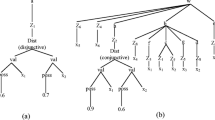
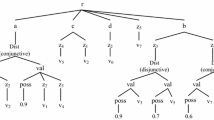
Abstract
Today the current state of the art in querying XML data is represented by XPath and XQuery, both of which rely on Boolean conditions for node selection. Boolean selection is too restrictive when users do not use or even know the data structure precisely, e.g. when queries are written based on a summary rather than on a schema. In this paper we describe a XML querying framework, called FuzzyXPath, based on Fuzzy Set Theory, which relies on fuzzy conditions for the definition of flexible constraints on stored data. A function called “deep-similar” is introduced to replace XPath’s typical “deep-equal” function. The main goal is to provide a degree of similarity between two XML trees, assessing whether they are similar both structure-wise and content-wise. Several query examples are discussed in the field of XML based metadata for e-learning.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
By contrast with classical set theory, there are different possible definitions for these operations, although some of them are more often adopted. For an overview of these definitions refer to Zadeh (1965).
Unfortunately, the same cannot be said for user-defined ComplexTypes. The reader interested in fuzzy matchings for complex XML types may read Damiani et al. (2004).
The vocabulary we use is called JWordNet, and is available at http://wordnet.princeton.edu/.
This turns comparing two paths S and T into computing deep-similarity of multiple pairs of subtrees (as many as the product of S and T node sets cardinalities) and taking the maximum of the resulting similarity values (coherently with the typical existential quantification of XPath conditions).
References
Amer-Yahia, S., Cho, S., & Srivastava, D. (2002). Tree pattern relaxation. In C. S. Jensen, K. G. Jeffery, J. Pokorńy S. Saltenis, E. Bertino, K. Böhm, et al. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 8th international conference on extending database technology: Advances in database technology (25 – 27 March 2002). Extending database technology (Vol. 2287, pp. 496–513). London: Springer-Verlag.
Amer-Yahia, S., Lakshmanan, L. V. S., & Pandit, S. (2004). Flexpath: Flexible structure and full-text querying for XML. In SIGMOD ’04: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data (pp. 83–94). New York: ACM.
Bosc, P., & Pivert, O. (1992). Fuzzy querying in conventional databases. In L. A. Zadeh & J. Kacprzyk (Eds.), Fuzzy logic for the management of uncertainty (pp. 645–671). New York: Wiley.
Bosc, P., Lietard, L., & Pivert, O. (1994). Soft querying, a new feature for database management systems. In D. Karagiannis (Ed.), Proceedings of the 5th international conference on database and expert systems applications (07 – 09 September 1994). Lecture notes in computer science, (Vol. 856, pp. 631–640). London: Springer-Verlag.
Bosc, P., Lietard, L., & Pivert, O. (1995). Quantified statements in a flexible relational query language. In SAC ’95: Proceedings of the 1995 ACM symposium on applied computing (pp. 488–492). New York: ACM.
Buche, P., Dibie-Barthèlemy, J., & Wattez, F. (2006). Approximate querying of XML fuzzy data. In Springer (Ed.), Proceedings of the 7th international conference FQAS 2006, (Vol. 4027/2006). Milan, Italy.
Calms, M. D., Prade, H., & Sdes, F. (2007). Flexible querying of semistructured data: A fuzzy-set-based approach. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 22(7), 723–737.
Ceravolo, P., Damiani, E., & Viviani, M. (2007). Bottom-up extraction and trust-based refinement of ontology metadata. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 19(2), 149–163.
Ciaccia, P., & Penzo, W. (2003). The collection index to support complex approximate queries. In Verlag, S. (Ed.), Proceedings of XSym 2003 (Vol. 2824, pp. 164–179).
Damiani, E., & Tanca, L. (2000). Blind queries to XML data. In MT. Ibrahim, J. Küng, & N. Revell, (Eds.), Proceedings of the 11th international conference on database and expert systems applications (04 – 08 September 2000). Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 1873, pp. 345–356). London: Springer-Verlag.
