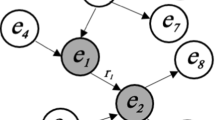
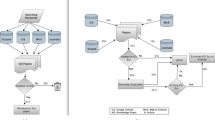
Abstract
We present an extended version of the \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) taxonomic reasoner for large ontologies. This new version provides fuller support for TBox reasoning, checking consistency, and retrieving instances. The \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) system is based upon the \(\mathcal {O}\mathcal {S}\mathcal {F}\) formalism. It is implemented on an entirely new architecture which includes several optimization techniques. We define a bidirectional mapping between \(\mathcal {O}\mathcal {S}\mathcal {F}\) graph structures and the Resource Description Framework (RDF) allowing a translation from \(\mathcal {O}\mathcal {S}\mathcal {F}\) queries into SPARQL for retrieving instances from an RDF triplestore. We carried out comparative performance evaluation experiments using \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) as well as well-known Semantic Web reasoners (such as FaCT++, Pellet, HermiT, TrOWL, and RacerPro) on very large public ontologies. For the same queries on the same ontologies, the results achieved by \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) were compared to those obtained by all the other reasoners. The results of experiments show that \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) consistently performs on a par with the fastest systems for concept classification, and several orders of magnitude more efficiently in terms of response time for Boolean query-answering over attributed concepts, as well as for ABox triplestore querying. The latter result is irrespective of the triplestore management used because the \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) reasoner uses its knowledge to optimize SPARQL queries before submitting them to the triplestore.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We shall use “sort” and “type” interchangeably for such a symbol denoting a set of values.
We use “sort” as a synonym of atomic “class” or “concept.” In particular, sorts are partially ordered sort symbols, where the ordering (“is-a”) denotes set inclusion.
The notation [[…]] denotes the formal meaning of whatever “ …” is.
See https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8uOgG6CJ8iY for a short slide presentation on this very question.
Op. cit., Section 6: Discussion, p. 7.
References
Agrawal, R., Borgida, A., & Jagadish, H.V. (1989). Efficient management of transitive relationships in large data and knowledge bases. In Clifford, J., Lindsay, B.G., & Maier, D. (Eds.) Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, (Vol. 18 pp. 253–262). Portland: ACM, SIGMOD Record. [Available online http://dbs.informatik.uni-halle.de/Lehre/DBSIIaSS02/p253-agrawal.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H. (2007). Data models as constraint systems—a key to the Semantic Web. Constraint Processing Letters, 1, 33–88. [Available online cs.brown.edu/people/pvh/CPL/Papers/v1/hak.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H. (2007). Description logic vs.order-sorted feature logic. In Calvanese, D., Franconi, E., Haarslev, V., Lembo, D., Motik, B., Turhan, A.-Y., & Tessaris, S. (Eds.) International Workshop on Description Logics (DL’07), (pp. 147–154). Brixen-Bressanone (Italy): CEUR Workshop Proceedings. [Available online http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-250/paper2.pdf] .
Aït-Kaci, H. (2013). Efficient encoding of very large partial orders—a specification. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 4, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available online cedar.liris.cnrs.fr/papers/ctr4.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H. (2014). \(\mathcal {H}\mathcal {O}\mathcal {O}\mathcal {T}\): A language for expressing and querying hierarchical ontologies, objects, and types—a specification. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 16, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available online cedar.liris.cnrs.fr/papers/ctr16.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H. (2014). A set-complete domain construction for order-sorted set-valued features. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 11, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available onlinecedar.liris.cnrs.fr/papers/ctr11.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H., & Amir, S. (2013). Classifying and querying very large taxonomies—a comparative study to the best of our knowledge. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 2, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available online cedar.liris.cnrs.fr/papers/ctr2.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H., & Amir, S. (2015). Classifying and querying very large taxonomies with bit-vector encoding. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 1–25. [Available online https://www.researchgate.net/...VeryLargeTaxonomieswithBit-VectorEncoding].
Aït-Kaci, H., Boyer, R., Lincoln, P., & Nasr, R. (1989). Efficient implementation of lattice operations. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 11 (1), 115–146. [Available online www.hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/encoding-toplas-89.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H., Dumant, B., Meyer, R., Podelski, A., & Roy, P.V. (1994), (prepublication edn). [Available online hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/WildLIFE-HANDBOOK.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H., & Nasr, R. (1986). LOGIN: A logic programming language with built-in inheritance. Journal of Logic Programming, 3, 185–215. [Available online hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/login-jlp-86.pdf].
