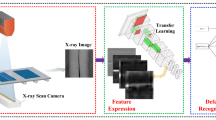
Abstract
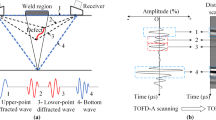
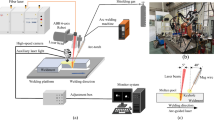
The weld defect recognition of titanium alloy is of great significance for ensuring the safety and reliability of equipment. This study proposes a method based on the enlighten faster region-based convolutional neural network (EFRCNN) to recognize titanium alloy weld defects. First, by designing defect test blocks and using probes with different frequencies, a dataset of time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) weld defect detections is constructed. Next, to overcome the problems of high data noise and low recognition accuracy, a parallel series multi-scale feature information fusion mechanism and a channel domain attention strategy are designed, and a deep learning network model based on the faster region-based convolution neural network (Faster R-CNN) is constructed. Finally, the proposed method is verified by the TOFD test data of titanium alloy welds. The results show that the proposed method can achieve a defect type recognition accuracy of more than 92%, especially in detecting cracks or a lack of fusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The TOFD data used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The software application used in this study is described in the text.
Abbreviations
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- BE:
-
Back-wall echo
- BP:
-
Back-propagation
- CFBP:
-
Cascade feed-forward back-propagation
- CF-RW:
-
Channel feature reweighting
- CR:
-
Crack
- EFRCNN:
-
Enlighten faster region-based convolutional neural network
- Faster R-CNN:
-
Faster region-based convolutional neural network
- IOU:
-
Intersection over union
- LF:
-
Lack of fusion
- LP:
-
Lack of penetration
- LW:
-
Later wave
- NDT:
-
Non-destructive testing
- NMS:
-
Non-maximum suppression
- PAUT:
-
Phased array ultrasonic testing
- PO:
-
Porosity
- RMSE:
-
Root mean squared error
- RNEF:
-
ResNet-50 extraction feature
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- RPN:
-
Region proposal network
- RT:
-
Radiographic testing
- SGD:
-
Stochastic gradient descent
- SI:
-
Slag inclusion
- TDW:
-
Tip diffracted wave
- TOFD:
-
Time-of-flight diffraction
- UT:
-
Ultrasonic testing
- ZSNF:
-
Z-score normalization and fusion
References
Ahmed, K., Redouane, D., & Mohamed, K. (2007). 2D gabor functions and FCMI algorithm for flaws detection in ultrasonic images. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 1(9), 2883–2887. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1062172
Al-Ataby, A., Al-Nuaimy, W., Brett, C. R., & Zahran, O. (2010). Automatic detection and classification of weld flaws in TOFD data using wavelet transform and support vector machines. Insight (northampton UK), 52(11), 597–602. https://doi.org/10.1784/insi.2010.52.11.597
Baby, S., Balasubramanian, T., Pardikar, R. J., Palaniappan, M., & Subbaratnam, R. (2003). Time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) technique for accurate sizing of surface-breaking cracks. Insight (northampton UK), 45(6), 426–430. https://doi.org/10.1784/insi.45.6.426.52885
Baniukiewicz, P. (2014). Automated defect recognition and identification in digital radiography. Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation, 33(3), 327–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-013-0216-6
Baskaran, G., Balasubramaniam, K., & Lakshmana, R. C. (2006). Shear-wave time of flight diffraction (S-TOFD) technique. NDT & E International, 39(6), 458–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2006.01.003
British Standards Institution. (1993). Guide to Calibration and Setting-Up of the Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) Technique for the Detection, Location and Sizing of Flaws, BS 7706. London: British Standards Institution.
