Abstract
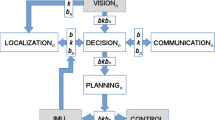
A real-time hybrid control architecture for biped humanoid robots is proposed. The architecture is modular and hierarchical. The main robot’s functionalities are organized in four parallel modules: perception, actuation, world-modeling, and hybrid control. Hybrid control is divided in three behavior-based hierarchical layers: the planning layer, the deliberative layer, and the reactive layer, which work in parallel and have very different response speeds and planning capabilities. The architecture allows: (1) the coordination of multiple robots and the execution of group behaviors without disturbing the robot’s reactivity and responsivity, which is very relevant for biped humanoid robots whose gait control requires real-time processing. (2) The straightforward management of the robot’s resources using resource multiplexers. (3) The integration of active vision mechanisms in the reactive layer under control of behavior-dependant value functions from the deliberative layer. This adds flexibility in the implementation of complex functionalities, such as the ones required for playing soccer in robot teams. The architecture is validated using simulated and real Nao humanoid robots. Passive and active behaviors are tested in simulated and real robot soccer setups. In addition, the ability to execute group behaviors in real- time is tested in international robot soccer competitions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin, R.: Behavior-Based Robotics. MIT Press (1998)
Arkin, R., Fujita, M., Takagi, T., Hasegawa, R.: An ethological and emotional basis for human–robot interaction. Robot. Auton. Syst. 42(3–4), (2003)
Brooks, R.: A robust layered control system for a mobile robot. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 2(1) (1986)
Jaeger, H., Christaller, T.: Dual dynamics: designing behavior systems for autonomous robots. In: Artificial Life and Robotic, vol. 2(3), pp. 108–112. Springer, Japan (1998)
Hertzberg, J., Jaeger, H., Zimmer, U., Morignot, P.: A framework for plan execution in behavior-based robots. Proceedings, pp. 8–13 (1998)
Behnke, S., Frötschl, B., Rojas, R.: Using hierarchical dynamical systems to control reactive behavior. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 186–195 (2000)
Behnke, S., Stückler, J., Strasdat, H., Schreiber, M.: Hierarchical reactive control for soccer playing humanoid robots. International Journal of Humanoid Robotic 5(3) (2008)
Hurdus J., et al.: Victor tango architecture for autonomous navigation in the Darpa Challenge. J. Aero. Comput. Inform. Commun. 5(12), 1542–9423 (2008)
Berger, R., Burkhard, H.: At Humboldt—team description 2007. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (RoboCup 2007) (2008)
Chernova, S., Arkin, R.: From deliberative to routine behaviors: a cognitively inspired action-selection mechanism for routine behavior capture. Adapt. Behav. 15(2), 199–216 (2007)
Huntsberger, T., Pirjanian, P., Trebi-Ollennu, A., Aghazarian, H., Das, H., Joshi, S., Schenker, P.: CAMPOUT: a control architecture for tightly coupled coordination of multirobot system for planetary surface exploration. In: Proc. SPIE Conf. Sensor Fusion and Decentralized Control in Robotic System III (2000)
Christensen, H., Pirjanian, P.: Theoretical methods for planning and control in mobile robotics. In: IEEE Conf. on Knowledge-Based Intelligent Electronic System (1997)
Maes, P.: Modelling adaptive autonomous agents. J. Artif. Life 1, 135–162 (1994)
Hoshino, Y., Takagi, T., Di Profio, U., Fujita, M.: Behavior description and control using behavior module for personal robot. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Robotic and Automation (2004)
Sawada, T., Takagi, T., Fujita, M.: Behavior selection and motion modulation in emotionally grounded architecture for QRIO SDR-4X II. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (2004)
Steinbahuer, G., Wotawa, F.: Enhacing plan execution in dynamics domains using model based reasoning. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science 5314, pp. 510–519 (2008)