Aït-Kaci, H., & Podelski, A. (1991). Towards a meaning of LIFE. In Maluszyński, J., & Wirsing, M. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Programming Language Implementation and Logic Programming (Passau, Germany), number 528 in Lecture Notes in Computer Science (pp. 255–274). Verlag: Springer. [Available online hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/meaningoflife.pdf] .
Aït-Kaci, H., & Podelski, A. (1992). Logic programming with functions over order-sorted feature terms. In Lamma, E., & Mello, P. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Extensions of Logic Programming (Bologna, Italy). LNAI 660 (pp. 100–119). Verlag: Springer. [Available online hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/elp-92.pdf] .
Amir, S., & Aït-Kaci, H. (2013). \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\): a fast taxonomic reasoner based on lattice operations—system demonstration. In Blomqvist, E., & Groza, T. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Posters & Demonstrations Track of the 12th International Semantic Web Conference (pp. 9–12). Sydney, Australia: CEUR Workshop Proceedings. [Available online ceur-ws.org/Vol-1035/iswc2013demo3.pdf] .
Amir, S., & Aït-Kaci, H. (2014). Design and implementation of an efficient semantic web reasoner. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 12, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available online cedar.liris.cnrs.fr/papers/ctr12.pdf].
Baader, F., McGuinness, D.L., Nardi, D., & Patel-Schneider, P.F. (Eds.) (2003). The Description Logic Handbook: theory, Implementation, and Applications. New York: Cambridge University Press. [Available online cdn.preterhuman.net/texts/.../TheDescriptionLogicHandbook...(2003).pdf].
Chen, M., Haque, R., & Mohand-Saïd, H. (2014). CedTMart—a triplestore for storing and querying blinked data. In \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Technical Report Number 7, \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project, LIRIS, Département d’Informatique, université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. [Available online cedar.liris.cnrs.fr/interns/MinweiChen/ctr7.pdf].
Constantopoulos, P., Jarke, M., Mylopoulos, J., & Vassiliou, Y. (1995). The software information base: a server for reuse. The VLDB Journal, 4(1), 1–43. [Available online https://www.researchgate.net/publication/...AServerforReuse].
Dentler, Kathrin, Cornet, Ronald, Teije, Annette ten, & Keizer, Nicolette de (2011). Comparison of reasoners for large ontologies in the OWL 2 EL profile. Semantic Web Journal, 2(2), 1–5. [Available online www.semantic-web-journal.net/.../swj1202.pdf].
Federhen, S. (2012). The NCBI taxonomy database. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 136–143. [Available online www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.../gkr1178.pdf].
Goodwin, J. (2005). Experiences of using OWL at the ordnance survey. In Cuenca Grau, B., Horrocks, I., Parsia, B., & Patel-Schneider, P. (Eds.) Proceedings of the OWLED’05 Workshop on OWL: Experiences and Directions, Galway, Ireland, November 11–12. CEUR Workshop Proceedings Vol 188. [Available online ftp.informatik.rwth-aachen.de/.../sub17.pdf].
Guo, Y., Pan, Z., & Jeff, H. (2005). LUBM: A benchmark for OWL knowledge base systems. Journal of Web Semantics, 3(2–3), 158–182. [Available online www.websemanticsjournal.org/.../70/68].
Hoehndorf, Robert, Harris, Midori A., Herre, Heinrich, Rustici, Gabriella, & Gkoutos, Georgios V. (2012). Semantic integration of physiology phenotypes with an application to the Cellular Phenotype Ontology. Bioinformatics, 28(13), 1783–1789. [Available online www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.../bts250.pdf].
Holsheimer, M., de By, R.A., & Aït-Kaci, H. (1994). A database interface for complex objects. In Van Hentenryck, P. (Ed.) Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Logic Programming (ICLP’94) (pp. 437–455). Santa Margherita Ligure (Italy): MIT Press. [Available online http://www.hassan-ait-kaci.net/pdf/iclp94.pdf].