Cenate, C. F.T., Sheela Rani, B., Ramadevi, R., Sangeetha, D. N., & Venkatraman, B. (2016). Optimization of the Cascade Feed Forward Back Propagation network for defect classification in ultrasonic images. Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 52(10), 557–568. https://doi.org/10.1134/s106183091610003x
Chen, J., Wu, E., Wu, H., Zhou, H., & Yang, K. (2019). Enhancing ultrasonic time-of-flight diffraction measurement through an adaptive deconvolution method. Ultrasonics, 96, 175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2019.01.009
Felice, M. V., & Fan, Z. (2018). Sizing of flaws using ultrasonic bulk wave testing: A review. Ultrasonics, 88, 26–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2018.03.003
Franco, F., Cardoso, F. A., Rosado, L. S., Ferreira, R., Cardoso, S., Piedade, M., et al. (2017). Advanced NDT inspection tools for titanium surfaces based on high-performance magnetoresistive sensors. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 53(4), 6200805. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmag.2016.2636807
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., & Wu, E. (2020). Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence; 42(8): https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8701503/
Huang, H., Hu, L., Li, B., Shen, C., Wang, H., & Chen, Z. (2019). Recognition of defect in TOFD image based on faster region convolutional neural networks. Nondestr Test (shanghai), 41(7), 12–18. https://doi.org/10.11973/wsjc201907004
Jiang, H., Wang, R., Gao, Z., Gao, J., & Wang, H. (2019). Classification of weld defects based on the analytical hierarchy process and Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 30(4), 2013–2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1369-4
Liu, J., Xu, G., Ren, L., Qian, Z., & Ren, L. (2017). Defect intelligent identification in resistance spot welding ultrasonic detection based on wavelet packet and neural network. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 90(9–12), 2581–2588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9588-y
Mihara, T., Otsuka, Y., Cho, H., & Yamanaka, K. (2006). Time-of-flight diffraction measurement using laser ultrasound. Experimental Mechanics, 46(5), 561–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-006-8885-z
Moles, M., Robertson, L., & Sinclair, T. (2012). Developments in time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD). In Proceedings of 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing. Durban, 16–20 April.
Peters, M., Kumpfert, J., Ward, C. H., & Leyens, C. (2003). Titanium alloys for aerospace applications. Advanced Engineering Materials, 5(6), 419–427. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200310095
Praveen, A., Vijayarekha, K., Abraham, S. T., & Venkatraman, B. (2013). Fourier analysis of ultrasonic TOFD signals for defect detection in austenitic stainless steel welds. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 71(9), 14–17. https://doi.org/10.5120/12385-8737
Rack, H. J., & Qazi, J. I. (2006). Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Materials Science & Engineering C: Materials for Biological Applications, 26(8), 1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2005.08.032
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2017). Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(6), 1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031
Silva, L. C., Simas Filho, E. F., Albuquerque, M. C. S., Silva, I. C., & Farias, C. T. T. (2020). Segmented analysis of time-of-flight diffraction ultrasound for flaw detection in welded steel plates using extreme learning machines. Ultrasonics, 102, 106057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2019.106057
Simas Filho, E. F., Souza, Y. N., Lopes, J. L. S., Farias, C. T. T., & Albuquerque, M. C. S. (2013). Decision support system for ultrasound inspection of fiber metal laminates using statistical signal processing and neural networks. Ultrasonics, 53(6), 1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2013.02.005
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.Y., et al. (2018). CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham,. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06521
Yang, L., & Jiang, H. (2021). Weld defect classification in radiographic images using unified deep neural network with multi-level features. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 32(2), 459–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01581-2
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., et al. (2018) Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. Munich, GERMANY. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.02758v2
Zhi, Z., Jiang, H., Yang, D., Cheng, Z., Gao, J., Wang, Q., et al. (2021). A deep learning fusion model of wave and image data for weld defect recognition. Journal of xi’an Jiaotong University, 55(5), 73–82. https://doi.org/10.7652/xjtuxb202105009
Zhu, Z., Sun, J., Li, J., & Huang, P. (2016). Investigation on the influence of tool wear upon chip morphology in end milling titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 83(9–12), 1477–1485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7690-1
Funding
This paper was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFF0210502), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2019JM-214), Research and Application of the TOFD Detection Technology for Fusion Welded Butt Joint of Titanium Pressure Equipment (2019KY05), and the Research and Development Project of the TOFD Auxiliary Recognition System for Detecting Weld Defects in Spherical Tank (SXTJKJXM-202003). The funder had no role in experimental design, model establishment, data analysis, manuscript writing, or decisions to submit articles for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ methodology, manuscript drafting, conceptualization, manuscript revision, experimental data curation, manuscript review, and supervision. HJ methodology, manuscript drafting, conceptualization, manuscript revision, experimental data curation, and manuscript review. DY experimental data curation and manuscript review. JG experimental data curation and manuscript review. QW supervision. XW supervision. JW supervision. YW supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, Z., Jiang, H., Yang, D. et al. An end-to-end welding defect detection approach based on titanium alloy time-of-flight diffraction images. J Intell Manuf 34, 1895–1909 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01905-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01905-w