Gat, E.: On Three Layer Architectures. Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Robots, pp. 195–210. AAIA Press (1997)
Matarić, M.: Behavior-based control: examples from navigation, learning and group behavior. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 9(2–3) (1997)
Lencer, S., Bruce, J., Veloso, M.: A Modular Hierarchical Behavior-based Architecture. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2377 (2002)
Proetzsch, M., Luksch, T., Berns, K.: Development of complex robotic systems using the behavior-based control architecture iB2C. Robot. Auton. Syst. 58, 46–67 (2010)
Friedmann, M., Kiener, J., Petters, S., Thomas, D., von Stryk, O., Sakamoto, H.: Versatile, high-quality motions and behavior control of humanoid soccer robots. In: Proc. IEEE Workshop on Humanoid Soccer Robot, pp. 9–16 (2006)
Ferrein, A., Potgieter, A., Steinbahuer, G.: Self-aware robots- what do we need from learning, deliberative and reactive control? In: Proc. Workshop on Hybrid Control of Autonomous Systems, pp. 1–5 (2009)
Berger, M., Endert, H., Joecks, S.: Combining learning, deliberation and reactive control in simulated soccer: DAInamite framework. In: Proc. Workshop on Hybrid Control of Autonomous Systems, pp. 57–62 (2009)
Korterkamp, D., Simmons, R.: Robotic systems architectures and programming, chapter A.8. In: Siciliano, B., Khatib, O. (eds.) Springer Handbook of Robotics, pp. 187–206. Springer (2008)
Mataric, M., Michaud, F.: Behavior-based systems, chapter E.38. In: Siciliano, B., Khatib, O. (eds.) Springer Handbook of Robotics, pp. 891–909. Springer (2008)
Bonasso, R.P., Kortenkamp, D., Miller, D.P., Slack, M.: Experiences with an architecture for intelligent, reactive agents. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 9, 237–256 (1997)
Müller, M.: Hierarchical activation spreading: a design pattern for action selection. In: Proc. Workshop on Hybrid Control of Autonomous Systems, pp. 63–70 (2009)
Guerrero, P., Ruiz-del-Solar, J.: Improving robot self-localization using landmarks’ poses tracking and odometry error compensation. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science 5001 (RoboCup 2007), pp. 148–158 (2008)
Guerrero, P., Ruiz-del-Solar, J., Díaz, G.: Probabilistic decision making in robot soccer. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science 5001 (RoboCup 2007), pp. 29–40 (2008)
Guerrero, P., Ruiz-del-Solar, J., Romero, M., Angulo, S.: Task oriented probabilistic active vision. Int. Journal of Humanoid Robotics 7(3), 451–476 (2010)
Ruiz-del-Solar, J., Guerrero, P., Palma-Amestoy, R., Marchant, R., Yañez, J.M.: UChile Kiltros 2009 Team description paper. In: RoboCup Symposium 2009, 29 June–5 July, Graz, Austria. CD Proceedings (2009)
Stroupe, A., Matrin, M., Balch, T.: Distributed sensor fusion for object position estimation by multi-robot systems. In: Proc. ICRA Conf. 2, pp. 1092–1098 (2001)
Schulz, R.: Active Vision in Anthropomorphic Humanoid Robots. Electrical Engineering Thesis, Universidad de Chile (2010) (in Spanish)
Aldebaran Robotics Official Website: http://www.aldebaran-robotics.com/. Accessed 19 December 2010
Boost Library Official Website: http://www.boost.org/. Accessed 19 December 2010
RoboCup Official Website: http://www.robocup.org/. Accessed 19 December 2010
RoboCup 2010 Official Website: http://www.robocup2010.org/. Accessed 19 December 2010
RoboCu SPL League Official Website: http://www.tzi.de/spl/bin/view/Website/WebHome. Accessed 19 December 2010
Darpa Challenge Official Website: http://www.darpa.mil/grandchallenge/index.asp. Accessed 19 December 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testart, J., Ruiz del Solar, J., Schulz, R. et al. A Real-Time Hybrid Architecture for Biped Humanoids with Active Vision Mechanisms. J Intell Robot Syst 63, 233–255 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-010-9515-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-010-9515-7