell, J.D., Barfoot, T.D., Srinivasa, S.S., Scherer, S.: Regionally accelerated batch informed trees (rabit*): A framework to integrate local information into optimal path planning 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 4207–4214 (2016)
Cowlagi, R.V., Tsiotras, P.: Hierarchical motion planning with dynamical feasibility guarantees for mobile robotic vehicles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 28(2), 379–395 (2012)
Daniel, K., Nash, A., Koenig, S., Felner, A.: Theta*: Any-angle path planning on grids. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 39, 533–579 (2010)
Denny, J., Greco, E., Thomas, S., Amato, N.M.: Marrt: Medial axis biased rapidly-exploring random trees 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 90–97 (2014). doi:10.1109/ICRA.2014.6906594
Denny, J., Colbert, J., Qin, H., Amato, N.M.: On the theory of user-guided planning 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 4794–4801. IEEE (2016)
Dong, Y., Zhang, Y.: Application of rrt algorithm to unmanned ground vehicle motion planning and obstacle avoidance Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Unmanned Systems, vol. 11 (2015)
Dong, Y., Zhang, Y., Ai, J.: Experimental test of unmanned ground vehicle delivering goods using RRT path planning algorithm. Unmanned Syst. 5(1), 45–57 (2017). doi:10.1142/S2301385017500042
Gammell, J.D., Srinivasa, S.S., Barfoot, T.D.: Informed rrt*: Optimal sampling-based path planning focused via direct sampling of an admissible ellipsoidal heuristic 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 2997–3004 (2014)
Gammell, J.D., Srinivasa, S.S., Barfoot, T.D.: Batch informed trees (bit*): Sampling-based optimal planning via the heuristically guided search of implicit random geometric graphs 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 3067–3074 (2015)
Garrido, S., Moreno, L., Abderrahim, M., Martin, F.: Path planning for mobile robot navigation using voronoi diagram and fast marching 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 2376–2381 (2006). doi:10.1109/IROS.2006.282649
Geraerts, R.: Planning short paths with clearance using explicit corridors 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 1997–2004. IEEE (2010)
Jaillet, L., Cortés, J., Siméon, T.: Sampling-based path planning on configuration-space costmaps. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(4), 635–646 (2010)
Jalel, S., Marthon, P., Hamouda, A.: A new path generation algorithm based on accurate nurbs curves. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 13, 10.5772/63072 (2016)
Kalisiak, M., van de Panne, M.: Faster motion planning using learned local viability models Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 2700–2705 (2007)
Karaman, S., Frazzoli, E.: Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 30(7), 846–894 (2011)
Kuffner, J.J., LaValle, S.M.: Rrt-Connect: an efficient approach to single-query path planning Proceedings. ICRA’00. IEEE International Conference On Robotics and Automation, 2000, vol. 2, pp 995–1001. IEEE (2000)
Latombe, J.: Robot Motion Planning. The Springer International Series in Engineering and Computer Science. Springer, USA (2012)
LaValle, S.M., Kuffner, J.J.: Randomized kinodynamic planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(5), 378–400 (2001)
Mirtich, B., Canny, J.: Using skeletons for nonholonomic path planning among obstacles Proceedings 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 3, pp 2533–2540 (1992). doi:10.1109/ROBOT.1992.220060
Neto, A.A., Macharet, D.G., Campos, M.F.: On the generation of trajectories for multiple uavs in environments with obstacles Selected papers from the 2nd International Symposium on UAVs, Reno, Nevada, USA June 8–10, 2009, pp 123–141. Springer (2009)
Oriolo, G., Vendittelli, M., Ulivi, G.: Path planning for mobile robots via skeletons on fuzzy maps. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2(4), 355–374 (1996)
Palmieri, L., Koenig, S., Arras, K.O.: Rrt-based nonholonomic motion planning using any-angle path biasing 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 2775–2781 (2016)
Plaku, E., Kavraki, L.E., Vardi, M.Y.: Discrete search leading continuous exploration for kinodynamic motion planning Robotics: Science and Systems, pp 326–333 (2007)
Plaku, K.L.E.E., Vardi, M.Y.: Motion planning with dynamics by a synergistic combination of layers of planning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(3), 469–482 (2010)
Rickert, M., Brock, O., Knoll, A.: Balancing exploration and exploitation in motion planning IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2008. ICRA, pp 2812–2817 (2008)
Rickert, M., Sieverling, A., Brock, O.: Balancing exploration and exploitation in sampling-based motion planning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 30(6), 1305–1317 (2014)
Rodriguez, T.X., Lien, J.M., Amato, N.M.: An obstacle-based rapidly-exploring random tree Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA 2006, pp 895–900 (2006). doi:10.1109/ROBOT.2006.1641823
Taïx, M., Flavigné, D., Ferré, E.: Human interaction with motion planning algorithm. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 67(3), 285–306 (2012)
Yang, D.H., Hong, S.K.: A roadmap construction algorithm for mobile robot path planning using skeleton maps. Adv. Robot. 21(1-2), 51–63 (2007)
Yang, K., Moon, S., Yoo, S., Kang, J., Doh, N.L., Kim, H.B., Joo, S.: Spline-based rrt path planner for non-holonomic robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 73(1-4), 763 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The research was partially supported by the ST Engineering-NTU Corporate Lab through the NRF corporate lab@university scheme. The authors are also indebted to Mr. Mohhamadali Askari Hemmat from Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering in Concordia University Canada for the discussion on this idea, and Mr. Reinaldo Maslim from School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering in Nanyang Technological University for the real test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(WMV 26.7 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Camci, E. & Kayacan, E. Faster RRT-based Nonholonomic Path Planning in 2D Building Environments Using Skeleton-constrained Path Biasing. J Intell Robot Syst 89, 387–401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-017-0567-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-017-0567-9