Damiani, E., Lavarini, N., Oliboni, B., & Tanca, L. (2004). An approximate query environment for XML data. In V. Loia, M. Nikravesh, & L. Zadeh (Eds.), Fuzzy logic and the internet, studies in fuzziness and soft computing (Vol. 137, pp. 71–94). Berlin: Springer.
Damiani, E., Oliboni, B., & Tanca, L. (2001). Fuzzy techniques for XML data smushing. In Proceedings of the international conference, 7th fuzzy days on computational intelligence, theory and applications (pp. 637–652). London: Springer.
Damiani, E., Tanca, L., & Arcelli-Fontana, F. (2000). Fuzzy XML queries via context-based choice of aggregations. Kybernetika, 16(3).
Dubois, D., Prade, H., & Sedes, F. (2001). Fuzzy logic techniques in multimedia database querying: A preliminary investigation of the potentials. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 13(3), 383–392.
Galindo, J., Medina, J., Pons, O., & Cubero, J. (1998). A server for fuzzy SQL queries. In T. Andreasen, H. Christiansen, & H.L. Larsen (Eds.), Proceedings of the third international conference on flexible query answering systems (13 – 15 May 1998). Lecture notes in computer science, (Vol. 1495, 164–175). London: Springer-Verlag.
Garofalakis, M., & Kumar, A. (2003). Correlating XML data streams using tree-edit distance embeddings. In PODS ’03: Proceedings of the twenty-second ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART symposium on principles of database systems (pp. 143–154). New York: ACM.
Kacprzyk, J., & Ziolkowski, A. (1986). Database queries with fuzzy linguistic quantifiers. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 16(3), 474–479.
Klir, G. J., & Yuan, B. (1995). Fuzzy sets and fuzzy logic: Theory and applications. New York: Prentice-Hall.
Levenshtein, V. I. (1966). Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions and reversals. Soviet Physics-Doklady, 10, 707–710.
Li, H. G., Aghili, S. A., Agrawal, D., & Abbadi, A. E. (2006). FLUX: Fuzzy content and structure matching of XML range queries. In Proceedings of WWW 2006, May 23-26, 2006. Edinburgh, Scotland.
Loiseau, Y., Prade, H., & Boughanem, M. (2004). Qualitative pattern matching with linguistic terms. AI Communications, 17(1), 25–34.
Mandreoli, F., Martoglia, R., & Tiberio, P. (2004). Approximate query answering for a heterogeneous XML document base. In Springer (Ed.), Proceedings of the 5th int. conf on web information systems engineering. Brisbane, Australia, November 22–24.
Mouchaweh, M. S. (2004). Diagnosis in real time for evolutionary processes in using pattern recognition and possibility theory (invited paper). International Journal of Computational Cognition, 2(1), 79–112. ISSN 1542–5908.
Nierman, A., & Jagadish, H. V. (2002). Evaluating structural similarity in XML documents. In Int’l workshop on the web and databases (WebDB). Madison,WI, 2002 June. http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/nierman02evaluating.html.
Reis, D. C., Golgher, P. B., Silva, A. S., & Laender, A. F. (2004). Automatic web news extraction using tree edit distance. In WWW ’04: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on world wide web (pp. 502–511). New York, NY, USA: ACM.
Schlieder, T. (2002). Schema-driven evaluation of approximate tree-pattern queries. In Proceedings EDBT (pp. 514–532). Prague, Czech Republic. http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/article/schlieder02schemadriven.html
W3C (1999). XML Path Language (XPath) Version 1.0. http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath.
Yu, C., & Jagadish, H. V. (2006). XML schema summarization. In U. Dayal, K. Whang, D. Lomet, G. Alonso, G. Lohman, M. Kersten, S. K. Cha, & Y. Kim, (Eds.), Proceedings of the 32nd international Conference on very large data bases (Seoul, Korea, September 12 – 15, 2006). Very large data bases. VLDB endowment (pp. 319–330).
Zadeh, L. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8(4), 338–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campi, A., Damiani, E., Guinea, S. et al. A fuzzy extension of the XPath query language. J Intell Inf Syst 33, 285–305 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-008-0066-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-008-0066-3