Jarke, M., Gallersdörfer, R., Jeusfeld, M.A., & Staudt, M. (1994). ConceptBase—a deductive object base for meta data management. Journal of Intelligent Information System, 2, 167–192. [Available online https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f4cb/6d9f864c03b52ea173bde125239f271a1c05.pdf].
Lawley, M.J., & Bousquet, C. (2010). Fast classification in Protégé: Snorocket as an OWL 2 EL reasoner. In Meyer, T., Orgun, M.A., & Taylor, K. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 2nd Australasian Ontology Workshop: Advances in Ontologies (AOW 2010) (pp. 45–50). Australia: ACS. [Available online krr.meraka.org.za/~aow2010/Lawley-etal.pdf].
Maglia, A.M., Leopold, J.L., Pugener, L.A., & Gauch, S. (2007). An anatomical ontology for amphibians. In Altman, R.B., Dunker, A.K., Hunter, L., Murray, T., & Klein, T.E. (Eds.) Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing (pp. 367–378): World Scientific. [Available online psb.stanford.edu/.../psb07/maglia.pdf].
Mylopoulos, J., Borgida, A., Jarke, M., & Koubarakis, M. (1990). Telos: Representing knowledge about information systems. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 8(4), 325–362. [Available online http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~jm/Pub/Telos.pdf].
U.S. National Library of Medicine (2014). Medical subject headings MeSH Web Site. [Available online www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/meshhome.html].
Pan, J.Z., Ren, Y., Jekjantuk, N., & Garcia, J. (2013). Reasoning the FMA ontologies with TrOWL. In Bail, S., Glimm, B., Gonçalves, R.S., Jiménez-Ruiz, E., Kazakov, Y., Matentzoglu, N., & Parsia, B. (Eds.) Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on OWL Reasoner Evaluation (ORE 2013) (pp. 107–113): CEUR Workshop Proceedings. [Available online ceur-ws.org/Vol-1015/paper18.pdf].
Cornelius, R., & Mejino, J.L.V. Jr. (2003). A reference ontology for biomedical informatics: the foundational model of anatomy. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 36 (6), 478–500. [Available online www.j-biomed-inform.com/.../pdf].
Shearer, R., Motik, B., & Horrocks, I. (2008). HermiT: A highly-efficient OWL reasoner. In Sattler, U., & Dolbear, C. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on OWL Experiences and Directions. Karlsruhe: OWLED’08, CEUR Workshop Proceedings. [Available online www.cs.ox.ac.uk/ian.horrocks/.../ShMH08b.pdf].
Sirin, E., & Parsia, B. (2007). SPARQL-DL: SPARQL query for OWL-DL. In Golbreich, C., Kalyanpur, A., & Parsia, B. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Workshop on OWL: Experiences and Directions (OWLED 2007). Innsbruck, Austria: CEUR Workshop Proceedings. [Available online ceur-ws.org/Vol-258/paper14.pdf].
Srinivas, K. (2009). OWL reasoning in the real world: Searching for Godot, In Grau, B.C., Horrocks, I., Motik, B., & Sattler, U. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 22nd International Workshop on Description Logics (DL 2009), Oxford, United Kindgom. Invited lecture: CEUR Workshop Proceedings [Available online www.cs.ox.ac.uk/DL2009/.../Srinivas.pdf].
Yamamoto, S., Asanuma, T., Takagi, T., & Fukuda, K.I. (2004). The Molecule Role Ontology: An ontology for annotation of signal transduction pathway molecules in the scientific literature. Comparative and Functional Genomics, 5(6–7), 528–536. [Available online downloads.hindawi.com/.../439679.pdf].
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mohand-Saïd Hacid and Rafiqul Haque, as well as the two anonymous reviewers, for their constructive feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was carried out as part of the \(\mathcal {C}\mathcal {E}\mathcal {D}\mathcal {A}\mathcal {R}\) Project (Constraint Event-Driven Automated Reasoning) under the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) Chair of Excellence grant N ∘ ANR-12-CHEX-0003-01 at the Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 (UCBL).
Additional information
This work was done while the authors were affiliated with the LIRIS, Département Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France. This article is a corrected and expanded version of (Amir and Aït-Kaci 2014).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amir, S., Aït-Kaci, H. An efficient and large-scale reasoning method for the semantic Web. J Intell Inf Syst 48, 653–674 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-016-0435-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-016-0435-2